![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
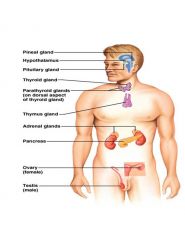
Purely endocrine organs
5ct |
Adrenal: 2 glands
....................Cortex ........................Medulla Parathyroid glands Pituitary gland Pineal gland Thyroid gland Endocrine cells in other organs = 4ct head - toe order |
Hypothalamus
Thymus Pancreas Gonads |
|
|
Adrenal: 2 glands
|
...........Cortex
............Medulla |
|
|
|
Endocrine cells in other organs
4ct |
Hypothalamus
Thymus Pancreas Gonads |
|
|
|
Where are the 3 glands in the brain
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
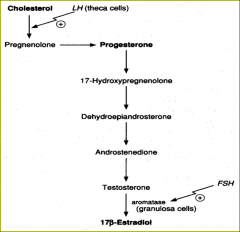
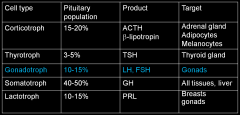
Know chart
|
.
|
|
|
|
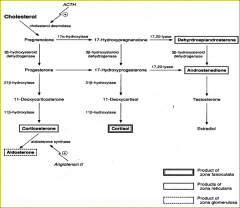
main source of the steroid sex hormones
|
Gonads
Nm them = |
testes
ovaries |
|
|
Testes
Leydig cells receive = |
LH
and produce = |
testosterone
|
|
|
Ovaries
|
Theca cells express receptors for LH and produce
___________ for granulosa cells. Granulosa cells express receptors for FSH and produce estradiol (an estrogen). Granulosa cells also produce progesterone and receptors for __ Corpus luteum (from an ovarian follicle) also secretes = 2ct |
androstenedione
LH. estrogen and progesterone |
|
|
Theca cells express receptors for
|
LH
and produce = |
androstenedione
for granulosa cells. |
|
|
Granulosa cells express receptors for =
|
FSH
and produce = |
estradiol (an estrogen).
|
|
|
Granulosa cells
also produce |
-progesterone
-receptors for LH. |
|
|
|
Corpus luteum (from an _____ _____ )
also secretes |
ovarian follicle
estrogen progesterone |
|
|
|
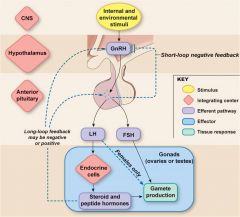
Regulation of the female monthly rhythm, is due to
interplay between the = |
ovarian
and hypothalamic -pituitary hormones: |
|
|
|
Secretion of AP hormone is controlled by =
|
“releasing hormones”
formed in the ______ and transported to the AP gland by the = |
hypothalamus
hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system. |
|
|
Intermittent, pulsatile secretion of GnRH by the _________ stimulates pulsatile release of ___ from the AP =
|
hypothalamus
LH |
|
|
|
Intermittent, pulsatile secretion of ____ by the hypothalamus stimulates pulsatile release of +
|
GnRH
LH from the AP |
|
|
|
GnRH is secreted in pulses lasting
__-__ minutes every ___-__ Hrs = |
5 to 25 min
every 1 to 2 hrs. The pulsatile release of ____cause intermittent output of __ secretion about every __ minutes. |
GnRH
LH 90 |
|
|
theca interna
is responsible for the production of ___________, and indirectly production of _______ aka: E2, |
androstenedione
17β estradiol, by supplying the neighboring granulosa cells with androstenedione that with the help of the enzyme ______ can be used as a substrate for this type of estradiol. ___ induces the granulosa cells to make aromatase that converts the androgens made by the theca interna into estradiol. |
aromatase
FSH Also, the theca interna is highly vascular and possesses LH receptors, not FSH. Note that the estradiol promotes the formation of LH receptors on granulosa cells, which also have FSH receptors. |
|
|
theca externa
is the outer layer of the theca folliculi. During ovulation, the surge in luteinizing hormone increases ____ |
cAMP
which increases progesterone and _____ production. The PGF2α induces the contraction of the smooth muscle cells of the theca externa, increasing intrafollicular pressure. This aids in rupture of the mature oocyte, |
PGF2α
|

