![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What form of the P450 complex gives the characteristic 450 nm absorbance? |
"Fe(2+) –CO |
|
|
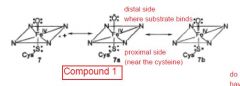
diagram the difference between the distal and proximal sides of the heme |
|
|
|
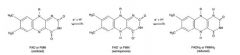
Draw The Oxidized, intermediate, and Reduced forms of flavins
|
|
|
|
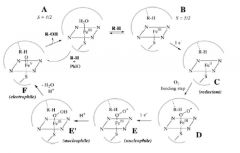
draw the p450 cycle |
|
|
|
FMO5 has little/no activity towards cannonical FMO substrates, what does it do?
|
It has been reported to be a bayer villagerase(it inserts oxygen adjacent to a carbonyl in a ring expansion reaction) |
|
|
How do you selectively inhibit p450's? |
P450 reductase antibodyMechanism based inhibitor (1-aminobenzotriazole "ABT")
|
|
|
How is uncoupling measured
|
by measuring the stoicheometries of the product
|
|
|
Kinetic Isotope Effect
|
A ratio of 2 rate constants for the identical reaction of 2 compounds that only differ in isotopic substitution
|
|
|
Match the isoform with it's preferred substrate type:2E1, 2C9, 1A2, 2B6, 2D6, 3A4, 2A6Big, Small, Basic, Acidic, Flat, Bent, Medium Planarity
|
2E1 - Small3A4 - Big2C9 Acidic2D6 - Basic2B6 - Bent1A2 - Flat2A6 - Medium Planarity |
|
|
Regioselectivity
|
relative reactivity towards different functional groups in the same molecule or different molecules
|
|
|
What are the "diagnostic" AO inhibitors?
|
Menadione, Raloxifene, Vanillin, Hydralazine
|
|
|
What are the 2 forms of Molybdenum Hydroxylases
|
Xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase
|
|
|
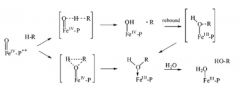
what are the 2 proposed paths for oxygen insert on a hydrocarbon from compound I? |
|
|
|
What are the absorbance peaks for oxidized, reduced, and ligand bound P450
|
oxidized - 412 nmreduced - 417 nmligand bound - 450 nm |
|
|
what determines whether a FMO can oxidize a soft nucleophile
|
Accessibility, FMO will oxidize just about any soft nucleophile the FAD-OOH encounters |
|
|
what do microsomal and mitochondrial p450's specialize in?
|
Drugs and xenobiotics // steroids and other endogenous compounds
|
|
|
What do XO and AO target?
|
SP2 carbons that are electron deficient because of adjacent nitrogens or oxygens
|
|
|
what does b5 do?
|
It donates and accepts single electrons (for the second reduction step). It's thought to increase coupling by increasing then decreasing the oxidation rates.
|
|
|
What does FMO stand for?
|
Flavin Containing Mono Oxygenases
|
|
|
What does it mean that the FMO reaction mechanism is ordered?
|
The cofactors and substrate all add to the enzyme before anything leaves
|
|
|
What form of the P450 complex gives the characteristic 450 nm absorbance?
|
Fe(2+) -CO(Bound to Carbon Monoxide)
|
|
|
What happens to KIEs when the distance between sites (on the molecule) is supressed?
|
The KIE ratio is "masked" / suppressed
|
|
|
What is "metobolic switching" in reference to KIEs?
|
when a P450 switches to a different site preference upon deuteration
|
|
|
What is a good FMO inhibitor for diagnostic purposes
|
there isn't a good chemical inhibitorFMO's are vulnerable to heat, so a slight raise in temperature can effectively inhibit them
|
|
|
What is a Reverse Type I substrate?
|
It displaces the H20 ligand, but the the heme stays in a low spin because of the 6th associated Fe ligand (can still be metabolized)
|
|
|
What is a True Intermediate
|
True Intermediates in a chemical reaction always give the same products, regardless of how the intermediate was produced
|
|
|
What is a Type I substrate?
|
it displaces the H20 ligand, converts a low spin complex to high spin complex, and doesn't associate with the heme |
|
|
What is a Type II substrate?
|
Displaces H20 and has a strong field ligand functional group that is usually nitrogen |
|
|
what is stereoselectivity
|
selection among several substrates or from several products
|
|
|
What is stereospecificity?
|
The retention, inversion or loss of stereoselectivity. A reaction is stereospecific if stereoisomeric substrates give specific stereoisomeric products
|
|
|
What is the (general) ease of hydroxylation, not counting orientation in the active site? |
tertiary (benzyllic and allylic) > secondary > primary |
|
|
What is the AO substrate probe? |
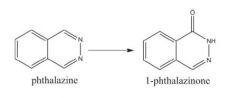
Pthalazine |
|
|
What is the classical endogenous FMO substrate? |
Frimethylamine (TMA)
|
|
|
what is the difference between high spin and low spin |
high spin - out of plane (usually unbound)low spin - in plane (usually bound to something)
|
|
|
What is the FAD catalytic cycle? |
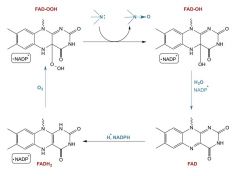
|
|
|
What is the flow of electrons in Molybdenm Hydrolase Complexes
|
From substrates to electron acceptors (usually oxygen)
|
|
|
What is the FMO posthetic group?
|
FAD-OOH It's weak compared to the Heme |
|
|
What is the general AO activity dogma?
|
it's high in monkeys and humans, low in rodents, and absent in dogs
|
|
|
What is the input of protons controlled by?
|
The proton transfer groove of the I helix: {ASTG}{ASTG}{DEQN}T{ASTG}
|
|
|
What is the major form of FMO in human livers? |
FMO3- adultFMO1- fetal
|
|
|
What is the p450 signature sequence?
|
FxxGxxxCxG
|
|
|
What is the rating of FMO selectivity?
|
FMO1 (least selective) -> FMO2 -> FMO3 (most selective) |
|
|
What is thought to be the purpose of the proximal cysteine?
|
It regulates the activity of the heme
|
|
|
Whate are the homology rates for families and subfamilies of p450? |
40% and 55% respectively
|
|
|
Where do the reductive electrons for p450s come from? |
NADPH -> CPR -> p450
|
|
|
Where does FMO oxidize
|
soft heteroatom nucleophiles (N,S,P,Se)
|
|
|
Where is FMO1 found in adults
|
the kidney |
|
|
where is the heme center in a p450 structurally?
|
buried beneath the I and L helices
|
|
|
Which cofactor is REQUIRED?
|
CPR (cytochrome P450 Reductase)
|
|
|
Why is FMO2 generally not considered in drug studies? |
polymorphisms (Q472X) render it inactive in all but a small population
|
|
|
what are the diagnostic MAO inhibitors |
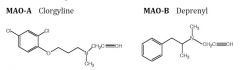
|
|
|
What does CES stand for and what does it do |
Carboxylesterases hydrolize esters |
|
|
What does EPHX stand for and what does it do? |
Epoxide Hydrolase, hydrolyses epoxides |
|
|
What structural class of enzymes do CES and EPHX belong to? |
alpha/beta hydrolase folds |
|
|
What is a catalytic triad? |
three amino acids that cooperate to actiate a water molecule and form OH- and H+, then use those ions in a chemical reaction |
|
|
Why are CES especially important from a clinical viewpoint? |
Ester derivatives are often used as prodrugs to improve absorption, bioavailability, taste, stability, and duration of action |
|
|
How many CES genes are there? |
at least 5: 1,2,3,4A, and 5A |
|
|
What is the CES catalytic triad? |
Ser (Glu/Asp), His |
|
|
What is the carboxylesterase catalytic cycle? |
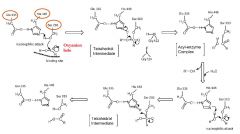
|
|
|
How do A and B esterases interact with organophosphates |
A esterases hydrolyze organophosphates B esterases are irreversibly inhibited by organophosphates |
|
|
What does PON1 Stand for |
Paraoxonase |
|
|
What does PON1 do? |
It is a lactonase and metabolizes phosphoric triesters, which can be toxic organophosphates |
|
|
What type of compound often is in insectisides? What bioactivates them? |
Organophosphates (OP) that are actiated by P450 into oxons (toxic) |
|
|
How are oxons toxic |
They bind irreversibly to acetylcholinesterase |
|
|
How does PON1 neutralize oxon toxicity? |
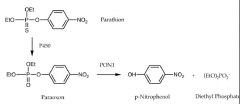
It hydrolyzes the oxon: |
|
|
What is the PON Mechanism? |
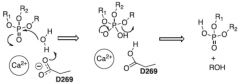
|
|
|
Where are carboxylesterases found? (CES) |
they're errywhere, but concentrated in the small intestine, lung, and liver |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes methyl-ester cocaine? |
CES1 |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes Meperidine |
CES1 (slowly) |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes delapril |
CES1 |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes 4-methylumelliferyl-acetate? |
Mostly CES2 (60,000) with some CES1(2000) |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes the benzoyl ester cocaine? |
CES2 |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes heroin? |
Mostly CES2, with some CES1 |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes 6acetyl morphine? |
Mostly CES2 with very very little CES1 |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes CPT11 |
Mostly CES2 with a little CES1 |
|
|
what effect does esterase activity have on clopidogrel efficacy? |
It drastically decreases the amount of active metabolite by hydroxylating the ester. Clopidogrel is a prodrug |
|
|
Why does prasugrel generate more active metabolite than clopidogrel? |
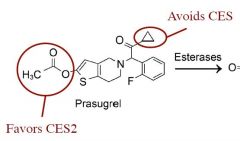
|
|
|
Which CES isoforms are in the liver |
BOTH! (but more CES1) |
|
|
Genetic CES1 polymorphisms have drastic effects on what drug? |
Methylpheidate (Ritalin) |
|
|
How were BChe Polymorphisms discovered? |
Paralysis medications lasted much longer than anticipated (patients required assisted breathing apparati) |
|
|
What does BChE stand for? |
Butyryl-cholinestease |
|
|
What is the dominant drug metabolizing enzyme of the eye? |
BChE |
|
|
where is BChE found? |
Ubiquitously, but we focus on plasma levels in metabolism |
|
|
What do epoxide hydrolases typically do? |
they catalyze the formation of vicinal diols from epoxides |
|
|
Which epoxide hydrolase is soluable and which is microsomal |
EH1 - microsomal |
|
|
where is microsomal epoxide hydrolase found? |
primarily in the liver but can be found in most tissues |
|
|
What are in vitro mEH probes |
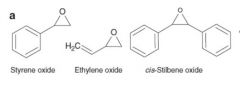
|
|
|
What is the mEH mechanism of epoxide hydrolysis? |
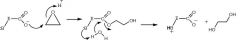
|
|
|
what does EH do with stereochemistry |
It inverts it |
|
|
What does valproic acid do with mEH |
it inhibits it and can lead to Drug Drug Interactions |
|
|
What are the phisiological roles of sEH and why do we care |
aracadonic, lineolic, and other fatty acid epoxides are metabolized by it, these are relevant because they regulate blood pressure and inflammation |
|
|
What is the general structure of the sEH inhibitors developed by Bruce Hammock? |
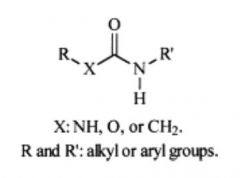
|
|
|
What is the proposed catalytic mechanism of sEH? |
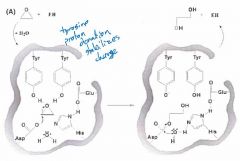
|
|
|
What is the most common metabolic reduction that drugs, xenobiotics, and endogenous compounds undergo? |
Reduction of carbonyls |
|
|
What does ADH stand for |
Alchohol dehydrogenase |
|
|
What does CR stand for |
Carbonyl Reductase |
|
|
What is the ADH cofactor? |
NADH, it is the only reductive nzyme that uses NADH, all the others use NADPH |
|
|
Draw the single electron reduction of quinones |
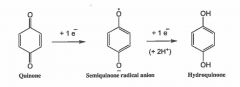
|
|
|
what is futile cycling |
when a cycle restarts itself, it can be a problem because it wastes resources without any useful production |
|
|
How can quinones cause toxicity |
they react with thiols to form protein adducts, and react with molecular oxygen to create Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in a futile cycling process |
|
|
Why is NQO reduction of quinones less toxic than other methods |
it's a 2 electron process that bypasses the radical forms of quinones |
|
|
What does NQO stand for? |
naptho-quinone oxido-reductase |
|
|
Why is NQO1 relevant to chemotherapy |
It's upregulated in some cancers? |
|
|
Where are azo and nitro reactions typically catalyzed |
Intestinal microflora |
|
|
Why is analine a structural alert |
oxidation by p450's results in very reactive species |
|
|
Why is reductive or oxidative dehalogenation of CCl4 very bad? |
Reductive - results in carbon radicals that lead to lipid peroxidation Oxidative - generates trifuuroacetylaldehyde - which leads to immune hepatitis |
|
|
What do N-acetyl-transferases (NAT) catalyze? |
the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to primary arylamines and hydrazine |
|
|
What is the exception to "xenobiotics containing primary amines are rarely subtrates for N-acetyltion?" |
Cysteine conjugates, which are formed from glutatione conjugates and are converted to mercaptic acids by N-acetylation in the kidney |
|
|
Where is NAT1 expressed? |
errywhere |
|
|
What does NAT1 acetylate? |
"monomorphic substrates" Ex: sulfamethiazole p-aminosalysilic acid |
|
|
Where is NAT2 expressed |
primarily liver and intestinal mucosa |
|
|
What does NAT2 acetylate? |
"polymorphic substrates" sulfamethiazine, isonazid, dapsone, sulfamethoxole, procainamide, hydralazine, and caffeine |
|
|
What drug first identified slow acetylators |
isonazid |
|
|
What is the primary cause of slow acetylators |
NAT2 polymorphism |
|
|
What is "wild type" NAT2 responsible for fast acetylation? |
NAT2*4 |
|
|
Diagram the role of NAT in amine genotoxicity |
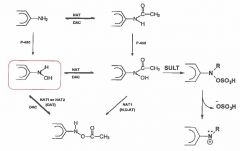
|
|
|
What is the methyl donor for S-methyl transferase, O-methyl-transferase, and N-methyl-transferase? |
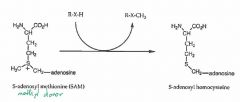
S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM) |
|
|
There are at least 2 distinct S-methyl transferase enzymes, what are they and what do they require? |
TMT- thiol methyl transferase |
|
|
What is COMT |
catechol o-methyl transferase |
|
|
What does COMT metabolize |
mainly neurotransmitters |
|
|
Where does COMT methylate |
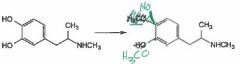
The meta position
|
|
|
What can decrease UDPGA stores in humans? |
Starvation and Alchoholism |
|
|
What does UDPGA stand for? |
Uradine diphosphate glucuronic acid |
|
|
How does UDPGA work? |
it creates a good leaving group, then a SN2 reaction with a nucleophile results in a glucuronide |
|
|
How do CYP metabolism and glucuronidation relate? |
Every time a CYP metabolizes a compound, it's a glucuronidation target |
|
|
how do C and S glucuronidation compare to O and N glucuronidation? |
C and S are much more rare |
|
|
What makes a site good for glucuronidation |
electron density/nucleophilicity |
|
|
Where are UGT's found |
the luminal side of the endoplasmic reticulum (CYPs are on the cytosolic side) |
|
|
How specific are UGTs? |
While there are some examples of specificty, not all reactions of UGT are specific |
|
|
What does UGT stand for? |
UDP glucuronosyl Transferase |
|
|
What iss thought of UGT dimerization? |
UGT can function as a dimer but might not have to be a dimer to function (it's not completely known) |
|
|
What domain is completely conserved across all UGT isoforms |
The cofactor binding domain |
|
|
Why can glucuronides result in analytical difficulties for drugs like statins or NSAIDs, |
futile cycling/ regeneration of aglycone |
|
|
What interesting thing can happen with acyl glucuronides |
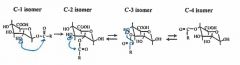
acyl migration |
|
|
What can happen to nucleophiles (like Cs) with Glucuronides |
they can Acylated which can then be immunogenic |
|
|
Why do we not freak out about protein conjugates of glucuronated drugs? |
only a small percentage actually gets there |
|
|
What is the difference between a diglucuronide and a bis-glucuronide |
diglucuronide - linked glucuronide bis-glucuronide - two distinct sites of glucuronidation |
|
|
What is PAPS |
3'phospho adenoside - 5 phosphosulfate |
|
|
what's the difference between cytosolic and Golgi SULTS? |
Cytosolic: metabolize small molecules |
|
|
How does sulfonation compare to glucuronidations substrate specificity |
It's a narrower range: only soft nucleophiles, no thiols or carbons |
|
|
What 3 peptides are glutatione formed from? What's the special linkage? |
Glutamate, cystein, and glycine. The amide bond between glutamate and cysteine is with the glutamate's side chain |
|
|
What is interesting about the Glutathione cysteine? |
It's redox active |
|
|
What type of drugs react with glutathione? |
Electrophillic drugs |
|
|
What is the "universal" GSH substrate |
1-chloro-2,4,dinitrobenzene CDNB |
|
|
When adding glutathione to an aryl amine, what drives dehydratin |
Rearomatization |
|
|
What are the 2 structurally unrelated forms of GST? |
MAPEG - membrane associated eiconasanoid and glutathione metabolism |
|
|
What is the functional form of a MAPEG |
trimers |
|
|
Where are MAPEGs found? |
the endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
What is the functional form of cytosolic GSTs |
Dimers |
|
|
What is the purpose of the GST "mu" loop |
it allows for diverse substrates |
|
|
What is interesting about GSH reactions with Isocyantes and isothiocyantes |
GSH addition is reversible and can accidentally transport the drug/toxin |
|
|
Why is APAP toxic |
Futile cycling can lead to depletion of Glutatione stores (NAPQI) |
|
|
What does glutathione do to isomerize double bonds |
It acts as a base, binds, then leaves (allowing the bond to isomerize) |
|
|
Describe the interaction between GSTs and GSH |
it is a weak but specific binding, it's acceptable because there's so much GSH |
|
|
What form of glutathion binds to GST? |
GS - |

