![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
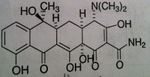
Tetracycline General
|
• MOA: Bind to 30S subunit of ribosomes blocking aminoacyl tRNA to mRNA ribosomal complex
• Issue: Have low affinity for mammalian ribosomes • PO, IV, NOT IM (tend to precipitates out of vehicle, which is painful) • Features: allergies are uncommon with this class—if does see response, it would be from cross allergenicity from other tetracyclines in the class • Problems with people that store these tablets because expired lots of these drugs produce very toxic substance (Fanconi syndrome) • Bacteriostatic • ADR: vestibular reactions (dizziness, vertigo—vomiting) with 35-70% incident rate, causes photosensitization manifested by sunburn, causes discoloration of newly formed bone & teeth (malformation AND discoloration in children when developing permanent teeth) • Classified as pregnancy category D o Present in breast milk |
|
|
Acyclovir, Zovirax®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs- Viral thymidine kinase puts on the first phosphate, mimics dG; causes premature DNA chain termination, binds irreversibly to viral DNA polymerase (competitive inhibition). Selectivity in the cells is only with viral DNA. NOT A PRODRUG Use: Herpes Simplex Virus, Herpes Zoster Virus, genital herpes, herpes labialis Dosage: Oral, IV, less effective topically |
|

|
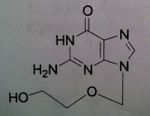
Valacyclovir, Valtrex®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs- Viral thymidine kinase puts on the first phosphate, mimics dG; causes premature DNA chain termination, binds irreversibly to viral DNA polymerase (competitive inhibition) Use: Herpes Simplex Virus (1&2), Herpes Zoster Virus, genital herpes, herpes, labialis Dosage: ORAL ONLY Notes: Prodrug (Acyc. In plasma); 5 x greater serum levels than Acyc. (reaches same levels of Acyc. IV) |
|
|
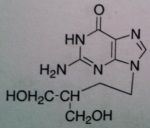
Penciclovir, Denavir®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs- Viral thymidine kinase puts on the first phosphate, mimics dG; causes premature DNA chain termination, binds irreversibly to viral DNA polymerase (competitive inhibition) Use: Herpes Simplex Virus (1&2) Dosage: Topically as 10 % cream Notes: Doesn’t have ether linkage (O→ CH2) and is opened up; NEED viral thymidine kinase or virus will become resistant; OH end can elongate, doesn’t prevent chain termination Viral viral DNA polymerase—lacks fidelity that human version has! fidelity of DNA polymerase—don’t have toxicity from it because it knows what is human and what is correct kinase. (initial step we’re counting on…drug won’t be effective without this) |
|
|
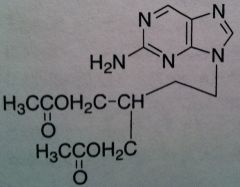
Famciclovir, Famvir®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs- Viral thymidine kinase puts on the first phosphate, mimics dG; causes premature DNA chain termination, binds irreversibly to viral DNA polymerase (competitive inhibition) Use: Herpes Simplex Virus (1&2), Herpes Zoster Virus Dosage: Oral (77% bioavailability) Notes: Prodrug of Penciclovir; can’t be acted upon until acetyls are hydrolyzed and purine is oxidized |
|
|
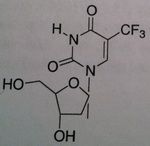
Trifluridine, Viroptic®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs -Mimics thymidine triphosphate Use: Certain severe viral infections, Herpes Simplex Virus (1&2) Dosage: Topical and Opthalmic ONLY Notes: Competes for incorporation into viral DNA (to some degree, it is incorporated into cellular DNA so it is primarily used topically). There is some toxicity with it |
|
|
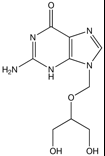
Ganciclovir, Cytovene®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs- reported to ultimately cause chain termination (even though it has OH group), inhibits viral DNA polymerase (once incorporaped into viral DNA strand), mimics dG. Must be converted to triphosphate for acctivity Use: CMV (occular), Herpes Simplex Virus, Varicella Zoster Virus, EBV (mononucleousis). Human Heptoma Type A Dosage: IV, po, topical opthalmicalso as an implant in the eye (for certain viraleye infections), lab animals, causes hypospermatosis (reduces sperm count) |
|
|
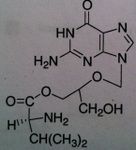
Valganciclovir, Valcyte®
M of A: Nucleoside Analogs- reported to ultimately cause chain termination, inhibits viral DNA polymerase, mimics dG Use: Life-threatening CMV (retinitis) ADR: Can cause blindness Dosage: Oral Notes: 10 x more bioavailable by oral route than Gancyc.- much more efficient; prodrug – valine ester of gan; same concerns teratogenic and carcinogenic effect; often used in immunocompromised pts (organ transplant); contraindicated in pts with liver transplant bc of hepatotoxicity) |
|
|
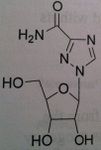
Ribavirin, Virazole®, Rebetol®
M of A: Don’t understand fully. Mimic dG, gets incorporated into viral RNA; guanosine analog, interferes with synthesis GTP; inhibits RNA dependent(?) polymerase Use: Hepatitis B orally (NOT MONOTHERAPY; together with interferon α-2a). Influenza A + B ADR: Teratogenic and immunogenic effects; embryonic toxic effects; have to be on 2 forms of contraception during treatment and 6 months after Dosage: Oral, by inhalation (nebulizer) Notes: Not specific for DNA containing viruses, mainly for RNA containing viruses |
|
|
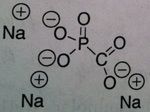
Foscarnet
M of A: Inorganic pyrophosphates- Reversibly inhibits pyrophosphate binding site on viral DNA and RNA polymerases, thereby terminating DNA chain elongation- Non-competitive inhibitor (alters binding site), Not a nucleoside Use: treats Resistant Acyclovir HSV and herpes zoster virus, CMV retinitis (can lead to blindness in HIV pts) ADR: sequestration of cations with K, Mg2+ & Ca2+ → can cause elimination of these salts - can develop hypomagnesemia/calcemia (electrolyte imbalanes)→ arrhythmias & seizures; can cause renal impairment, watch serum creatinine levels (MAJOR). NEPHROTOXICITY Dosage: IV ONLY (POOR PO ABSORPTION) Notes: Doesn’t require metabolic activation (not dependent on thymidine kinase) can overcome viral resistance; not totally selective for viral DNA |
|
|
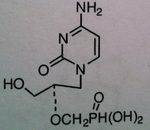
Cidofovir
M of A: Nucleotide Analogs- Cytosine phosphate mimic; incorporated into viral DNA chains, causes chain termination (even though it has OH group); host changes to diphosphate, not dependent on thymidine kinase. Phosphonate not phosphate Use: Effective against resistant viruses that produce thymidine kinase. CMV ADR: nephrotoxicity (renal tubular damage) 1/2 is 17 - 65 hours Dosage: IV ONLY Notes: Doesn’t require initial phosphate; phosphonic acid – carbon spacer that is now linked to phosphate (makes it more stable – if it was phosphate acid – would be destroyed by plasma phosphatase); |
|
|
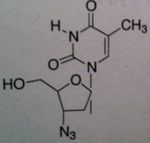
Zidovudine (AZT)
Structure: thymidine derivative;these agents lack the necessary 3 hydroxyl to permit further chain elongation Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. Needs to be converted to their nucleotide triphosphate form to exert their antiviral effects Use: HIV, AIDS ADR: bone marrow suppression Dosage: orally active, can be administed IV but is impractical for AIDS, 200 mg TID Notes: fiedelity of our DNA polymerase doesn’t recognize this as a substrate |
|
|
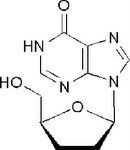
Didanosine, Videx ® (ddI)
Structure: purine base, mimics adenosine; undergoes modification at 6 oxo group, double bond to O turns into NH) (then to triphosphate) Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. Use: HIV, AIDS ADR: dose dependent pancreatitis, acid labile, thus given as a buffer-chewable tablet Notes: incorporated into viral DNA particle due to lack of fidelity of viral RT Can be used synergistically with AZT (thymidine) because because it mimics a different structure and they are not competing with one another |
|
|
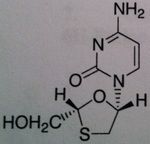
Lamivudine
Structure: Pyrimidine base, mimics cytosine ; attached to cylic structure with Oh group – monophophate goes here and then TP Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. by Dennis Liotta at Emory University |
|
|
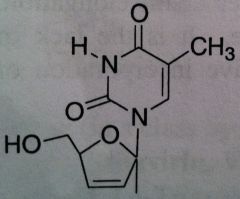
Stavudine, Zerit ® (d4T)
Structure: thymidine mimic; doesn’t have OH group Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. Use: HIV, AIDS, Dosage: excellent oral BA (>85%) ADR: dose related sensory neuropathy, pancreatitis Notes: DON’T USE WITH AZT: likely to be competitive for viral thymidine kinase for activation; They will work against each other |
|
|
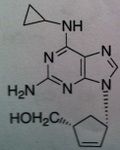
Abacavir, Ziagen ®
Structure: guanosine analog Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. Use: HIV, AIDS Notes: Used as triple therapy, Trizivir. Ziagen (ABC), Lamivudine (3TC) , and Zidovudine (AZT), thus mimicking deoxyguanosine, deoxycytosine, and deoxythymidine |
|
|
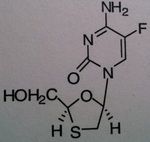
Emtricitabine, Emtriva ® (formerly Coviracil)
Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs), Cytosine mimic M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. Use: HIV, AIDS, often used in combination therap Notes: unusually drug; No possibility of chain elongation because of the thiazole; Part of the combo drugs Truvada and Atipla; When withdraw from the therapy, one can get a wicked/suddle Hep B infection |
|
|
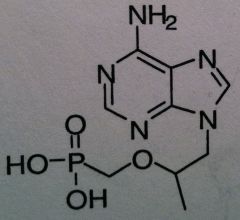
Tenofovir disoprxil fumarate, Viread ® (TDF or PMPA)
Structure: adenosine mimics, no cyclic ring, deoxy mimic Carbonate is a vulnerable to esterase which changes it to the monophosphate active form Relying on Lack of fidelity of reverse transcriptase Class: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) M of A: They get incorporated into the growing DNA chain of the viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and prevent chain elongation, terminating DNA synthesis Not associated with incorporation into mammalian cells. Chain termination b/c of lack of free OH to allow elongation Use: HIV, AIDS, chronic Dosage: cascading prodrug, phosphonate converts to bisphosphate ADR: HBV exacerbation |
|
|
Nevirapine, Viramune®
Class: Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTs) - selective noncompetitive inhibors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, no cross-resistance observed with NRTIs, M of A: Binds at different site (other than site associated with activity) that disrupts overall conformation of RT and therefore affects its ability to take on a viral RNA and convert it to DNA Use: AIDS ADR: Hepatotoxicity (monitor liver function), Refampine is known to decrease the levels of the drug thru cyp 450 induction Dosage: Oral ( >90% bioavailability) Notes: NEVER USE THESE AS MONOTHERAPY. COMBINATION THERAPY with AZT; NO effect on human DNA polymerase; Has unique property – if administered to pregnant individuals who are HIV positive, within 3 days of delivery as well an onset of labor, transmission of HIV from mother to newborn is prevented. MAJOR BREAKTHROUGH-prevention of HIV to newborns, must be given 72 hours before birth and 7 days after |
|

|
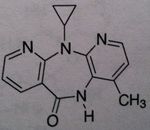
Delavirdine, Rescriptor®
Class: Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTs) M of A: Binds at different site (other than site associated with activity) that disrupts overall conformation of RT and therefore affects its ability to take on a viral RNA and convert it to DNA Use: AIDS Dosage: Oral (high bioavailability), BA is reduced in presence of antacids and H2 antagonists, don't use as monotherapy ADR: teratogenic in rats, thus has potential to cause birth defects. |
|
|
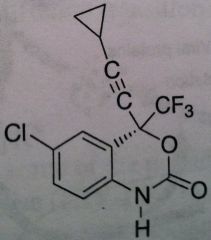
Efavirenz, Sustiva®
Class: Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTs) M of A: Binds at different site (other than site associated with activity) that disrupts overall conformation of RT and therefore affects its ability to take on a viral RNA and convert it to DNA Use: AIDS ADR: Can produce some CNS effects, thus administer at night T1/2: 44-55 hrs Dosage: Oral Notes: Never use as monotherapy. induces its own metabolism → leads to self-induced resistance – constantly need more and more of the drug to produce the same level of efficacy ; CYP3A4 is enzyme associated with metabolism. Birth Defects concern. |
|
|
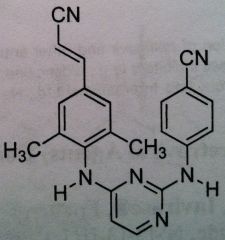
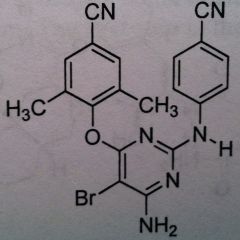
Rilpivirine, Edurant
Class: Nonnucleoside Riverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTs) MUST BE USED WITH OTHER AGENTS. More of an adjunct therapy. not the primary therapy |
|
|
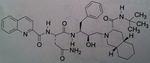
Etravirine, Intelence
Class: NNRTI Use: HIV Improvement on rilipivirine, the very best of all the NNRTI’s, not much resistance, so NEVER USE AS MONOTX! Can induce 3a4. And it is a substrate for it as well, but we do not have self induced resisatnace. Again, its efficacy against the broad spect of HIV viruses makes this the most promising among the NNRTI’s. J+J is making this free to countries that cannot afford the drug. |
|
|
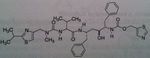
Saquinavir
Class: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals) M of A: Inhibits an aspartate protease that normally hydrolyzes proteins/cuts them. These prevent the post-translational processing or “budding” of infected particles from the membranes of infected cells Use: AIDS Dosage: Oral, poor bioavailability (4%), need a truckload to achieve efficacy. At least 10000 mg BID. Can't always infuse it, pts would need to be hospitalized. Have tablets and capsules Notes: Several chiral centers→ difficult to synthesize compound→ HIGH cost; |
|
|
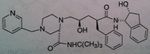
Ritonavir, Norvir®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation Administation: Tablets, caps, soln Use: AIDS (mostly as a booster → 100mg + another PI) Notes: Has a secondary OH; potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, and all of the CYP A family (inc. levels of other PIs). Taken in combo with saquinivir. if used alone (not preferred), you would give 600 mg BID |
|
|
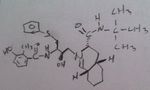
Indinavir, Crixivan®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation; transition state inhibitor Use: AIDS Can see where the active site is, avail as Caps. |
|
|
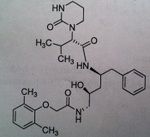
Nelfinavir, Viracept®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation, mimic transition state Use: AIDS ADR: Diarrhea (can be dose limiting) Dosage: Oral- HIGH DOSE Notes: Inducer and competitive inhibitor of CYP3A4; benefits by use of Ritonavir as booster P. If use rifampin, for whatever reason, it induces 3a4. That would decrease nelfinavir concentration. Nothing too magical about it, more huge doses. 2.5 g per day. WITH MEALS. Split dose. |
|
|
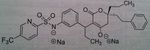
Lopinavir, a component of Kaletra®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation Use: AIDS Dosage: Oral Notes: ONLY AVAILABLE IN COMBO WITH RITONAVIR (insufficient bioavailability alone); blood levels are increased by low doses of Ritonavir, a potent inhibitor of cytochrome p450 3A4 You cant get this if its not combined with rotimovir. 400L/ 100R. to prevent degradation |
|
|
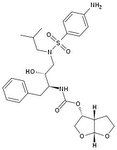
Tipranavir Disodium, Aptivus®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation- DIFF. BINDING SITE Use: When other PI’s are resistant Dosage: Oral Notes: Usually coadministered with Ritonavir Go to website, there is a video on it. Works on a broader range of resistant HIV than the others. There is no secondary hydroxyl. No tetrahedral intermediate. So there is something different here. tends to bind differently as a PI. And that is what is responsible for its acitivity vs HIV1 resistant strains. Concern with Hepato toxicity. Fatal instances have been recorded. Measure LFT ALT. intracranial hemmorage recorded, but we don’t know how it occurred. |
|
|
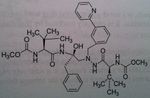
Darunavir
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation Use: AIDS ADR: Risk of Steven Johnson’s Syndrome (can start off as mild rash → fulminant eruption) T1/2: 15 hrs Dosage: Oral (relatively high dose) in combo with Ritonavir Notes: 14 fold increase in systemic levels when taken with Ritonavir Developed in academia, by Dr. Arun K Ghosh. Used typically with rotinivir. 600mg Dar/ 100 mg Rotinovir. Because darunavir is a substate for CYP3a. probably the cheapest one, still at 9 grand a year. Going to mention this guy, Yellapragada Subbarao. – invented Methotrexate. Denied a green card for USA. Somewhat of a folk hero Well known in India. Discovered ATP. Dr. Lavoie’s HERO! |
|
|
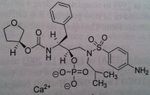
Atazanavir, Reyataz®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation Use: AIDS Dosage: Oral (lower dose with Ritonavir); higher dose req. in absence of Ritonavir Notes: Less chiral centers→ reduces cost of manufacturing THIS HAS secondary alcohol. So back to the regular mechanism. Is a stable compound taken with FOOD. Not all are affected by food. But when they are it’s a problem with achieveing good levels of drug. 300 atz/100 Rito. |
|
|
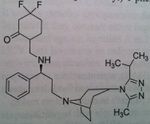
Fosamprenavir, Lexiva®
M of A: Protease Inhibitors (Antiretrovirals)- reversibly inhibit an aspartate proteinase that is essential for the final step of viral proliferation Use: AIDS Dosage: Oral Notes: Prodrug (replaced Amprenavir which was too hazardous to administer with Ritonavir), To try and get a more consistant and reasonable lvl of this drug absorbed. Prodrug is preffered. Still used clinically. Not a low dose, not a significant advantage. 7:1 ratio with rotinovir. BID. |
|
|
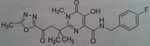
Maraviroc, Selzentry®
M of A: Fusion inhibitor/Entry inhibitor (blocks fusion between viral particle and T-cell)- CHEMOKINE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST- binds to CCR5 and blocks site that HIV would use to be active (on human T-cell) and prevents entry of virus into the cell. Use: AIDS Dosage: Oral Notes: Much less costly; substrate for CYP3A 150 mg in presence of CYP 3a inhibitor twice a day 300 mg in the absence of an inhibitor or inducer twice a day 600 mg in the presence of an inducer of CYP 3a twice a day |
|
|
Raltegravir, Isentress®
M of A: Integrase inhibitor (inhibits HIV enzyme that integrates the viral genetic material into human chromosomes)- “strand transfer inhibitors” (Dna strand transfer from the viral genome to the host genome). Metabolized away via glucuronidation. Use: Individuals whose infection has proven resistant to other HAART drugs Dosage: Oral Notes: Used in combination, not as monotherapy |
|
|
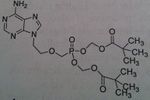
Adefovir, Hespera®
M of A: Diphosphate inhibits in a competitive fashion with ATP, causing chain termination. mimics adenosine (close to Tenofovir, no methyl) Use: Hepatitis B Dosage: Oral, mimics Adenosine Notes: Cascading prodrug → requires esterase to unravel and forms diphosphate; once hydrolyzed → phosphonate (longer and more stable than phosphate) 10 mg once daily |
|
|
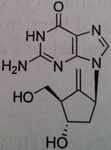
Entecavir, Baraclude®
M of A: Set up to be phosphorylated and form a triphosphate which is responsible for its antiviral activity against HVB reverse transcriptase; mimics dG, superior to Lavovudine and Adefovir. Use: Hepatitis B Dosage: Oral, not a prodrug Patients is not be is not concurrent for HIV, does not treat HIV, only HVB. |
|
|
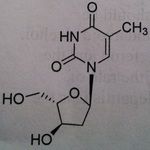
Telbivudine, Tyzeka®
M of A: Associated with replication of Hep B even though it is a DNA virus; mimics thymidine (pyrimidine base), activated to the triphosphate, the chiral at the 3 prime position are inverted, otherwise does look like thymidien. Use: Hepatitis B Dosage: Oral Notes: NOT a prodrug |
|
|
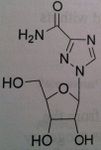
Ribavirin
Not used alone but used with peginterferon. Used for hepatitis C Depends upon body weight, if more than 75 kg, give 600 mg daily + 3 million units of interferon alpha (TID SQ) ADR: Pregnancy category X. extreme concern to be toxic to the fetus but also be teratogenic and major birth defects. malformation of the eye, GI track, skull, limb. Avoid pregnancy during therapy and for 6 months after completing treatment. The drug gets compartmelized and stays in the body. Use at least 2 forms of contraception during and after treatment. Same applies to women who are not being treated but are together with men who are treated |
|
|
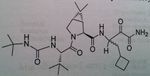
Boceprevir,
Hepatitis C protease, NS3/4A, inhibitor This protein is chopped up into 4 fragments No transition state inhibition Keto amide crucial for protease inhibition, No monotherapy Take orally as a capsule 4 capsule TID (800 mg TID) After four weeks treatment of pegylated interferon A and ribavirin, use boceprevir |
|
|
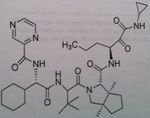
Telaprevir
Direct Protease inhibitor, NS3/4A, important for proteolytic cleavage of the HVB C Also given in combination with pegylated interferon A and ribavirin. Not said if 4 weeks treatment is needed prior |
|
|
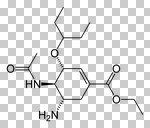
Oseltamivir
Neuroaminidase inhibitors Prevents the release of virus progency from infected cells, which results in a limitation of the severity ad spread of viral infections Use for Influenza A + Influenza B Orally active (the only one form the group) H5n1, avian influenza Used prophylactically and if have a flu Stockpiled |
|
|
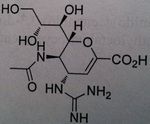
Zanamivir (Youtube, Administration technique for Zamnamivir Disk Inhaler)
Neuroaminidase Inhibitor Not orally used Need an oral inhaler (dry powder inhaler) Stockpiled One of the more effective Influenza A and B |
|
|
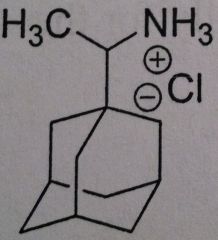
Ramantadine
Used as a prophylactic treatment Used against Influenza A Inhibits M2 proton channel, located in the viral envelope. The channel is crucial at uncoating the virus. thus the drug inhibits the uncoating Has to be taken within 48 hours of the onset of the infection or totally prophylactic |
|
|
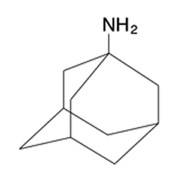
Amantadine
Prophylactic agent Used Against Influenza A 100 mg dose BID Top dose is 300 mg Inhibitor of the M2 proton channel Has to be taken within 48 hours of the onset of the infection or totally prophylactic |
|
|
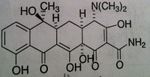
o Naphthacene NOT naphthalene
o Very effective—60-70% absorption & bioavailability • Bacteria tend to concentrate drug inside bacteria cell to make it even more effective o Half-life: 6 hours o Eliminated in urine—need dose adjust in renally impaired patients |

