![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
227 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
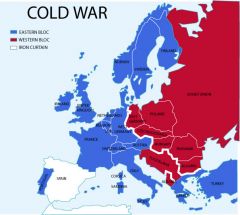
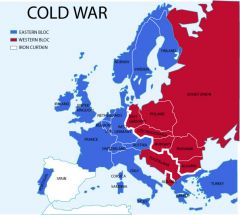
Nonviolent hostility between the U.S. & Soviet Union that arose during the 1950s.
|

Cold War
|
|
|
Emerged from World War II as superpowers.
|
U.S. & Soviet Union
|
|
|
Resulted in competing Communist & Western alliances.
|

Cold War
|
|
|
One contributing factor to the Cold War was the fact that Stalin broke a promise he had made at Yalta for ___________.
|
free elections in Eastern Europe
|
|
|
Both the U.S. & the Soviet Union formed them with the countries they protected or occupied.
|
military alliances.
|
|
|
Consisted of the U.S. and its Western European allies.
|

North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
|
|
|
Included the Soviet Union and its satellite countries.
|

Warsaw Pact
|
|
|
A country whose policies are dictated by another country.
|
satellite
|
|
|
Division of Europe into Communist and Democratic regions.
|
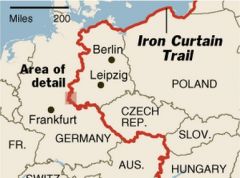
Iron Curtain
|
|
|
At Yalta they agreed to divide it into four occupation zones.
|
Germany
|
|
|
Germany
|
The occupation zones resulted in a democratic and a communist _________.
|
|
|
Democratic Germany
|
West Germany
|
|
|
Communist Germany
|
East Germany
|
|
|
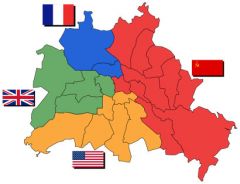
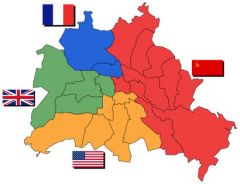
In addition to dividing Germany after WWII ________ was also divided.
|
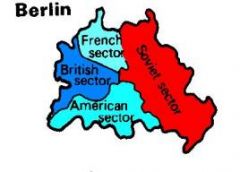
Berlin
|
|
|
West Berlin was completely surrounded by ________.
|
East Germany
|
|
|
Was created so people could not escape to West Berlin.
|

Berlin wall
|
|
|
In East Germany, Poland, Hungary, & Czechoslovakia there were revolts against____.
|
Soviet domination
|
|
|
USSR
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
First major leader to succeed Stalin.
|

Nikita Khrushchev
|
|
|
When the Soviets developed Nuclear Weapons in 1949 the result was a _________.
|

Nuclear arms race
|
|
|
Building up nuclear weapons to keep an opponent from using their nuclear weapons.
|
nuclear deterrence
|
|
|
The belief that if nuclear weapons were balanced between sides, neither side would use its weapons because it would result in their own destruction.
|
Mutual Assured Destruction (MAD)
|
|
|
Made the U.S. & USSR reluctant to become involved in direct military conflict.
|

fear of global nuclear destruction
|
|
|
To reduce the threat of nuclear war the two sides met in ______.
|
disarmament talks
|
|
|
Resulted in two agreements, one in 1972 & one in 1979, to limit the number of nuclear weapons.
|

SALT (Strategic Arms Limitation Talks)
|
|
|
Missiles designed to shoot down incoming missiles.
|
Anti-ballistic missiles (ABMs)
|
|
|
ABMs were dealt with in SALT treaties because of the fear that they might make _____.
|
Nuclear deterrence ineffective
|
|
|
Missile defense program launched by Ronald Reagan.
|
Star Wars
|
|
|
Critics of the Star Wars defense system believed it violated an ______.
|
ABM treaty
|
|
|
Nuclear Arms treaty reached in 1991.
|
Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START)
|
|
|
American and Soviet arms control agreements led to an era of _________.
|
détente
|
|
|
Relaxation of tensions between the U.S. and the USSR in the 1970s.
|
détente
|
|
|
As more nations developed nuclear weapons, a group of nations agreed not to develop nuclear weapons or stop their proliferation.
|
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)
|
|
|
Ended the period of détente.
|
Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
|
|
|
When WWII ended the Soviets were assisting communist forces in ________.
|
China & Korea
|
|
|
Doctrine giving military and economic aid to help countries block communist takeovers.
|

Truman Doctrine
|
|
|
The Truman doctrine was in effect the policy of _____.
|
containment
|
|
|
U.S. leaders attempted to keep communism from spreading to other nations in a policy of ______.
|
containment
|
|
|
As nations sought independence from imperial powers after WWII some sought the support of the U.S. others sought the support of the ___.
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
At times the Cold War got "hot" and erupted into "shooting wars" especially in _______.
|
Korea & Vietnam
|
|
|
Led a successful revolution and Communist takeover in Cuba.
|

Fidel Castro
|
|
|
Unsuccessful invasion of Cuba by U.S. trained Cuban exiles supported by President Kennedy.
|
Bay of Pigs
|
|
|
Kennedy uses naval blockade to stop Soviet nuclear weapons from being placed in Cuba.
|

Cuban Missile Crisis
|
|
|
While Western democracies supported free markets Communism supported a _____.
|
command economy
|
|
|
Production & prices are based on supply and demand.
|
free market
|
|
|
Production & prices are determined by the government.
|
command economy
|
|
|
Fear that communists inside the U.S. might try to undermine the government. (late 1940s early 1950s)
|
Red Scare (actually second Red Scare)
|
|
|
Led a hunt for communists he thought were in the U.S. government.
|

Senator Joseph McCarthy
|
|
|
The newly created United Nations' headquarters were in ______.
|
New York City
|
|
|
During the 1950s and 1960s the U.S. experienced a post war economic _____.
|
boom
|
|
|
During the post war boom many Americans left the cities for the _____.
|
suburbs
|
|
|
The post war economic boom was brought to an end by ________.
|
high oil prices
|
|
|
The post war economic boom ended with the _______.
|
recession of 1974
|
|
|
Despite the post war economic boom in the U.S. minorities still suffered from __________.
|
segregation & discrimination
|
|
|
Even though it made segregated schools unconstitutional it did not end the practice in the South.
|
Brown versus Board of Education
|
|
|
Gifted preacher who emerged as a leader of the Civil Rights movement.
|

Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
|
|
|
The civil rights movement inspired the women's rights movement to end _______.
|
gender based discrimination
|
|
|
The U.S. gave massive economic aid which revived Western European economies after WWII.
|
Marshall Plan
|
|
|
After WWII many Western democracies started to move toward assuming the basic responsibility for people's economic well being by building the ________.
|
Welfare State
|
|
|
The Welfare state requires higher _____.
|
taxes
|
|
|
Promoted free trade and economic cooperation among the nations of Western Europe. (formed 1957)
|
European Community (Common Market)
|
|
|
Led the U.S. occupation of Japan after WWII.
|

General Douglas MacArthur
|
|
|
Under U.S. occupation Japan established a parliamentary democracy and experienced an amazing _________.
|
economic recovery
|
|
|
Japan's economic miracle relied on _____.
|
exports
|
|
|
After Japan's defeat civil war resumed in China between the ____________.
|
Communists & Nationalists
|
|
|
Leader of the Communists in China after WWII.
|

Mao Zedong (Mao Tse-tung)
|
|
|
Leader of the Nationalists in China after WWII.
|

Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-Shek)
|
|
|
Communists won control of mainland China in _____. (year)
|
1949
|
|
|
The communists won in China in large part because they won the support of the _____.
|
peasants
|
|
|
After defeat the Chinese Nationalists fled to ____.
|
Taiwan
|
|
|
Under Chinese communism Buddhism, Confucianism and other traditional beliefs were ____.
|
suppressed
|
|
|
Mao forced people to move from small villages and individual farms to communes of thousands of people on thousands of acres.
|
Great Leap Forward
|
|
|
The "Great Leap Forward" proved to be a dismal failure and as many as 55 million Chinese are thought to have ___________.
|
starved to death
|
|
|
Mao Zedong put down any dissent with ___.
|
beatings, imprisonment, & execution
|
|
|
In 1966 Mao urged young Chinese to purge China of "bourgeois" tendencies in the ____.
|

Cultural Revolution
|
|
|
Resulted in bands of Chinese teenagers humiliating, beating, and even killing anybody they considered to be "bourgeois."
|

Cultural Revolution
|
|
|
Skilled workers & managers were forced to work on farms or in labor camps in China.
|

Cultural Revolution
|
|
|
It resulted in a slowed economy and the threat of civil war until Mao had the army restore order.
|

Cultural Revolution
|
|
|
When China first became communist it was supported by the Soviet Union but as the two nations grew to distrust each other the Soviets _______.
|
withdrew their aid and advisors
|
|
|
By "playing the China card" or improving relations with Communist China the U.S. hoped to _____.
|
isolate the Soviets
|
|
|
In 1971 the U.S. allowed the Communists to replace Taiwan in the United Nations and in 1979 the U.S. established _________.
|
diplomatic relations with China.
|
|
|
After WWII the U.S. and Soviet forces agreed to divide this nation at the 38th parallel.
|
Korea
|
|
|
Communist Dictator of North Korea after WWII.
|

Kim Il Sung
|
|
|
The North Koreans attacked the South in June of _________.
|
1950
|
|
|
Because of the absence of the Soviet Union it condemned the North Korean invasion and used a force made up mostly of U.S. troops to fight the North Koreans.
|
United Nations
|
|
|
The North Koreans overran most of the South until they were stopped by the U.N. forces, the U.N. forces then counter attacked and drove back close to the ______.
|
Chinese border
|
|
|
After Mao Zedong sent hundreds of thousands of Chinese troops to help the North Koreans the U.N. forces were driven back to the _____.
|
38th parallel
|
|
|
The Korean War turned into a stalemate and both sides signed an armistice to end fighting in ____. (year)
|
1953
|
|
|
After the Korean War nearly two million North and South Koreans remained dug in on either side of the _____.
|
demilitarized zone (DMZ)
|
|
|
Conquered Indochina in the 1800s and controlled it until it was overrun by Japan in WWII.
|
French
|
|
|
During WWII the Japanese faced stiff resistance in Indochina (especially in Vietnam) from _______.
|
guerrillas
|
|
|
Small groups of loosely organized soldiers who make surprise raids.
|
guerrillas
|
|
|
After the Japanese were defeated they set out to re-establish authority in Indochina.
|
French
|
|
|
Leader of the Vietnamese who fought the French.
|

Ho Chi Minh
|
|
|
Ho Chi Minh was both a nationalist and a ______.
|
communist
|
|
|
Vietnamese victory over the French in 1954 that convinced the French to leave Vietnam
|
Dienbienphu
|
|
|
Indochina countries that had gained independence separate from Vietnam.
|
Cambodia & Laos
|
|
|
After 1954 the struggle for Vietnam became part of the _______.
|
Cold War
|
|
|
After 1954 Western and communist powers agreed to a temporary division of _______.
|
Vietnam
|
|
|
After Vietnam was divided Ho Chi Minh's communists controlled North Vietnam and South Vietnam was controlled by noncommunist led by ____.
|

Ngo Dinh Diem
|
|
|
Ngo Dinh Diem and the South Vietnamese were supported by the ______.
|
United States
|
|
|
The agreement to divide Vietnam included an agreement to hold elections to reunite Vietnam, these elections were never held because _______.
|
Diem and the U.S. feared the communists would win
|
|
|
The majority of South Vietnamese actually supported ___________.
|

Ho Chi Minh
|
|
|
Catholic and pro-French Vietnamese favored ___.
|
South Vietnam
|
|
|
The U.S. supported Ngo Dinh Diem's regime because they feared the _________.
|
spread of communism
|
|
|
Ngo Dinh Diem's dictatorial regime alienated many Vietnamese because of its __________.
|
corruption and brutal tactics
|
|
|
Many Vietnamese believed South Vietnam was under the foreign domination of the ____.
|
U.S.
|
|
|
By the early 1960s many South Vietnamese communist guerrilla fighters, with the support of North Vietnam were fighting against the ____.
|
South Vietnamese forces
|
|
|
Belief that if one country falls to communism its neighbors would also fall.
|

Domino Theory
|
|
|
National Liberation Front, the South Vietnamese communist rebels trying to overthrow the government of South Vietnam.
|

Viet Cong
|
|
|
Ho Chi Minh determined to unite Vietnam supported the _____.
|

Viet Cong
|
|
|
The first attack on an American destroyer by the North Vietnamese was provoked by a South Vietnamese raid on the North, the second attack didn't actually happen, it was only a false sonar reading.
|
Gulf of Tonkin Incident
|
|
|
Claimed that both the first attack in the Gulf of Tonkin and the second (which didn't happen) were both unprovoked.
|

President Lyndon Johnson
|
|
|
Used the Gulf of Tonkin Incident to get congress to authorize his enormous escalation of U.S. forces in Vietnam.
|

President Lyndon Johnson
|
|
|
In August of 1964 it was passed by Congress giving President Johnson the authority to use whatever force he thought necessary in Vietnam.
|

Gulf of Tonkin Resolution
|
|
|
Number of U.S. men sent to Vietnam from 1964 to 1973.
|
2.5 million
|
|
|
A large percentage of the men who served in Vietnam and often as high as two thirds of the men who served in combat were______.
|
drafted
|
|
|
About 80% of the soldiers who served in Vietnam came from the ______.
|
working and lower classes
|
|
|
U.S. Soldiers in Vietnam were generally not trying to take more territory, their primary objective was to increase the _______.
|
body count
|
|
|
Because they came from the Vietnamese peasants the U.S. soldiers had a great deal of difficulty finding and identifying the _______.
|
Viet Cong
|
|
|
Because many Vietnamese villagers gave refuge to the Viet Cong the villages themselves sometimes became _____.
|
military targets
|
|
|
A coordinated attack against cities and bases in South Vietnam by the Viet Cong & North Vietnamese in 1968.
|

Tet Offensive
|
|
|
Converted many Americans to the view that the Vietnam war could not be won.
|

Tet Offensive
|
|
|
Due to opposition to the Vietnam war he chose not to run for reelection in 1968.
|

Lyndon Johnson
|
|
|
Under increasing pressure to end U.S. involvement in Vietnam he negotiated the Paris Peace Accord in 1973.
|

Richard Nixon
|
|
|
The U.S. agreed to withdraw its troops and North Vietnam agreed not to send any more troops into the South.
|
Paris Peace Accord
|
|
|
Two years after the U.S. had withdrawn from Vietnam the _______.
|
North Vietnamese conquered South Vietnam
|
|
|
Also fell to communism after the U.S. withdrawal from Vietnam
|
Cambodia & Laos
|
|
|
Communist guerrillas who came to power in Cambodia.
|

Khmer Rouge
|
|
|
Ruler of the Khmer Rouge who oversaw work camps and the genocide of more than a million Cambodians.
|

Pol Pot
|
|
|
After Cambodia and Laos communism did not spread any farther in ______.
|
Southeast Asia
|
|
|
It was unable to produce the incentive in the people to produce enough goods to keep the people happy.
|
command economy
|
|
|
When Hungarians tried to break free of Soviet control in 1956, he sent tanks in to enforce obedience.
|

Nikita Khrushchev
|
|
|
Brief period of liberalization in Czechoslovakia in 1968.
|
Prague Spring
|
|
|
Ordered the invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968 to halt the reform movement there.
|

Leonid Brezhnev
|
|
|
The Cold War arms race put more pressure on the Soviets than the U.S. because of the ____.
|
Stagnant Soviet economy
|
|
|
The Soviet Vietnam.
|
Afghanistan
|
|
|
The Soviet supported government of Afghanistan attempted to ________.
|
modernize
|
|
|
Afghan warlords opposed _______.
|
land redistribution
|
|
|
Afghan Muslims opposed communist _____.
|
atheism
|
|
|
When rebels attempted overthrow the Soviet backed government of Afghanistan _____.
|
Soviets troops moved in
|
|
|
Muslim religious warriors who fought the Soviets in Afghanistan.
|
Mujahedin
|
|
|
Soviet leader who came to power and urged reforms in 1985.
|

Mikhail Gorbachev
|
|
|
Signed arms control treaties with the U.S. and pulled Soviet troops out of Afghanistan.
|

Mikhail Gorbachev
|
|
|
Gorbachev's policy of openness and ending censorship.
|
glasnost
|
|
|
Gorbachev's policy of restructuring the government and the economy.
|
perestroika
|
|
|
Gorbachev's policies actually spread unrest across the ______.
|
Soviet empire
|
|
|
Independent labor union that demanded changes in Poland.
|

Solidarity
|
|
|
Leader of Solidarity and eventually president of Poland.
|

Lech Walesa
|
|
|
Dissident writer and human rights activists who gets elected president of Czechoslovakia.
|

Vaclav Havel
|
|

The Berlin Wall came down in 1989 and in 1990 __________.
|

Germany was reunified
|
|
|
When Gorbachev was prepared to sign a treaty reducing the power of the soviet government in 1991 ______________.
|
Communist hardliners tried to seize control
|
|
|
Russian President who defied the Communist hardliners and forced them to give up control.
|

Boris Yeltsin
|
|
|
On December 8, 1991, leaders of the Soviet Republics agreed to _______.
|
dissolve the Soviet Union
|
|
|
In 1992 it was divided into Slovakia and the Czech Republic.
|
Czechoslovakia
|
|
|
In the 1940s, tension between Hindus and Muslims led to violence in ______.
|
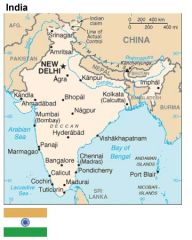
India
|
|
|
The British decided to partition India into ____.
|
two countries
|
|
|
After the British partition areas where Hindus were a majority became ____.
|
India
|
|
|
After the British partition areas where Muslims were a majority became _____.
|
Pakistan
|
|
|
Pakistan and India became independent nations in _____.
|
1947
|
|
|
After the partition of India millions of Muslims and Hindus moved to the country where their _________.
|
faith was the majority
|
|
|
As Muslims and Hindus moved to new countries on the Indian sub-continent they often ____.
|
attacked and killed each other
|
|
|
India and Pakistan have fought wars over the disputed region of ________.
|
Kashmir
|
|
|
The tension between India and Pakistan is of even greater concern to the rest of the world because they both have developed ______.
|
nuclear weapons
|
|
|
The British colony of Ceylon gained independence in 1948 and changed its name in 1972 to _____.
|
Sri Lanka
|
|
|
In Sri Lanka the minority Hindu Tamils have fought for a separate nation against the majority _____.
|
Sinhalese Buddhist majority
|
|
|
India's first Prime Minister made attempts to improve the conditions of the dalits (outcastes).
|

Jawaharlal Nehru
|
|
|
When Nehru died in office his daughter replaced him in office.
|

Indira Gandhi
|
|
|
Religious minority in India but the majority in the province of Punjab.
|

Sikhs
|
|
|
In 1984, in an effort to gain independence for Punjab, Sikhs occupied their holiest shrine the __________.
|
Golden Temple
|
|
|
After talks failed she sent troops to oust the Sikhs from the Golden Temple and Thousands of Sikhs were killed.
|

Indira Gandhi
|
|
|
She was killed by her Sikh bodyguards.
|

Indira Gandhi
|
|
|
World's most populated democracy.
|
India
|
|
|
A thousand miles separated West Pakistan from _______.
|
East Pakistan
|
|
|
In 1971 the Bengalis declared East Pakistan an independent nation ____.
|
Bangladesh
|
|
|
Pakistan tried to crush the Bengali rebels, but the rebels were successful because of support from ___.
|
India
|
|
|
A new movement started in 1955 which supported political and diplomatic independence from both Cold War superpowers.
|
nonalignment
|
|
|
In Southeast Asia, Thailand and Malaysia have prospered as __________.
|
market economies
|
|
|
In Southeast Asia Myanmar has suffered under _____.
|
autocratic government
|
|
|
A nation of 13,000 islands gained independence after WWII and is 90% Muslim.
|
Indonesia
|
|
|
When Indonesia first won independence it was ____.
|
democratic
|
|
|
In 1966, an army general, Suharto took power and ruled as dictator until 1998.
|
Indonesia
|
|
|
After Suharto was forced to resign in 1998, a series of democratically elected governments tried to restore stability.
|
Indonesia
|
|
|
In 1975 Indonesia seized the former Portuguese colony _____.
|
East Timor
|
|
|
Mostly Catholic fought and gained independence from Indonesia in 2002.
|
East Timor
|
|
|
Gained freedom from U.S. control in 1946.
|
Philippines.
|
|
|
The Filipino constitution created a democratic government but politics were controlled by a ______.
|
wealthy elite
|
|
|
Elected President of the Philippines in 1965, abandoned democracy and made himself dictator.
|

Ferdinand Marcos
|
|
|
When Marcos finally held elections in 1986 she was elected.
|

Corazon Aquino
|
|
|
Marcos tried to deny the results and prevent Aquino from becoming president, but demonstrations in Manila forced him to resign.
|
"people power" revolution
|
|
|
In the Philippines, communist and Muslim rebels continue to _______.
|
fight across the country
|
|
|
After WWII many African nations demanded independence, a few developed peace and democracy, but most experienced _________.
|
civil wars, military rule, or corrupt dictators
|
|
|
Because Europeans had divided Africa into colonies without regard for ethnic groups, when African countries did gain independence they often had ________.
|
ethnic conflicts
|
|
|
Most of the people in the Middle East are ______. (religion)
|
Muslim
|
|
|
There are Christian and other religious minorities in the Middle East and Israel is largely _______.
|
Jewish
|
|
|
Borders drawn by Europeans divided their homeland among Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey.
|
Kurds
|
|
|
In all the countries where they live Kurds are a _____.
|
minority
|
|
|
Kurds have faced the greatest discrimination in ________.
|
Turkey & Iraq
|
|
|
Jews had been driven out of what is today Palestine in the first century, but started to return in the _______.
|
1800s
|
|
|
The Holocaust created worldwide support for a _______.
|
Jewish Homeland in Palestine
|
|
|
After WWII Jews migrated in large numbers to ______.
|
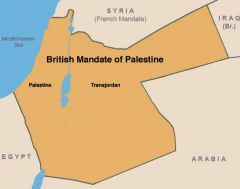
Palestine
|
|
|
The U.N. drew up a plan to divide Palestine into an ______.
|
Arab and a Jewish state
|
|
|
Rejected the idea of a Jewish state in Palestine.
|
Arabs
|
|
|
When Britain withdrew from Palestine the Jews proclaimed the independent state of ______.
|

Israel
|
|
|
After Israel declared its independence the Arabs ______.
|
launched the first of several wars against them
|
|
|
Victors in the Arab Israeli wars.
|
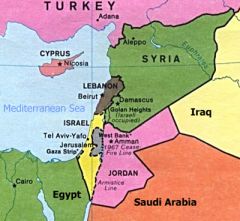
Israel
|
|
|
As a result of the first Arab Israeli war 700,000 Palestinian Arabs ________.
|
fled Palestine
|
|
|
The Middle East is of great importance to the U.S. and other powers because of its huge ______.
|
oil reserves
|
|
|
The Middle East nations with large oil reserves are part of _________.
|
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
|
|
|
In 1973, OPEC blocked oil shipments to the U.S. to protest the ________.
|
U.S. support of Israel
|
|
|
The OPEC oil embargo contributed to a _____.
|
World Wide Recession
|
|
|
Some Middle Eastern countries have secular, or non-religious, _________.
|
governments & laws
|
|
|
By the 1970s some Muslim leaders were calling for a return to ___________.
|
Sharia law
|
|
|
Laws based upon the Quran and the Hadith.
|
Sharia law
|
|
|
Their rights are severely limited in countries governed by Sharia law.
|
Women
|
|
|
Is strategically important because it shares a border with Israel and controls the Suez Canal.
|
Egypt
|
|
|
Seized power in Egypt in 1952, worked to modernize Egypt and end Western domination.
|

Gamel Abdel Nasser
|
|
|
Nationalized the Suez Canal ending British and French Control. (person)
|

Gamel Abdel Nasser
|
|
|
Nasser fought two unsuccessful wars against __.
|
Israel
|
|
|
Nasser's successor who made peace with Israel.
|

Anwar Sadat
|
|
|
Assassinated Anwar Sadat for not ending corruption & poverty & for making peace with Israel.
|
Muslim fundamentalists (Islamists)
|
|
|
Ruled Iran, with U.S. support.
|

Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
|
|
|
The Shah's attempts to Westernize Iran upset _________.
|
Islamic Fundamentalists
|
|
|
The Shah's secret police used terror to drive his critics into ______.
|
exile
|
|
|
In the 1970s the Shah's foes rallied behind the cleric ___________.
|

Ayatollah Khomeini
|
|
|
Massive protests drove the Shah into exile, Khomeini returned and Iran became an ____.
|
Islamic Republic
|
|
|
After the Iranian Revolution Islamists seized the American embassy and held 52 Americans ____.
|
hostage for more than a year
|

