![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
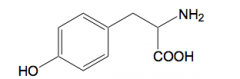
|
L tyrosine |
|
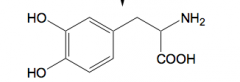
|
Levodopa not good solubility at ph = & used for Parkinsons - can pass BBB - central activity |
|
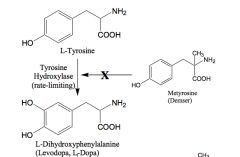
Why does metyrosine inhibit? |
similar structure to L-tyrosine, competes and L-tyrosine can't bind |
|
|
L-tyrosine to Levodopa |
Tyrosine hydroxylase - rate limiting step |
|
|
Levodopa to Dopamine |
L-Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase |
|
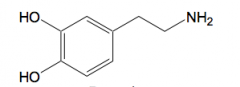
|
Dopamine - COOH removed can't cross BBB at ph 7 - highly ionized |
|
|
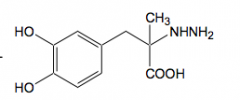
Carbidopa Inhibitor similar to L-Dopa
|
|
|
Why is Carbidopa used with levodopa? |
for parkinsons takes advantage of inhibition of enzyme to slow down L-dopa metabolism to dopamine = longer time to cross BBB |
|
|
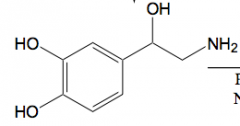
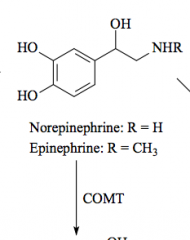
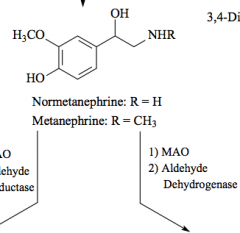
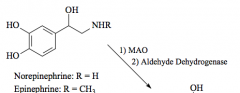
Norepinephrine Primary amine (addition of OH) |
|
|
enzyme between Dopamine and Norepinephrine |
Dopamine B-hydroxylase |
|
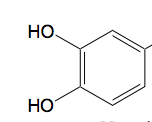
Functional group |
Catechol |
|
|
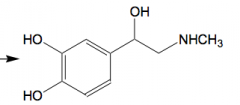
Epinephrine secondary amine |
|
|
enzyme between norepinephrine and epinephrine |
Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (adrenal medulla) |
|
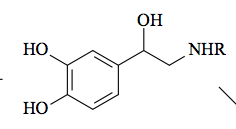
|
R=H: Norepinephrine R=CH3: Epinephrine |
|
|
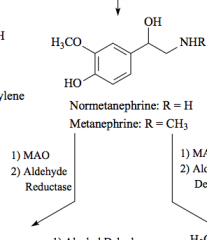
MAO |
monoamine oxidase |
|
|
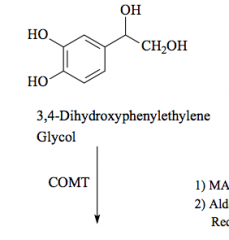
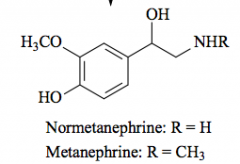
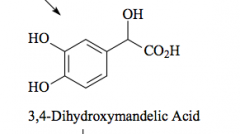
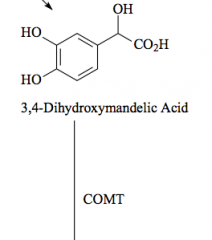
COMT |
Catechol O-methyl transferase |
|
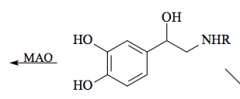
|
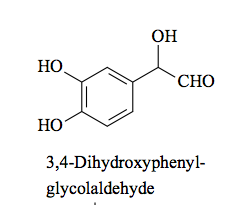
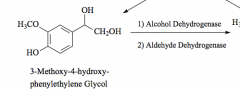
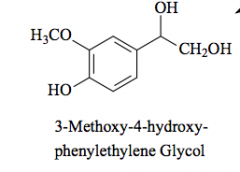
Oxidation - forms aldehyde
|
|
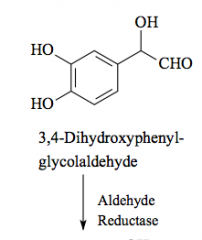
|
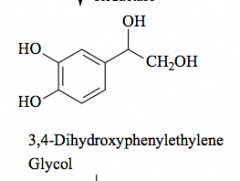
forms alcohol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
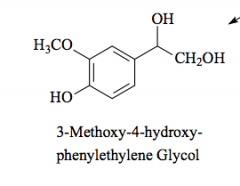
methylation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
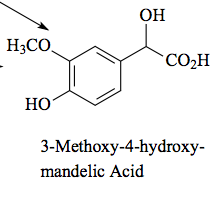
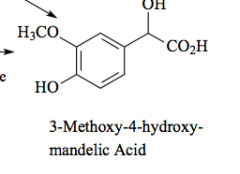
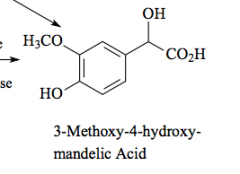
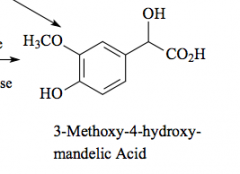
Major metabolite of norepinephrine and epinephrine |
|
|
|
Arterioles receptor type and response |
a1,a2 Constriction |
|
|
Vascular smooth muscle receptor type and response |
B2, dilation |
|
|
eye (radial muscle) receptor type and response |
a1, constriction (dilation) |
|
|
Fat cells, receptor type and response |
a1, b3 lipolysis |
|
|
heart receptor type and response |
B1 increased rate and force increased conduction velocity |
|
|
intestine receptor type and response |
a1, B2 decreased motility |
|
|
liver receptor type and response |
a1, b2 increased gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis |
|
|
lungs receptor type and response |
B2 relaxation |
|
|
uterus receptor type and response |
a1, b2 contraction relaxation |
|
|
a1 stimulation |
vasoconstriction |
|
|
a2 stimulation |
decreased sympathetic activity (targets pre-synaptic) |
|
|
B1 stimulation |
increase rate (chronotropic) and force (inotropic) of cardiac contratction stimulate renin secretion |
|
|
B2 stimulation |
smooth muscle relaxation bronchodilation vasodilation glycogenolysis |
|
|
b3 stimulation |
adipose tissue, increase lipolysis |
|
|
D1 stimulation |
dilation of renal blood vessels |
|
|
precursor for neurotransmittors |
tyrosine |
|
|
A1 agonist indications |
nasal decongestants opthalmic vasoconstriction |
|
|
B2 agonists |
bronchodilators (asthma) anaphylactic shock |
|
|
a2 agonist indication |
glaucoma hypertension |
|
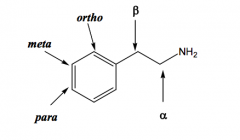
|
B-phenylethylamine |
|
|
catecholamine ionization at ph 7 |
98% |
|
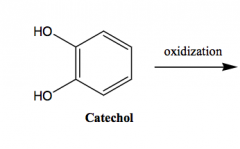
|
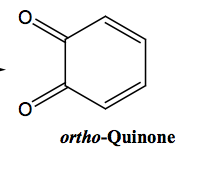
|
|
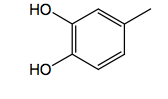
|
Catechol (isoproterenol) B selectivity |
|
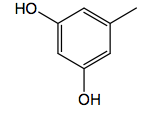
|
Resorcinol R1=CH(CH3)2: Metaproterenol
B2: no COMT` |
|
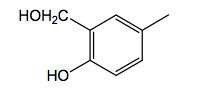
|
meta-hydroxymethyl Albuterol: R1=C(CH3)3
B2: no COMT |
|
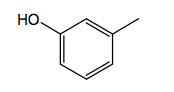
|
only meta-OH Phenylephrine R1=CH3
a1 |
|
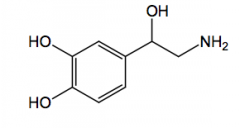
|
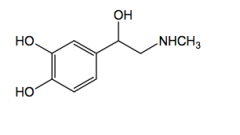
Norepinephrine Direct acting
a, B1 agonist IV - not orally active hypotensive emergency air-oxidized to o-quinone |
|
|
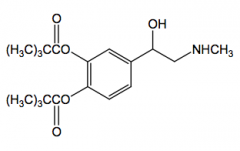
Epinephrine direct acting easily oxidized a,B1, B2 agonist not orally active
nasal decongestant, local anesthetics asthma, anaphylactic
open-angle glaycoma - epinephryl borate |
|
|
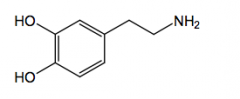
Dipiverferin direct acting
glaucoma: alpha 2 lipophilic activated by esterase's (prodrug) |
|
|
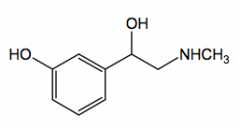
Dopamine no b-hydroxy
Renal D1-receptor agonist - renal vessel dilation direct and indirect B1-agonist treatment of shock: increase BP and HR IV |
|
|
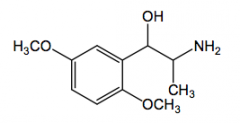
Phenylephrine direct acting a1 agonist - vasoconstrictor
used for hypotensive shock mydriatic and glaucoma active orally no CNS stimulation |
|
|
Methoxamine direct acting a1 agonist - vasoconstrictor
maintain adequate arterial BP in surgery |
|
|
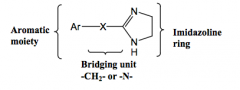
General structure of imidazoline a-agonist (direct acting) |
|
|
|
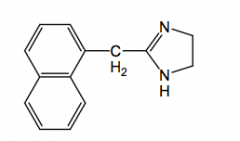
Naphazoline direct acting alpha1 agonist
nasal and opthalmic decongestant pka-10 (at ph 7, over 99% ionized, no CNS activity)
|
|
|
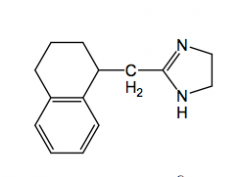
Tetrahydrozoline
direct acting alpha1 agonist
nasal and opthalmic decongestant pka-10 (at ph 7, over 99% ionized, no CNS activity) |
|
|
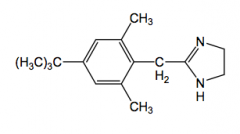
Xylometazoline
direct acting alpha1 agonist
nasal and opthalmic decongestant pka-10 (at ph 7, over 99% ionized, no CNS activity) |
|
|
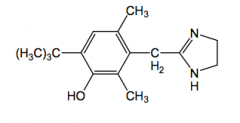
Oxymetazoline
direct acting alpha1 agonist
nasal and opthalmic decongestant pka-10 (at ph 7, over 99% ionized, no CNS activity)
|
|
|
Clonidine c
antihypertensive 1/2 life: 8-12hrs pka 8
good lipophilicity stimulate both a2-adrenoreceptors and imidazoline receptors in CNS
analgesic, ocular hypotensive effects |
|
|
selective a2 agonists; direct centrally-acting imidazolidines |
activation of presynaptic a2-receptors, inhibit NE release, decrease sympathetic outflow and lower BP
(need access to CNS, must be centralyactive) |
|
|
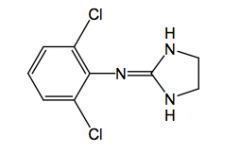
apraclonidine |
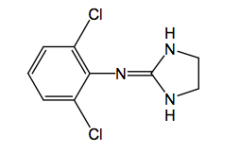
+ a para NH2 glaucoma pka: 9 t1/2 = 6 hrs
selective a2 agonist |
|
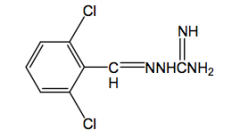
|
Guanabenz selective a2 agonist
open ring imidazolidine antihypertensive 1/2 life = 6hr |
|
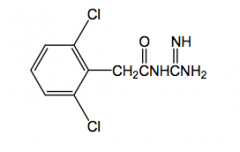
|
Guanfacine selective a2 agonist
antihypertensive t1/2 = 17hrs |
|
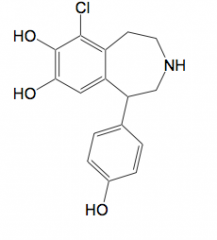
|
CNS a2 agonist Fenoldopam (phenylethylamine derivative)
Selective dopaminergic-D1 agonist, moderate affinity for a2-receptor
peripheral arteriolar dilator used for hypertensive crises
racemic mixture used, (R)-isomer active |
|
|
Isopreterenol direct acting B-adrenergic agonist
B1=B2 potent bronchodilator, cardiac stimulant
inhale,inject, sublingual |
|
|
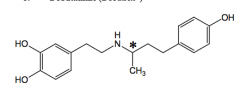
Dobutamine direct acting dopamine analog
+isomer: b1 and b2 agonist
- isomer a1 agonis
racemic mixture stronger inotropic (strength of contraction) than chronotropic
CHF, surgery |
|
|
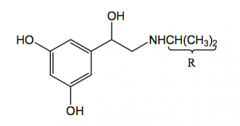
Metaproteranol direct acting, selective B2 agonist
bronchodilator for asthma
active orally lower B2 affinity than isoproterenol, longer duration
bulkier R = more b2 selectivity |
|
|
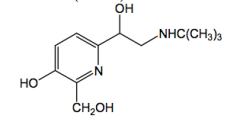
terbutaline |
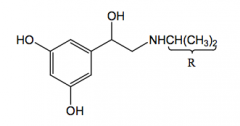
R=C(CH3)3 B2 agonist |
|
|
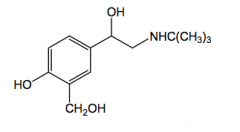
Albuterol selective B2-agonist
active orally long duration |
|
|
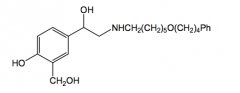
Pirbuterol more lipophilic
selective B2-agonist |
|
|
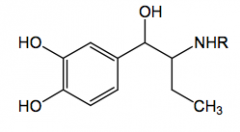
Salmeterol Ph=phenyl
much higher lipophilicity
selective b2-agonist |
|
|
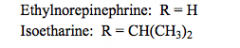
selective b2 agonist |
|
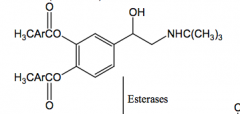
|
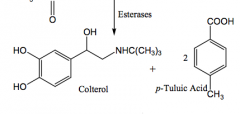
Bitelterol - inhalation for bronchial asthma (prodrug) selective b2 agonist
colterol=active metabolite |
|
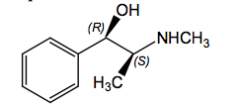
|
Ephedrine direct and indirect acting a and b adrenergic agonist nasal decongestant, allergy, colds mild analeptic (CNS stimulant) antiasthmatic, oral, IV,IM, topical
|
|
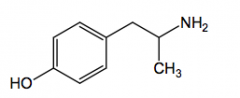
|
Hydroxyamphetamine
indirect acting adrenergic, release endogenous NE
lack benzylic hydroxyl or with inappropriate stereochemistry
OH on phenyl makes too polar to cross BBB |
|
|
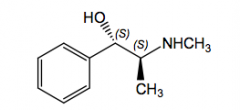
Pseudoephedrine nasal decongestant, many OTC preparations
indirect acting adrenergic, release endogenous NE
lack benzylic hydroxyl or with inappropriate stereochemistry
|

