![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name some Poultry Class breeds
|
American
Asiatic English Mediterranean |
|
|
Cornish Game Hen factors for slaughter
|
5 to 6 weeks old
less than 2 lbs |
|
|
Broiler or Fryer factors for slaughter
|
less than 13 weeks old, but most are 6 1/2 to 7 1/2 weeks old
2 1/2 to 3 1/2 lbs |
|
|
Roaster factors for slaughter
|
3 to 5 months old
|
|
|
Capon factors for slaughter
|
Castrated Male
Less than 8 months old |
|
|
Hen Fowl or Baking for slaughter
|
Mature Female
greater than 10 months old |
|
|
What are the factors for Poultry Grading?
|
Condition (wholesomeness)
Class (by sex and age) Quality (desirability of carcass; how many dressing defects, amount of meat, thickness of muscling, color of skin) |
|
|
What is something that they look for in chicken when grading that they dont look for in other species?
|
Broken bones in wings and legs
|
|
|
What do they look at when grading eggs?
|
Interior Quality
Exterior Quality Weight |
|
|
What do they look for when grading the interior quality of eggs?
|
White and yolk
Size of the air cell |
|
|
What do they look for when grading the exterior quality of eggs?
|
Cleanliness of shell
Soundness of shell |
|
|
What are the grades of eggs?
|
AA
A B inedible or loss |
|
|
What are the egg sizes?
|
Jumbo 30 oz
Extra Large Large Medium Small Peewee 15 oz |
|
|
What is the most widely consumed meat?
|
Pork and accounts for 40% of the world's meat consumption
|
|
|
What animal is being slaughtered the most?
|
Hogs
|
|
|
What are the top states for cattle slaughter?
|
Nebraska
Kansas Texas |
|
|
What are the top states for Hog slaughter?
|
Iowa
North Carolina Minnesota |
|
|
What are the top states for Chicken slaughter?
|
Georgia
Arkansas Alabama |
|
|
What are the top states for Turkey slaughter?
|
Minnesota
North Carolina Arkansas |
|
|
For Broiler production in the U.S, what rank is Oklahoma?
|
11th
|
|
|
What are the top 3 Chicken industries on the market?
|
Pilgrims Pride
Other Tyson Foods |
|
|
What is the ideal flesh condition of feeder cattle?
|
light medium
|
|
|
What term is given to feeder cattle of predominantly English breed type?
|
Okies
|
|
|
What breed type would be called a "Featherneck" or "Whiteface?"
|
Hereford
|
|
|
Which muscling score of feeder cattle is the thickest?
|
1
|
|
|
What is the top reason for selling cows?
|
Old age
|
|
|
Which body condition score is the most ideal for cattle?
|
(In the middle) 4, 5, 6 range
|
|
|
What was the first and most well known USDA Certified Program?
|
Certified Angus Beef
|
|
|
What was the most effective instrument to predict cutability of live animals?
|
Ultrasound
|
|
|
What is a negative of beef instrument grading?
|
Cant estimate maturity
|
|
|
What was the first instrument that used to measure cutability to determine value in pork?
|
Fat-O-Meter
|
|
|
How many hogs are slaughtered in U.S. each year?
|
Over 100 million
|
|
|
What is the number one importer of US pork on a value basis?
|
Japan
|
|
|
What is the avg dressing percentage of hogs?
|
75%
|
|
|
What fat thickness measurement is used to calculate US grade?
|
Last rib
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT used to calculate fat free lean?
A. loin eye area B. hot carcass weight C. 10th rib fat thickness D. first rib back fat |
First rib
|
|
|
What are the top 5 swine producing countries?
|
China 52.5 million tons
European Union United States Brazil Russia |
|
|
Where does the U.S. rank in terms of swine production?
|
2nd
|
|
|
What are the top 6 swine producing states?
|
Iowa
North Carolina Minnesota Illinois IndianaNebraska |
|
|
Where is oklahoma with swine production?
|
Ranked 8th
|
|
|
Many hog farms are becoming ___________ ___________.
|
Vertically integrated
|
|
|
What does it mean to be vertically integrated?
|
The owner owns all phases of production
|
|
|
Describe the geographic shift in hog production
|
Sows are leaving the corn states
Hogs went to N.C. because N.C. developed a better system Hogs are moving west to get away from rain and people |
|
|
Name a few ways the trends are changing in the U.S. swine industry.
|
Fewer and bigger hog farms
Specialization Integration of production and packing |
|
|
What are the top 3 US Hog Farms?
|
Smithfield Foods
Conti Group Seaboard Farms |
|
|
What is the estimated daily slaughter # at Smithfield foods?
|
A little over 80,000
|
|
|
What are the pork production phases?
|
Breeding/gestation
Farrowing Nursery Growing/Finishing |
|
|
What does the farrowing process involve?
|
process of the sow/gilt giving birth
farrowing stalls |
|
|
What are all-in/all-out types of production?
|
Completely empties a barn between groups of hogs that allows for cleaning, disinfection, and better disease control
|
|
|
How do you categorize swine breeds?
|
Colored: Paternal - muscle, growth traits, leanness
White: Maternal - milk, litter size, mothering ability |
|
|
Hybrid Vigor (heterosis)
|
occurs when the offspring are better than the average of their parents for a particular trait
|
|
|
Approximately what percentage of hogs marketed annually in the U.S. are crossbred?
|
95%
|
|
|
Rotational Crossbreeding System
|
use either three breeds rotated in order or two breeds in a criss-cross manner
-maintain 86% heterosis in offspring and sows -most common crossbreeding system |
|
|
Terminal Crossbreeding system
|
differs from a rotational in that all offspring from the terminal mating are marketed and no replacements are kept
Two types: 1) Two breeds 2) Two breed X-bred mated to boar of third breed -Maintain 100% heterosis in both the sows and market animals |
|
|
Rotaterminal System
|
Combines the rotational and terminal breeding systems. Top females are selected and used in a rotational cross that produces replacement gilts. Maternal breed purebred boards are used in this rotation. The replacement gilts are then mated to terminal boars for market production.
|
|
|
What are things unique of pork as a meat species?
|
1. Highly susceptible to stress (metabolism)
2. Dressed/harvested (slaughtered) differently a. Monogastric digestive system (simple stomach) b. Skin on c. Feet on d. shortest gestation; litter size = largest |
|
|
Characteristics of visual evaluation on hogs.
|
-Subjective
-Less accurate than real-time ultra sound -Less expensive, more convenient -Still important for selection decisions -Still important for marketing decisions |
|
|
What are the value determining traits in Hogs?
|
Weight
Dressing % Leanness Muscle |
|
|
Leanness characteristics for Hogs
|
10th rib
Last rib fat thickness |
|
|
Muscle characteristics for Hogs
|
Loin muscle area
USDA muscle score |
|
|
Average live weight for Hogs
|
280 lbs
|
|
|
Average DP for Hogs
|
75%
|
|
|
Affecting factors for DP of Hogs
|
Fill, muscle, fat
|
|
|
Average carcass weight for Hogs
|
210 lbs
|
|
|
Average length for Hogs
|
31 inches
|
|
|
How do Hogs get fat?
|
top to bottom
front to rear gender effects - gilts are leaner than barrows |
|
|
What is the shape of a hogs ass that is desirable?
|
Upside down cup
|
|
|
Lean hogs have an eye view shape of what?
|
Hour glass shape
|
|
|
Fat hogs have an eye view shape of what?
|
Boat shape
|
|
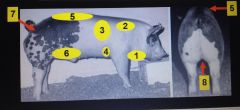
|
1. Jowl
2. Blades 3. Forerib 4. Elbow Pocket 5. Loin edge 6. Flank 7. Tail Head 8. Ham Seam |
|
|
Describe Last Rib Fat Thickness in Hogs
|
Used for calculation of USDA grade
Only measure of fat on the carcass used in the industry |
|
|
Describe 10th rib fat thickness
|
3/4 lengths of the eye muscle; corresponds with "loin edge"
Used to calculate % muscle Avg: 0.7 inches |
|
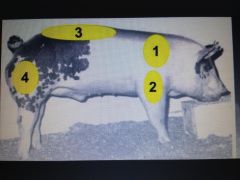
|
1. Shoulder
2. Forearm 3. Loin (top) 4. Ham/stifle |
|
|
What muscle does the LEA come from?
|
Longissimus dorsi
|
|
|
What is the average LEA?
|
6.0 in. squared
|
|
|
2 Factors of USDA carcass grading for hogs?
|
1. Last rib back fat
2. muscle score |
|
|
How do you determine the USDA grade for a hog carcass?
The formula |
(4 * LRBF) - MS
|
|
|
As far as grading, what happens with thin muscled hogs?
|
ineligible for USDA #1
|
|
|
Thick = ?
Average = ? Thin = ? |
3
2 1 |
|
|
Avg of three backfat measurements for Hogs:
|
First Rib
Last Rib Last Lumbar Vertebrae |
|
|
What is the formula to determine average back fat for hogs?
|
ABF = (First Rib + Last Rib + Last Lumbar Vertebrae) / 3
|
|
|
How do you find pounds fat free lean for hogs?
Formula |
55 + LEA - (12*10th rib fat depth)
|
|
|
Give some beef grading fact
|
Optional
Paid for by packers and processors Must be inspected 60% of all beef harvested is federally graded |
|
|
Positive for USDA Grading
|
Sorts carcasses based on relative palatability and cutability
Fast (over 400/hr) Non-invasive Relatively inexpensive |
|
|
What is a negative for USDA Grading?
|
Criticized for its "subjectivity" and human "fallibility"
|
|
|
Name some beef grading instruments
|
NMR, NIR, Ultrasound, VIA, CAT-Scan
|
|
|
What are some instrument grading negatives?
|
Cant determine skeletal maturity
Adjusted PYG (fat thickness) KPHOperator error |
|
|
Live evaluation tools:
|
Probes
Scales Ultrasound K^40 Counter Anesthetic CT-Scan MRI |
|
|
Describe the Fat-O-Meter
|
Backfat thickness and loin muscle thickness in mm and lean reflectance
The carcass lean meat percentage |
|
|
Describe AutoFom
|
Carcass Lean Meat Percentage
Fat Thickness The commercial value of each carcass Weight salable meat on specific commercial cuts |
|
|
Describe UltraFom 300
|
Backfat thickness and loin muscle thickness in mm
Carcass Lean meat percentage Ham Fat thickness |
|
|
What is QUALITY?
|
A product that conforms to a set of standards
A product that meets consumers wants and needs |
|
|
What does it mean to say "calves are even?"
|
this means less than 150 lbs variation in weight from light to heavy for yearling cattle; 100 lbs variation in calves
|
|
|
What does it mean to "calves are uneven?"
|
means weight variance in yearling cattle between 150 lbs & 200 lbs; 100 & 150 lbs for calves
|
|
|
What does it mean to say "calves are VERY uneven?"
|
means variance over 200 lbs for yearling cattle; over 100 lbs for calves
|
|
|
For calves, what does it mean to say "short age?"
|
Not used with yearling cattle, ONLY calves and those in excellent condition and still their mothers
|
|
|
What does it mean to "Medium age?"
|
Calf with an average home (not starved)
|
|
|
What does it mean to say "Long age?"
|
A calf that has had very poor growing conditions
|
|
|
Flesh condition
|
Do not try to sell this type; buy feed and improve their condition
|
|
|
Flesh condition
For feeder cattle, what does it mean to say "Thin?" |
Lightly fleshed due to possible poor pasture conditions
|
|
|
Flesh condition
For feeder cattle, what does it mean to say "light medium?" |
(slightly fleshy) - these are ideal feeder calves; strong and healthy with little fat
|
|
|
Flesh condition
For feeder cattle, what does it mean to say "medium?" |
fleshy
|
|
|
Flesh condition
For feeder cattle, what does it mean to say "heavy medium?" |
very fleshy
|
|
|
What are the three condition scores for feeder cattle?
|
Thin
|
|
|
Define Okies (#1,2,,3)
|
Predominantly English; possible cross with Dairy or Exotic
|
|
|
Define Exotics (Exotic #1,2,3)
|
Cross of at least 3/4 continental breeding
|
|
|
Define Brahman crosses (Cross #1,2,3)
|
1/8 to 3/4 Brahman
|
|
|
Define Purebred or High Grade (Brangus #1, Hereford #2, Holesteins)
|
Use breed name and classifications
|
|
|
How are feeder calves and yearling evaluated?
|
Frame Size
Muscle Score |
|
|
Feeder cattle muscling #1
|
Moderately thick throughout; showing a rounded appearance through the back and loin with moderate width between the legs
|
|
|
Feeder Cattle muscling #2
|
Slightly thick throughout; showing a rounded appearance through the back and loin with slight width between the legs
|
|
|
Feeder Cattle muscling #3
|
Thin through the forequarter and the middle parts of the round; back and loin have a sunken appearance; legs are set close together
|
|
|
Feeder Cattle muscling #4
|
Less thickness than the minimum required for #3
|
|
|
Cull Cows bring in how much gross income for ranches?
|
20%
|
|
|
Non-fed cattle brings in what percentage of the US Beef Supply?
|
20%
|
|
|
What season during the year does culling occur?
|
Fall
|
|
|
What are the top reasons for culling cows?
|
Old age (teeth)
Non-pregnancy status Economic status, drought, herd down-sizing poor production lameness, eyes, disposition |
|
|
What are the two factors affecting price within season?
|
Dressing %
Body Condition |
|
|
How do you determine the DP?
|
CW / LW * 100
|
|
|
Factors affecting DP
|
Fatness or Body Condition
|
|
|
Packers who slaughter "cull cows" NEVER use official ________ _______.
|
USDA grades
|
|
|
For the body condition scoring system, what does #1 mean and what does #9 mean?
|
#1 = Emaciated
#9 = Obese |
|
|
Describe White Fat Market Cows
|
Most cows culled are on pasture and/or hay
Yellow color to fat tissue Cows can be fed grain (corn, milo) for 60 days Produces carcass with white fat (more desirableappearance) Only certain packing plants (direct sale) |
|
|
Which breed of swine is characterized by erect ears and black with a white belt?
|
Hampshire
|
|
|
Which breed of swine is solid red in color?
|
Duroc
|
|
|
What is the usual gestation length of sows?
|
3 months 3 weeks 3 days
|
|
|
How are piglets identified for pig # and litter?
|
Ear notches
|
|
|
what is the primary product made from pork bellies?
|
Bacon
|
|
|
What is the typical weight of market barrows and gilts?
|
230 lbs
|
|
|
Which of the following is not one of the four lean cuts of a pork carcass?
A. Ham B. Loin C. Belly D. Picnic shoulder |
C. Belly
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a factor used to determine fat free lean of pork carcasses?
A. HCW B. LEA C. 10th rib fat thickness D. Last rib fat thickness |
D. last rib fat thickness
|
|
|
What instrument was first used to measure lean percentage of pork carcasses and still used in many packing plants today for value based pricing assessment?
|
Fat-O-Meter
|

