![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
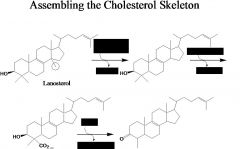
name products, reactants, enzymes, and # of carbons.
|
answer
|
|
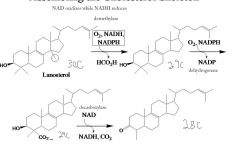
no. of carbons, enzymes, reactants, byproduct.
|
answer
|
|
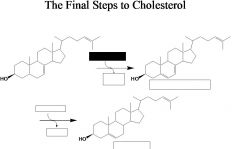
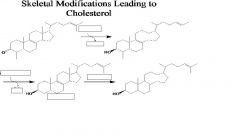
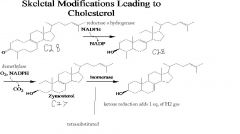
number of carbons, enzymes, name, in&out.
|
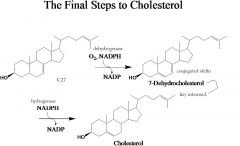
answer
|
|
|
Cholesterol mimic present in fungi(1). Most antifungal agents inhibit __(1). (Most end in __(2))
|
(1) ergosterol
(2) azole |
|
|
Used in bacteria as cholesterol mimics
|
Hopanoids
|
|
|
__(1) binds to receptor and induces expression of __(2). calcium useless without (1).
|
(1) Vitamin D
(2) calcium binding protein |
|
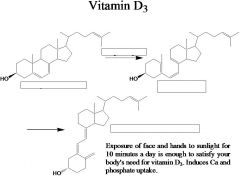
# carbons
|
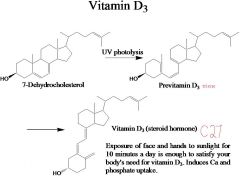
answer
|
|
|
__(1) and __(2) solubilize cholesterol and aid the reabsorption of Vitamin __(3) from the __(4).
|
(1) Bile Salts
(2) Phospholipids (3) D (4) intestine |
|
|
process by which bile salts(stored in gallbladder) are secreted into the intestines and are then reabsorbed with dietary lipids. Occurs 6-12 times daily
|
Enterohepatic circulation
|
|
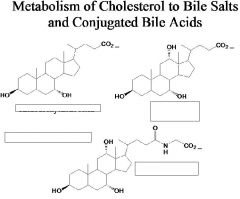
number of carbons and name.
|
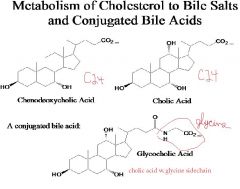
answer
|
|
|
True/False
Blood contains lipids at concentration far above their solubility in water |
True
|
|
|
Lipids are kept in solution by their incorporation into spherical particles called__(1). The polar head groups of phospho- and sphingolipids are arrayed at the surface and very hydrophobic molecules such as cholesterol __(2) are buried into the hydrophobic region of the (1).
|
(1) lipoproteins
(2) esters |
|
|
HDL-contains HIGH levels of __(1) and low levels of __(2) and is responsible for transporting excess __(3) to the __(4) for further metabolism to __(5).
|
(1) cholesterol
(2) triacylglycerol (3) cholesterol (4) liver (5) bile salts |
|
|
bile salts are needed for what?
|
needed to digest fats
|
|
|
LDL - Responsible for transporting __(1), __(2), and __(3) from one __(4) to another. A second major role is the regulation of __(5) biosynthesis.
|
(1) cholesterol
(2) cholesterol esters (3) triacylglyerols (4) tissue (5) cholesterol |
|
|
__(1) regulates cholesterol biosynthesis by passing through the liver, which recognizes the amount of __(2) present in the __(1) and determines whether __(2) needs to be synthesized by regulating the rate determining step in __(2) biosynthesis, __(3).
|
(1) LDL
(2) cholesterol (3) HMG CoA reductase |
|
|
Weighs heavily towards sequesteration in the cell membrane
|
Cholesterol
|
|
|
What is CETP and what does it do and where does it bind?
|
Cholesterol ester transfer protein - bound to HDL and is responsible for the xfer of cholesterol from HDL to LDL.
|
|
|
__(1) on cholesterol can become esterified and becomes part of the __(2) area. Once ester is formed it is embedded it never comes out. But cholesterol has a diffusion coefficient(99.9% in the membrane)
|
(1)Alcohol
(2) hydrophobic |
|
|
__(1) has LDL receptors to endocytize LDL(which has all the cholesterol clusters). Once inside (enzyme(2) hydrolyze __(3) to form free __(4)
|
(1) LIVER
(2) cholesterol esterase (3) esters (4) cholesterol |
|
|
People with low LDL receptors have too much__(1). this is why some people have __(2)
|
(1) HMG-CoA reductase.
(2) Hypercholestoremia |
|
|
Slowest step in cholesterol biosynthesis
|
HMG-CoA reductase
|
|
|
1. What is the sex hormone is females? What does it do?
2. Sex hormone in males? What is it coverted to and what does it do? |
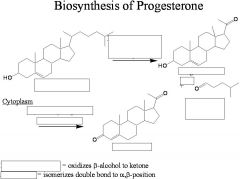
1. Progesterone(females) is responsible for maintaining the uterine endometrium and is a differentiation factor for mammary glands.
2. Testosterone is converted to dihydrotesterone and is responsible for the production of sperm proteins and secondary sex characteristics. |
|
|
what does 17β-estradiol(females) do?
|
In females this hormone regulates the ovarian cycle and has similar effects as progesterone.
|
|
|
what does 17β-estradiol(males) do?
|
In males this hormone is a negative feedback inhibitor of Leydig cell synthesis of testosterone.
|
|
|
Name the two classes of steroid hormones
|
1. sex and progestational hormones
2. adrenal hormones |
|
|
draw and number cholesterol
|
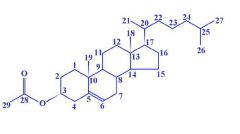
answer
|
|
|
Sex and Progestational Hormones:
Draw Progesterone, Testosterone, and 17β-estradiol |
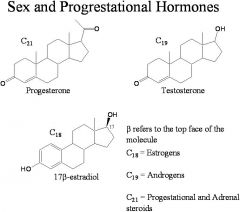
|
|
|
How many carbons in: estrogens(1), Androgens(2), and progestational and adrenal steroids(3)?
|
(1) 18
(2) 19 (3) 21 |
|
|
this hormone is different because it has no methyl group at C10(aromaticity possible and planarity)
|
17β-estradiol
|
|
|
What is Cortisol and what does it do?
|
It is a stress hormone that elevates liver glycogen, elevates high blood pressure, has a killing effect on some T-cells and effects sodium uptake.
|
|
|
What does Aldosterone do?
|
Causes sodium uptake and occurs at high levels during stress. It too raises blood pressure and also increases fluid volume.
|
|
|
ADRENAL steroids: Draw them
|

|
|
|
Estradiol binds at which Carbon?
|
C17
|
|
|
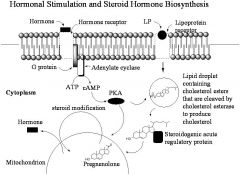
__(1) hormone(can go through cell membrane) have to be told to be made by __(2) hormones(cannot go through cell membrane)
|
(1) steroid hormones
(2) peptide hormones |
|
|
__(1) hormone(extracellular surface always)
|
(1) Peptide hormones
|
|
|
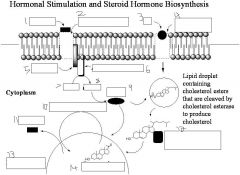
This will phosphorylate cholesterol esterase
|
PKA
|
|
|
Lipoproteins within cells much smaller lipoproteins to increase surface area
|
Lipid droplet
|
|
|
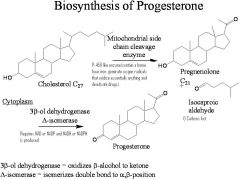
What is the key intermediate in steroid biosynthesis?
|
Pregnenolone
|
|
|
What is STAR protein? What does it do?
|
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. transport protein that regulates cholesterol transfer within the mitochondria, which is the rate-limiting step in the production of steroid hormones.
|
|
|
Steroid hormone that is
|
|
|
|
|
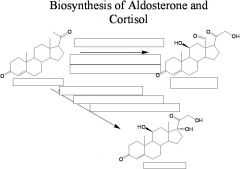
|
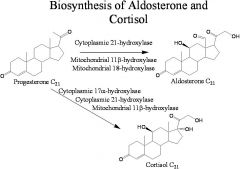
|
|
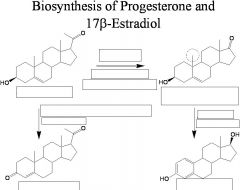
|
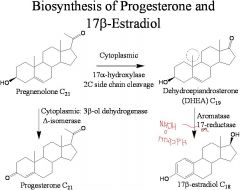
|
|
|
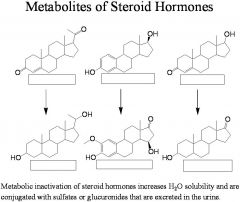
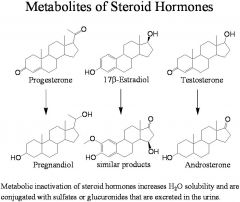
Metabolic inactivation of steroid hormones increases H20 solubility and are conjugated with __(1) or __(2) t hat are excreted in the urine.
|
(1) sulfates
(2) glucuronides |
|
|
|
|
|
These peptide hormones regulate release of which steroid hormones:
(1) Adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH) (2) Angiotensin II/III (3) Luteinizing Hormone(anterior pituitary gland) (4) Follicle-Stimulating hormone(Ovarian follicle) (5) Luteinizing hormone(Corpus luteum) (6) Parathyroid hormone(Makes Vit D3 in kidney) |
(1) cortisol
(2) Aldosterone (3) Testosteron (4) 17B-estradiol (5) Progesterone (6) 1,23(OH)2D3 **recall that a hormone must bind to a receptor to initiate steroid hormone biosynthesis. |
|
|
They can secrete testosterone and are often closely related to nerves
|
Leydig cell
|
|
|
most superficial layer of adrenal cortex and secretes aldosterone.
|
adrenal Zona Glomerulosa
|
|
|
Produces glucocortocoids such as cortisol
|
adrenal zona fasciculata
|
|
|
Corticosteroid-binding globulin(CBG) binds 75% of __(1), 22% of which is bound to __(2), and the remainder is in free form. The free form can permeate cells and elicit biological responses. Only 10% of aldosterone is bound to CBG and __(3) percent to albumin.
|
1. cortisol
2. albumin 3. 60% |
|
|
Name the four major plasma proteins responsible for mobilization of steroid hormones.
|
(1) Corticosteroid-binding globulin(CBG)
(2) Sex hormone binding globulin (3) Androgen binding protein(ABP) (4) Albumin |
|
|
The most abundant plasma protein and represents 50% of the total plasma proteins found in humans and binds to a lot of hydrophobic molecules.
|
Albumin
|
|
|
The presence of __(1) decreases the amount of SHBG in blood and __(2) increases the production of SBHG.
|
(1) testosterone
(2) 17B-estradiol |
|
|
Sex hormone binding globulin binds 10% of __(1), 1-3% unbound, and the remainder bound to __(2). Prior to puberty both males and females have the same amount of SHBG, but the onset of puberty results in a significant decrease in SHBG for (males/females)(3) and a small decrease in (males/females)(4) resulting in a greater amount of free __(5) and __(6), respectively. Adult (males/females)(7) have 1/2 as much SHBG as adult (males/females)(8).
|
1. testosterone
2. albumin 3. males 4. females 5. testosterone 6. 17B-estradiol 7. males 8. females |
|
|
Why do men have a 40-fold increase of free testosterone compared to women?
|
Adult males have 1/2 as much SHBG as adult females.
|
|
|
(True/False)
You don't make less of sex hormone but the Sex hormone binding globulin. |
True
|
|
|
Molecular chaperone
|
Hsp90-modulate steroid hormone receptors.
|
|
|
Molecular chaperone binds to __(1) and bind to and clamp forming __(2) to stabilize and prevent side chain interactions
|
(1) ribosome
(2) polypeptides |
|
|
what would be the result of inhibiting Hsp90
|
prevents protein folding
|
|
|
What will stimulation of Hsp90 do?
|
Collect misfolded proteins, refold them and throw them to the proteosome.
|
|
|
Steroid hormone receptor is exressed and remains in the __(1)
|
1. cytoplasm
|
|
|
what is refractory cancer
|
Caner can become hormone independent
|
|
|
Only activated __(1) complex can cross the nuclear membrane and binds to __(2).
|
(1) activated RECEPTOR complex
(2) DNA consensus sequence. |
|
|
Hormone receptor binding to consensus sequence: Proximity is important since RNA polymerase must bind to __(1) and __(2)
|
(1) transcription factor
(2) hormone receptor |
|
|
What bodily functions do prostaglandins mediate?
|
contraction of intestinal and uterine muscles. Also play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure, inflammation, pain and fever. (arthritis and mediates gastric acid secretion)
|
|
|
Prostaglandings are produced in all mammalian cells except __(1) and they are used immediately.(short half-life)
|
1. RBCs
|
|
|
All of these are derived from 20 carbon fatty acids
|
Prostaglandins
|
|
|
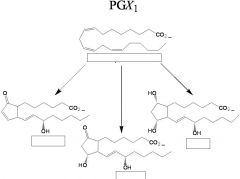
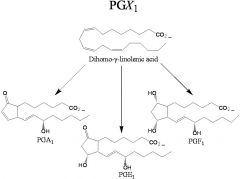
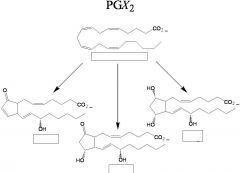
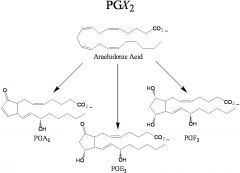
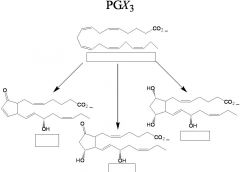
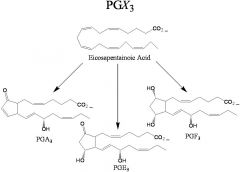
Draw A, E, and F prostaglandins.
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Lower systemic arterial pressure by vasodilation, resulting in increased bloodflow and decreased resistance
|
PGE(n) and PGA(n)
|
|
|
reduce signs of inflammation
|
PGE1 and PGE2
|
|
|
P-450 like enzyme converts to product, adds at least one molecule of __(1)
|
1. oxygen gas
|
|
|
|
|
|
used to terminate pregnancy
|
PGE2 and PGF2
|
|
|
induce signs of inflammation, released from hypothalamus(where temperature is regulated and promotes clotting)
|
PGE2
|
|
|
Cats deprived of sleep will accumulate __(1)
|
arachidonic Acid
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
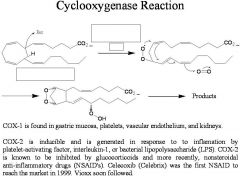
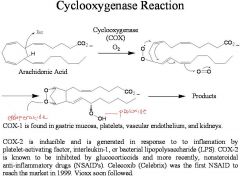
Where is COX-1 found?
|
Gastric mucosa, platelets, vascular endothelium, and kidneys.
|
|
|
Constitutively expressed-always expressed at same concentration
|
COX-1
|
|
|
INDUCIBLE
|
COX-2
|
|
|
Why causes COX-2 to be expressed?
|
generated in response to inflammation by platelet-activating factor, interleukin-1or baterial lipopolysaccharide(LPS).
|
|
|
Known to be inhibited by glucocorticoids and more recently, NSAIDS. Celecoxib and vioxx
|
COX-2
|
|
|
Most abundant reducing agent in your cell. Endoperoxide are unstable intermediates reduced by these.
|
Glutathione
|
|
|
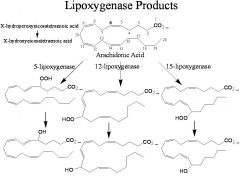
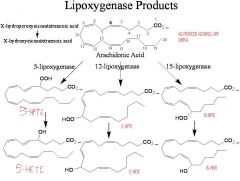
Responsible for the oxidation of arachidonic acid to eicosatetetraenoic acid.
|
Lipoxygenases
|
|
|
Where can one find Lipoxygenases?
|
Plants, fungi, and mammals. CANNOT find in yeasts or most prokayotes.
|
|
|
The active site of lipoxygenases contain an atom of __(1), which is responsible for the radical initiated reaction performed by the lipoxygenases
|
1. iron
|
|
|
Aspirin can kill enzyme permanently by acylating __(1) attached to it. What is this called?(2)
|
1. Nitrogen
2. irreversible inhibitor or suicide substrates |
|
|
Aspirin selectively binds to and inhibits __(1)
|
COX-1
|
|
|
draw structure of aspirin
|
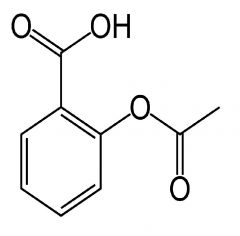
|
|
|
draw structure of salicylic acid
|
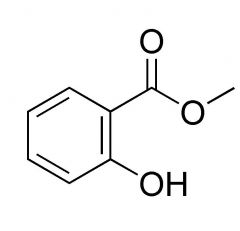
|
|
|
Glutathione will reduce any peroxide around to corresponding __(1)
|
1. hydroxyl group
|
|
|
|
|
|
REVIEW SLIDE 51&52
|
REVIEW SLIDE 51&52
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
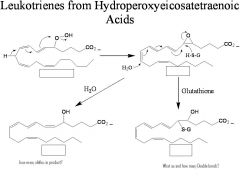
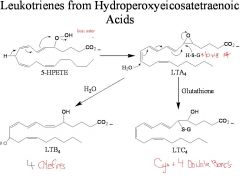
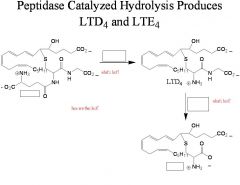
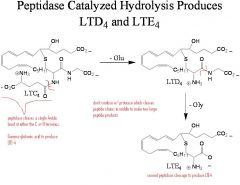
The thiol containing peptides LTC4, LTD4 and LTE4 cause...
|
contraction of smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract and airways resulting in bronchoconstriction and inflammation.
|
|
|
Current drugs used for the treatment of asthma act specifically by inhibiting_(1) and the ligand-receptor complexes
|
5-LOX(5-lipoxygenase)
|
|
|
__(four different) exert their biological action through ligand-receptor complexes
|
LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4
|
|
|
__(1) exist in the body for ~4 h, until further metabolized
|
1. leukotrienes
|

