![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
.ORAL CAVITY
|
.a stratified squamous epithelium
(Non keritanized in general) with a submucosa present only in certain regions. |
|
|
|
.ORAL MUCOSA
3ct |
.Epithelium is non-keratinized stratified squamous
Lamina propria Submucosa |
|
|
|
.ORAL MUCOSA exception =
|
.Epithelium is non-keratinized stratified squamous except that keratinization occurs on outer margin of lip (
vermilion border), gingiva, hard palate filiform papillae of tongue. |
|
|
|
Lips contain
3c |
stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium
Transitional or Red Area Hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands are not present in this zone. The red margin has numerous sensory nerve endings in dermis and is extremely sensitive to touch. |
|
|
|
Cheeks called =
HAs what epithelial Tissue |
buccinator
subcutaneous connective tissue subcutaneous connective tissue lined mucous membrane. |
|
|
|
tongue muscle =
|
striated skeletal muscle
and glands. |
|
|
|
*** 4 types of papillae are present on the tongue:
|
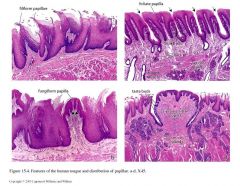
filiform
fungiform circumvallate foliate |
|
|
|
Taste buds
Clinical correlation: Type I familial dysautonomi |
Riley-Day syndrome
causes severe hypogeusia (decreased ability to detect taste). |
|
|
|
Taste receptor cells have a lifespan of
|
10 to 14 days
|
|
|
|
Types of taste buds -
5ct |
Sweet
sour bitter salty fifth taste is umami the taste of monosodium glutamate |
|
|
|
The _________ nerve carries the five taste sensations;
|
facial nerve
|
|
|
|
lacks papillae
|
posterior third of the upper surface of tongue
|
|
|
|
Glands of the Tongue:
|
mucous glands
serous glands mixed acini |
|
|
|
Hard Palate:
is covered by |
stratified squamous
keratinizing epithelium |
|
|
|
Soft Palate covered by
|
covered inferiorly by stratified squamous nonkeratinizing epithelium.
nasal side the soft palate is covered by the pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium |
|
|
|
Pharynx
pharynx is lined by |
nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
|
In adult human, has __ teeth =
|
32 permanent teeth
list them 4 set types |
2 incisors,
1 canine, 2 premolars 3 molars. |
|
|
The permanent teeth are preceded by
____ (baby) teeth. |
20 deciduous
There are no deciduous precursors of |
12 permanent molar teeth.
|
|
|
The organic matrix of dentin is secreted by
|
odontoblasts
|
|
|
|
The odontoblasts produce organic matrix only at the dentinal surface. The cytoplasm of each of these cells contains a nucleus at its base, a large Golgi complex, many ribosomes and secretory granules containing procollagen.
info |
.
|
|
|
|
Each prism is formed by a single =
|
ameloblast
|
|
|
|
The susceptibility of enamel crystals to dissolution in acidic pH is the basis for
|
dental caries
|
|
|
|
meloblasts are tall _________ cells
|
columnar
|
|
|
|
Like dentin, enamel is laid down rhythmically, and cross sections of the tooth crown show
|
concentric,
parallel, incremental lines of Retzius. |
|
|
|
Cementum, like bone, is a _________
tissue that reacts to stresses and under certain circumstances can undergo resorption or hyperplasia. |
labile tissue
|
|
|
|
fibers from the periodontal membrane which penetrate the cementum as _______ fibers. These do not calcify.
|
Sharpey’s
|
|
|
|
The pulp of the tooth is _______________ in origin
|
mesenchymal
|
|
|
|
Pulp
The main cell type is __________ and resemble mesenchyme |
stellate
|
|
|
|
Beneath the layer of odontoblasts is a relatively cell—free area, the zone of __________
|
Weil.
|
|
|
|
All pulpal vessels are _______ walled and are thus pressure sensitive, lying as they do in an unexpandable chamber. Thus relatively mild inflammation and edema can cause occlusion of the blood vessels and consequent death of the pulp.
|
thin
|
|
|
|
periodontal membrane or ligament is a special type of dense fibrous connective connective
the suspensory ligament of the tooth in its socket. |
Periodontal ligament
|
|
|
|
Periodontal ligament
|
Strong, thick bundles of collagenous fibers
extending into the bone and cementum as ____ fibers. |
Sharpey’s
|
|
|
gingiva or gum
Keratinized or Non-Keritanized |
keratinizing
stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
linked to
tooth enamel by cuticle epithelial attachment of ________ recedes with advancing age |
Gottlieb,
|
|
|
|
furrow surrounding crown, the ________ ________ which is lined by ____________ stratified squamous epithelium.
|
gingival crevice,
nonkeratinizing |
|

