![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The causes of cancer are many and varied (e.g., chemical, environmental, viral, and mutagenic), but all ultimately lead to an aberration in the expression of what?
|
protooncogenes
|
|
|
What are protooncogenes?
|
the products of which control normal cell life
|
|
|
When protoonco genes mutate they become what?
|
oncogenes
|
|
|
Oncogenes (e.g., myc and ras) can either overexpress or underexpress what? What does this result in?
|
regulatory biochemicals, resulting in preferential and accelerated cellular growth.
|
|
|
Can tumor suppressor genes (e.g., anti-oncogenes like p53, p21,pINK4A, and retinoblastoma) be inhibited?
|
yes
|
|
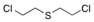
Which structure is this?
|
Sulfur mustard
ex. mustard gas |
|
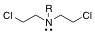
What is this structure?
|
Nitrogen mustard
|
|
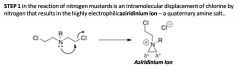
What is the structure on the right called?
|
Aziridinium Ion
|
|
|
What is the simplest therapeutic nitrogen mustard?
|
Mechlorethamine(Mustargen)
|
|
|
How is Mechlorethamine(Mustargen) administered as?
|
an iv solution HCl sal
|
|
|
Mechlorethamine(Mustargen) is a severe ___? What kind of agent?
|
Is is a severe vesicant (blistering agent, like the sulfur mustards)
|
|
|
In the case of skin contact, mechlorethamine is deactivated by treatment with What?
|
sodium thiosulfatesolution.
|
|
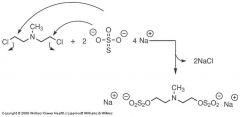
What is the first structure in this reaction?
|
Mechlorethamine(Mustargen)
|
|
|
Melphalanand Chlorambucilhave aromatic rings which stabilize what? What does it slow the formation of? What does this inturn reduce?
|
the nitrogen lone pair and slow the formation of the aziridinium ion – reducing side effects and increasing distribution in the body.
|
|
|
The carbamate functional group in Estramustine offers what?
|
resonance stabilization to nitrogen lone pair.
|
|
|
The carbamate functional group in Estramustineoffers resonance stabilization to nitrogen lone pair. The estradiol carrier aids in what?
|
selectively delivering drug to steroid-dependant prostate tissue.
|
|
|
What are two examples of Nitrogen Mustard prodrugs?
|
Cyclophosphamide and ifosphamide
|
|
|
Cyclophosphamideand ifosphamide are prodrugs which require what?
|
bioactivation by liver metabolism
|
|
|
Cyclophosphamideand ifosphamide are prodrugs which require bioactivation by liver metabolism . This means lower what?
|
This means lower GI tox and less nonspecific tox overall,
|
|
|
Cyclophosphamideand ifosphamide are prodrugs which require bioactivation by liver metabolism . This means lower GI tox and less nonspecific tox overall, but the acrolein formed during bioactivation is very what? What does this cause?
|
very electrophilic and causes extensive damage to the cells of the kidney and bladder when excreted.
|
|
|
The tertiary aziridine in Thiotepa is much less reactive than what? How does it effect this compound?
|
quaternary aziridine and thus this compound is a very weak alkylator.
|
|
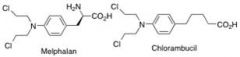
What are these 2 structures?
|
Melphalan and Chlorambucil
|
|

What are these two structures?
|
Cyclophosphamide and ifosphamide
|
|

What is this structure?
|
Thiotepa
|
|
|
The primary metabolism of cyclophosphamide is by which enzyme subtype?
|
CYP2B6 liver enzyme subtype.
|
|
|
CYP3A4 primarily acts to yield what? It results in addational ___ and ____ ___ ___
|
inactive metabolites and results in additional neuro- and nephrotoxic metabolite chloroactealdehyde.
|
|
|
Ifosphamide metabolism is similar to what? What is different?
|
cyclophosphamide, but enzyme subtypes involved are different.
|
|
|
_____ is a very efficient alklyator of sulfhydryl containing proteins in bladder cells?
|
Acrolein
|
|
|
To minimize the risk of bladder toxicity from acrolein what should be done?
|
fluids should be forced and the bladder irrigated.
|
|
|
What is also is available as adjuvant therapy in case of overt toxicity or as a prophylactic protectant?
|
Mesna(Mesnex)
|
|
|
Mesna concentrates in what? What does it prevent?
|
the bladder and will prevent damage to those cells
|
|
|
Mesna concentrates in the bladder and will prevent damage to those cells. It does not concentrate to any appreciable extent in the nephron and, therefore, is not good protection against what?
|
cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity.
|
|
|
The nitrosoureas are what kind of structures? Where do they decompose?
|
The nitrosoureas are unstable structures that decompose readily in the aqueous environment of the cell.
|
|
|
The nitrosoureas are unstable structures that decompose readily in the aqueous environment of the cell. Nonenzymatic fragmentation is stimulated by what?
|
by the loss of proton from the urea moiety.
|
|
|
DNA Cross-Linking Agents Nitrosoureas
Cyclization of the resultant anion to an unstable oxazolidine what pathway? |
pathway A
|
|
|
DNA Cross-Linking Agents - Nitrosoureas
Cyclization of the resultant anion to an unstable oxazolidine (pathway A) is followed by what? |
decomposition to vinyldiazotic acid and a substituted isocyanate, both of which release a gaseous fragment (nitrogen and carbon dioxide, respectively) to generate cytotoxic electrophiles.
|
|
|
DNA Cross-Linking Agents - Nitrosoureas
Vinyl carbocation, acetaldehyde, and 2-chloro-ethylamine generated from what? What are they all capable of? |
generated from the 2-chloroethylisocyanate moiety of carmustine are all capable of alkylating DNA.
|
|
|
DNA Cross-Linking Agents - Nitrosoureas
A second decomposition mechanism (pathway B) ultimately produces what? What is it capable of? |
electrophilic 2-chloroethylcarbocation capable of DNA alky-lation at guanine N7 and O6, as well as an isocyanate that can carbamylate amino acid residues (e.g., Lys).
|
|
|
Both carmustineand lomustine are highly what? What can they not be administered in?
|
are highly lipophilic and therefore cannot be administered in a purely aqueous solution.
|
|
|
Both carmustineand lomustine are highly lipophilic and therefore cannot be administered in a purely aqueous solution. What is used instead?
|
A 10% ethanol solution is used instead
|
|
|
Carmustine degrades within ___ minutes of admin?
|
15
|
|
|
Lomustine is stable enough to be offered in what kind of formulation?
|
capsule
|
|
|
The glucopyranose moiety of streptozocinconfers both what?
|
islet cell specificity and high water solubility to this nitrosourea-based antineoplastic.
|
|
|
The glucopyranose moiety of streptozocinconfers both islet cell specificity and high water solubility to this nitrosourea-based antineoplastic. As a result, it is used exclusively in what?
|
metastatic islet cell carcinoma of the pancreas and is administered IV in D5W or normal saline.
|
|
|
The glucopyranose moiety of streptozocin Lacks the 2-chloroethyl substituent of carmustine and lomustine which makes it much less reactive as what?
|
less reactive as a DNA alky-lating agent
|
|
|
Procarbazineand the triazenes (dacarbazineand temozolomide) act by different mechanisms, but they all exert what kind of effect?
|
exert an antineoplastic effect through the O6 methylation of guanine nucleotides.
|
|
|
O6-methyl-guanine pairs preferentially with what?
|
thymine
|
|
|
O6-methyl-guanine pairs preferentially with thymine, and these “mispairs” prompt what during what?
|
prompt point mutations during subsequent DNA replication cycles
|
|
|
O6-methyl-guanine pairs preferentially with thymine, and these “mispairs” prompt point mutations during subsequent DNA replication cycles and trigger what through what?
|
cell destruction through the activation of the normal postreplication mismatch repair (MMR) system.
|
|
|
Patients who are able to repair this damage through the action of O6 alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase, which transfers the offending ___ group to a ___ residue on ____ protein?
|
CH3 group to a Cys residue on the alkyltransferase protein,
|
|
|
Patients who are able to repair this damage through the action of O6 alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase, which transfers the offending CH3 group to a Cys residue on the alkyltransferase protein will exhibit what?
|
will exhibit resistance to these agents, whereas those who under express this protein should respond well
|
|
|
Because the alkyltransferase is irreversibly inactivated in the DNA rescue process, what is at risk?
|
enzyme depletion (and subsequent loss of DNA repair capability) is a significant risk.
|
|
|
Procarbazinemetabolism involves which two enzymes?
|
CYP1A and CYP2B enzymes
|
|
|
Procarbazinemetabolism involves CYP1A and CYP2B enzymes, and DNA alkylation operates through what mechanism?
|
a free radical mechanism.
|
|
|
Procarbazinemetabolism involves CYP1A and CYP2B enzymes, and DNA alkylation operates through a free radical mechanism. The major degradation pathway involves what?
|
benzylic oxidation of azoprocarbazine
|
|
|
he major degradation pathway involves benzylic oxidation of azoprocarbazine, producing what? What does this generate? Through what intermediate?
|
methylhydrazine that generates a methyl radical through an unstable diazene intermediate.
|
|
|
The major degradation pathway involves benzylic oxidation of azoprocarbazine, producing methylhydrazine that generates a methyl radical through an unstable diazene intermediate. In addition to O6 methylation, the reactive methyl radical formed can alkylate what positions of guanine?
|
the C8 and N7 positions of guanine.
|
|
|
In contrast to procarbazine, the triazenes (dacarbazine and temozolamide) methylate what, how?
|
methylate DNA guanine via diazomethane and/or methyl carbocation generated in situ
|
|
|
temozolomide is converted to the diazomethane precursor _____
|
MTIC
|
|
|
the conversion of dacarbazine to MTIC depends on the action of what enzymes?
|
CYP1A1and CYP1A2 enzymes, with a smaller contribution by CYP2E1
|
|
|
What positions of guanine are the most vulnerable to triazenemethylation?
|
O6 and N7
|
|
|
Altretamine is believed to damage what cells?
|
damage tumor cells
|
|
|
Altretamine is believed to damage tumor cells through the production of what?
|
the weakly alkylating species formaldehyde, a product of CYP450-mediated N-demethylation.
|
|
|
Altretamine is administered how?
|
orally
|
|
|
Administered orally, altretamine is extensively metabolized on which pass?
|
1st
|
|
|
Administered orally, altretamine is extensively metabolized on first pass, producing what two metabolites?
|
primarily mono- and didemethylated metabolites.
|
|
|
Administered orally, altretamine is extensively metabolized on first pass, producing primarily mono- and didemethylated metabolites. Additional demethylation reactions occur in tumor cells, releasing what?
|
formaldehyde in situ before the drug is excreted in the urine.
|
|
|
The carbinolamine (methylol)intermediates of CYP450-mediated metabolism also can generate what species?
|
electrophiliciminiumspecies
|
|
|
The carbinolamine (methylol)intermediates of CYP450-mediated metabolism also can generate electrophiliciminium species that are capable of reacting covalently with what?
|
DNA guanine and cytosine residues as well as protein.
|
|
|
Chemically, busulfan is classified as an ____?
|
alkylsulfonate.
|
|
|
Chemically, busulfan is classified as an alkylsulfonate. One or both of the methylsulfonate ester moieties can be displaced by what? What does this lead to?
|
the nucleophilic N7 of guanine, leading to mono alkylated and cross-linked DNA.
|
|
|
What are effects of busulfan?
|
Serious bone marrow hypoplasia and myelosuppression are possible with this agent
|
|
|
recovery from busulfan-induced pancytopenia can take up to how long?
|
2 years
|

