![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The adult spleen is not essential to life, its loss makes the patient more vulnerable to
3ct |
anemia
leukopenia overwhelming infections. |
|
|
|
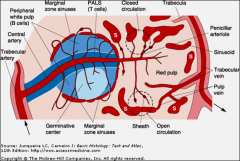
organization of the spleen
|
1. Capsule
2. Pulp |
|
|
|
Splenic Capsule Describe =
|
dense C.T.
trabeculae subdivide the organ into communicating compartments. indented hilus splenic artery vein, lymphatic nerves |
Capsule: dense C.T. tissue capsule which extends trabeculae to subdivide the organ into communicating compartments. The capsule is indented at the hilus, through which splenic artery, vein, lymphatic vessels and nerves pass.
|
|
|
Splenic Pulp Describe =
lacks a cortex and a medulla. |
a. red pulp
b. white pulp c. marginal zone white pulp and merges into red pulp. |
White pulp, marginal zone and red pulp each possess a distinctive stroma made up of reticular meshwork. These meshwork consist of branched reticular cells, which synthesize and lie upon reticular fibers.
|
|
Know the structure
|
.
|
|
|
|
White pulp
is a lymphatic tissue equivalent to the cortex of lymph nodes 3 parts |
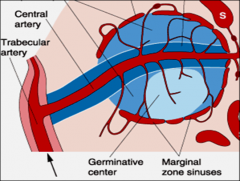
1. periarterial lymphatic sheath
2. lymphatic nodules T-lymphocytes are concentrated in the periarterial sheath and B-lymphocytes are concentrated in the nodules. |
|
|
|
Red pulp
The red pulp consists of 2 |
a reticular meshwork (filtration bed) supplied by
A. arteries B. drained by an anastomosing system of special veins called venous sinuses which drain into pulp veins. The reticular meshwork a branching system of cords splenic cords complementary to branching venous sinuses |
|
|
|
Red pulp contains =
|
splenic sinusoids lined by elongated endothelial cells.
Splenic cords also known as cords of Billroth, separate splenic sinusoids macrophages, and blood cells |
|
|
|
In the cords
there are 4 fctns = |
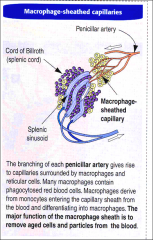
-circulating monocytes
are trapped differentiate into = -platelets are stored -- Erythropoiesis -destruction of old damaged erythrocytes |
macrophages
|
|
|
2 types of blood circulations
have been described in the red pulp: |
1 a closed circulation,
arterial vessels connect directly splenic sinusoids. 2 vessels opening directly into the red pulp spaces, entering through the interendothelial cell slits of the splenic sinusoids. |
|
|
|
Functions of the Spleen
2ct |
PHAGOCYTOSIS
IMMUNOLOGICAL DEFENSE |
|
|
|
Functions of the Spleen
|
filter
phagocytose mount immunological responses blood-borne antigens. The spleen contains all the components (B and T lymphocytes, APCs phagocytic cells |
|
|
|
white pulp of the spleen
production site of = |
Lymphocytes
|
|
|
|
white pulp
The hemoglobin they contain is broken down into several parts. = |
The protein, globin, is hydrolyzed to amino acids that are reused in protein synthesis.
Iron is released from heme and, joined to transferrin, is transported in the blood to the bone marrow, where it is reused in erythropoiesis. Iron-free heme is metabolized to bilirubin, which is excreted in the bile by liver cells. |
|
|
|
Asplenia
|
the Kupffer cells of the liver sinusoids complement the role of the white pulp in the detection and removal of bacteria circulating in blood.
|
|

