![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the MA for a Lever?
|
load/
effort effort distance/ load distance |
|
|
What is the MA for a Pulley?
|
load/
effort count the number of supporting strands |
|
|
What is the MA for a Gears?
|
number of teeth on driven gear/
number of teeth on driving gear |
|
|
What is the MA for a Sheaves?
|
driving diameter/
driven diameter |
|
|
What is the MA for a Inclined Plane?
|
horizontal length/
vertical rise |
|
|
What is the MA for a Wheel & Axel
|
radius of wheel/
radius of axle |
|
|
speed of pulleys in a system
|
speed1 x diameter1 = speed2 x diameter2
|
|
|
when a gas is compressed
|
it heats up
|
|
|
when a given amount of gas expands
|
its pressure drops & the gas cools
|
|
|
when a gas cools without a change in outside pressure
|
it loses volume
|
|
|
water pressure law:
|
total flow through a pipe system is the same everywhere
|
|
|
when liquid speeds up
|
pressure falls
|
|
|
when liquid slows down
|
pressure rises
|
|
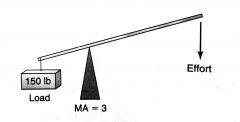
|
class 1 lever
|
|
|
examples of class 1 levers
|
seesaw, scissors
|
|
|
examples of class 2 levers
|
wheelbarrow
|
|
|
examples of class 3 levers
|
tweezers, tongs, human forearm
|
|
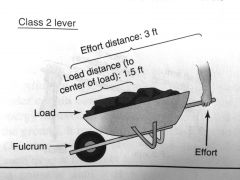
|
class 2 lever
|
|
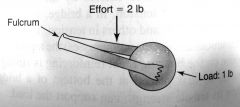
|
class 3 lever
|
|
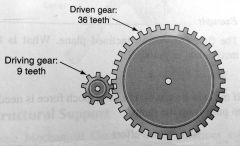
|
gear
|
|
|
chemical energy
|
energy stored in chemicals or released in a chemical action
|
|
|
compound machine
|
a machine made up of two or more simple machines working together
|
|
|
compression
|
a force that pushes materials together
|
|
|
effort
|
in a lever, the point where you apply force
|
|
|
effort arm
|
in a lever, the distance from the force to the fulcrum
|
|
|
electrical energy
|
energy in moving electrons
|
|
|
flexibility
|
the ability of a material to bend without breaking
|
|
|
friction
|
the force the resists the relative motion of two surfaces in contact
|
|
|
fulcrum
|
the stationery element that holds a lever but also allows it to rotate
|
|
|
gravity
|
an attractive force between objects
|
|
|
kinetic energy
|
energy in a moving object
|
|
|
load
|
in a lever, the distance from the load to the fulcrum
|
|
|
load arm
|
in a lever, the distance from the load to the fulcrum
|
|
|
mechanical advantage
|
the amount by which a machine multiplies the force applied to it
|
|
|
potential energy
|
energy that can be released under certain conditions
|
|
|
tension
|
a force that pulls materials apart
|
|
|
what are the six types of simple machines
|
lever, wheel and axle, pulley, inclined plane, wedge, and screw
|
|
|
torque formula for lever
|
weight x distance from the fulcrum
|
|
|
formula for speed
|
distance divided by time
|
|
|
how much work can a 1 hp machine do in one second
|
550 ft. lb.
|

