![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sodium channel inhibitor |
Tetrodoxin (TTX) |
|
|
|
Potassium channel inhibitor |
Tetraethylammonium (TEA) |
|
|
|
Current clamp |
Measures membrane potential, injects current |
I-clamp |
|
|
Voltage clamp |
Holds membrane potential constant, measures current (ion flow) |
V-clamp |
|
|
Positive Ions flowing in mean a negative or positive current? |
Negative |
|
|
|
Positive Ions flowing out mean a negative or positive current? |
Positive |
|
|
|
Ohms law |
V= I R |
V - voltage or membrane potential I - current or ion flow R - resistance, or membrane permeability |
|
|
Name of cell membrane model |
Fluid mosaic by singer Nicholson |
|
|
|
Most common membrane lipid is made of |
Choline head and fatty acyl chain |
|
|
|
Types of lipid movement in the membrane (5) |
Lateral diffusion Flexion Rotation Bobbing Flip flopping |
|
|
|
What is the cause of asymmetric distribution of lipid membrane components |
Lipid rafts Tethering by cytoskeleton (eg spectrin) |
|
|
|
What is the cause of asymmetric distribution of lipid membrane components |
Lipid rafts Tethering by cytoskeleton (eg spectrin) |
|
|
|
What is the role of cholesterol in lipid membrane |
Controls membrane fluidity |
|
|
|
What is the cause of asymmetric distribution of lipid membrane components |
Lipid rafts
|
Tethering by cytoskeleton (eg spectrin) |
|
|
What is the role of cholesterol in lipid membrane |
Controls membrane fluidity |
|
|
|
What is FRAP |
Fluorescence recovery after photo bleaching |
Used to study membrane dynamics |
|
|
Define non-confluent |
Dissociated (in epithelium) Confluent epithelium creates sheets |
|
|
|
What protein is responsible for flip flopping in the membrane |
Flippase |
Also called phospholipid exchange protein (PLEP) |
|
|
What protein is responsible for flip flopping in the membrane |
Flippase |
Also called phospholipid exchange protein (PLEP) |
|
|
How can PLEP contribute to cancer? |
Hyperactive when MDR1 gene expressed Works as efflux pump for drugs |
|
|
|
What is hydro patchy index |
Based on oil-water partition coefficient Used to analyse sequence of amino acids to identify transmembrane helices in a protein |
|
|
|
What is the simplest possible model of lipid membrane |
Liposome |
|
|
|
What is the simplest possible model of lipid membrane |
Liposome |
|
|
|
What is the name for a lipid with a polar head and non polar tail |
Amphiphatic lipid |
|
|
|
What does perfect osmometer mean |
Animal cells such as RBCs grow or shrink proportionally to h2o volume |
|
|
|
What are water channels called |
Aquaporins |
|
|
|
What does AQP4 mutation cause |
Incorrect cerebral water balance |
|
|
|
What does AQP4 mutation cause |
Incorrect cerebral water balance |
|
|
|
What does AQP5 mutation cause |
So saliva production |
|
|
|
What does AQP2 mutation cause |
Increased water retention (because of problems in distal tubule on kidney) |
|
|
|
What does AQP2 mutation cause |
Increased water retention (because of problems in distal tubule on kidney) |
|
|
|
What is the least specific passive type of membrane transport? |
Basal leak |
|
|
|
What does AQP2 mutation cause |
Increased water retention (because of problems in distal tubule on kidney) |
|
|
|
What is the least specific passive type of membrane transport? |
Basal leak |
|
|
|
What is reptation |
Long protein and molecules squeeze through the membrane passively by a snake-like movement |
|
|
|
What chemical inhibits gap junctions |
Hexanol |
|
|
|
What chemical inhibits gap junctions |
Hexanol |
|
|
|
Where do gap junctions help? |
Electrical and chemical coupling in smooth muscle and heart
Activity coordination in hepatocytes |
|
|
|
What is a nAChR channel inhibitor? |
Bungarotein |
|
|
|
What is the fastest simple transporter? |
Band 3 anion exchanger HCO3 and Cl antiport Allows co2 efflux from cells |
|
|
|
What can inhibit the NKCC transporter |
Anti-loop diuretics |
|
|
|
What can inhibit the NKCC transporter |
Anti-loop diuretics |
|
|
|
What can inhibit the Na/H transporter antiport? |
Amiloride |
|
|
|
How does glucose transport in the intestine work? Name the channels |
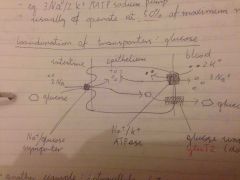
Na/glucose symport Na/K/ATPase Glucose uniport Glut2 |
|
|
|
What causes cystic fibrosis? |
Defective Cl- channels |
|

