![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_________ 1. 6O2 +________ 6H2O + Energy + 6CO2 |
CR: C6H12O6
|
|
|
_________4. ________+ 6H2O ________ + C6H12O6 |
P: 6CO2, 6O2 |
|
|
2.Photosynthesis is a series of reactions that uses ____________________ energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide into ____________________ and oxygen. |
light, glucose |
|
|
3.Photosynthesis takes place in a plant cell’s ___________________________. |
chloroplast |
|
|
4.Circle the pictures that go through photosynthesis.
|
flowers, trees, cactus, wigwam
|
|
|
5.Plants gather the sun’s energy with light-absorbing molecules called ________________________
|
pigments
|
|
|
6.Plants produce glucose (C6H1206), circle which Biomolecule represents glucose.
|
carbohydrates
|
|

|

|
|
|
7. Explain how a student would collect data on the rate of photosynthesis: observe the color? count gas bubbles? Check temperature of water? |
Count gas bubbles |
|
|
8. If a type of eubacteria contains chlorophyll, what does this type of bacteria have in common with plants? |
capable of photosynthesis |
|
|
9. Explain why light energy is written about the arrow in the equation for photosynthesis? |
it is necessary for the reaction to occur |
|
|
10. What molecule is represented by X? |
ATP |
|
|
11. Where is energy stored in a molecule of ATP? |
in the bonds! |
|
12. |

|
|
|
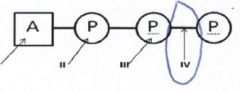
13. Which pictures go through cellular respiration? |
ALL of them! |
|
|
14. Cellular respiration uses one molecule of glucose to make ______ ATP |
36 |
|
|
15.Aerobic and Anaerobic are two types of Cellular Respiration. Fill in the following T-Chart with the correct words. ( with oxygen, without oxygen, fermentation, 36ATP, low ATP, lactic acid, running a marathon, sprinting, baking/brewing, mitochondria) |
aerobic: with oxygen, 36 ATP, running a marathon, mitochondria anaerobic: without oxygen, sprinting, fermentation, low ATP, lactic acid, baking/brewing, mitochondria |
|
|
16. In order list the main stages of cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen |
glycolysis, krebs cycle, eletron transport chain |
|
|
17. Many molecules are involved in the production of ATP from food. What is the essential carrier for energy for all of these molecules? |
high energy electrons |
|
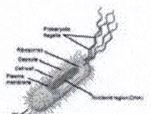
18. Is the following picture a prokaryote or eukaryote? Explain |
prokaryote- no nucleus, no organelles |
|
|
19. Explain the condensation reaction and how it relates to amino acids and proteins. |
allows amino acids to join together to build proteins |
|
|
20. Explain the cellular process that takes place in the ribosomes that are bound to the ER. |
synthesize (make) proteins |
|
|
21. A substrate is affected by an enzyme . In order for an enzyme to be effective it must bind to the ______ transform the substrate in to ______ and release the products. |
substrate, products |
|
|
22. During cell respiration energy is transferred from ___________ to ____________ |
glucose to ATP |
|
23. |
|
|
|
24. Energy is captured and stored in the chloroplast/mitochondria and released in the chloroplast/mitochondria |
chloroplast, mitochondria |
|
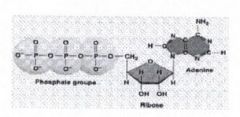
25. The removal of a third phosphate group from ATP will result in release, creation, absorption of energy |
release |
|
|
26. The type of energy transformation that occurs in photosynthesis is: electrical to mechanical, light to chemical, heat to electrical |
light to chemical |
|
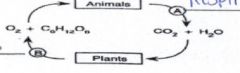
27. Label the processes that are represented the A and B |
A- Cell Respiration B- Photosynthesis |
|
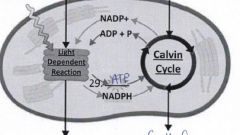
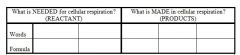
28. Label reactants and products |
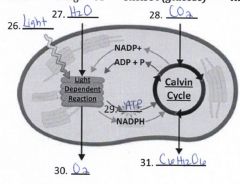
|
|
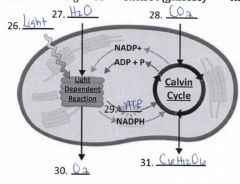
32. What materials move out of the chloroplast from the calvin cycle? |
C6H12O6 |
|
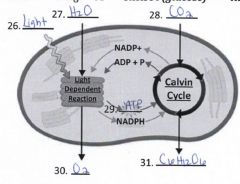
33. What materials move out of the chloroplast from the light dependent reactions? |
oxygen, ATP, NADPH |
|
|
34. Fill in the blank on the diagram |
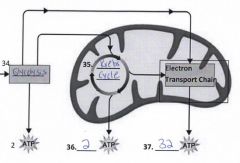
|
|
|
38. List the main ATP producing pathway during aerobic respiraton |
Electron Transport Chain |
|
|
39. What process occurs during the electron transport chain? High energy electrons from the __________cycle convert ___________ to ATP |
Krebs, ADP |
|
|
40. Compare and contrast photosynthesis from cellular respiration. Explain why they are considered complimentary |
contrast: photosynthesis takes place in chloroplast, cell resp. takes place in mitochondria complimentary: oxygen and glucose are produced during photosynthesis and used during cellular respiration (same formula but reversed) |

