![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
226 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
World History Set 2-2
|
Rise of Authoritarian Dictators & WWII
|
|
|
Shattered a sense of optimism which had grown in the West since the Enlightenment.
|
World War I
|
|
|
New technologies connected people around the world and created a ________ shared by the World's developed countries.
|
mass culture
|
|
|
African Americans combined Western harmonies with African rhythms to create____.
|

Jazz
|
|
|
Another name for the "Roaring Twenties" in the U.S.
|

Jazz Age
|
|
|
During the 1920s many young people who had been disillusioned by the war rejected the moral values of the __________.
|
Victorian Age
|
|
|
Symbol of the rebellious Jazz Age youth.
|

flapper
|
|
|
Nickname given to young women of the 1920s who defied convention and broke norms.
|

flapper
|
|
|
New technologies and attitudes of the 1920s allowed some women to be emancipated from traditional roles and to pursue ________.
|
careers
|
|
|
The fact that many people opposed the freer lifestyle of the Jazz age was demonstrated by _______.
|

Prohibition
|
|
|
Outlawed the production and sale of alcohol in the U.S.
|

Prohibition (18th Amendment)
|
|
|
Caused an explosion of organized crime in the U.S.
|

Prohibition
|
|
|
Illegal bars.
|

Speakeasies
|
|
|
Christian movement in the U.S. in the 1900s which stressed a more literal interpretation of the bible.
|
fundamentalism
|
|
|
Brought national attention to the theory and teaching of evolution.
|

Scopes Trial
|
|
|
Young adults in Europe and America in general, and writers in particular, who had become disillusioned with the world and Western values after World War I.
|

the Lost Generation
|
|
|
Cultural movement where African American artists and writers explored and expressed pride in their unique culture.
|

Harlem Renaissance
|
|
|
Her findings and the findings of others proved that atoms were not solid and indivisible.
|

Marie Curie
|
|
|
Measurements of space and time are not absolute but are determined by the relative position of the observer.
|

Theory of Relativity
|
|
|
Developed the theory of relativity.
|

Albert Einstein
|
|
|
Discovered that atoms could be split.
|
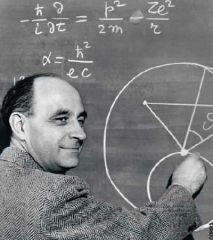
Enrico Fermi
|
|
|
His discovery of penicillin paved the way for the development of antibiotics to treat infections.
|

Alexander Fleming
|
|
|
View that the subconscious mind drives much of behavior.
|

Psychoanalysis
|
|
|
Founder of Psychoanalysis.
|
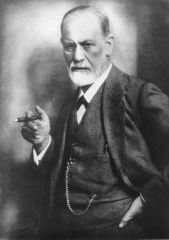
Sigmund Freud
|
|
|
Abstract, dada, & surrealism were all artistic movements which broke from traditional styles and an effort to __________.
|
reproduce the real world
|
|
|
Attempted to portray the workings of the unconscious mind.
|

surrealism
|
|
|
Largely responsible for the rise of authoritarian dictators in Europe following WWI.
|
failures of the Versailles Treaty
|
|
|
Had to deal with growing socialism and the Irish question after WWI.
|
Great Britain
|
|
|
In 1922 it was divided into two parts; the largest part became an independent state, but the Northern part remained under English rule.
|
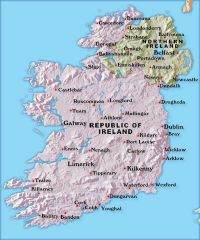
Ireland
|
|
|
Fought a guerrilla war against the British before 1922 and continued to fight for Irish unification after 1922.
|

Irish Republican Army
|
|
|
After WWI political parties here competed for power causing many changes in government.
|
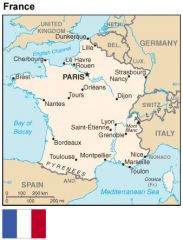
France
|
|
|
In the U.S. fear of radicals and the Bolshevik Revolution resulted in police rounding up suspected foreign-born radicals, and expelling a number from the country.
|

Red Scare
|
|
|
French Fortifications against Germany.
|

Maginot Line
|
|
|
In 1925 Germany and France promised they would never again make war against each other
|
Locarno Pact
|
|
|
Almost every nation of the world agreed to renounce war as an instrument of national policy
|
Kellogg-Briand peace pact
|
|
|
The Kellogg-Briand peace pact was NOT ____
|
enforceable
|
|
|
Attempts at making and ensuring peace among European nations in the 1920s. (including the Kellogg-Briand peace pact)
|
Spirit of Locarno
|
|
|
In the spirit of Locarno the great powers pursued _______.
|
disarmament
|
|
|
It was unable to stop aggression, a weakness noted by dictators.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
Owed huge war debts to the U.S. after World War I.
|
Britain & France
|
|
|
In Great Britain in 1926 over three million workers went on a ________.
|
general strike
|
|
|
Enjoyed an economic boom in the 1920s.
|
U.S.
|
|
|
Overproduction and a crisis in finance in the U.S. led to the _______.
|

Stock Market Crash
|
|
|
Triggered a depression in the U.S. that spread world wide
|

Stock Market Crash
|
|
|
Programs introduced by Franklin Roosevelt in an attempt to end the Great Depression.
|
New Deal
|
|
|
Created a fertile ground for extremists who promised radical solutions.
|

Great Depression
|
|
|
Caused many people to lose faith in democracy.
|

Great Depression
|
|
|
First European country to become fascist.
|
Italy
|
|
|
Fascist dictator of Italy.
|

Benito Mussolini
|
|
|
Believed workers of all countries should unite in a class struggle
|
communists
|
|
|
Feared high inflation and or high unemployment might lead to a communist revolution
|
middle and upper class
|
|
|
Have the most to lose in a communist revolution
|
middle and upper class
|
|
|
Middle and upper classes supported Mussolini because they feared a ______-
|
communist revolution
|
|
|
Won support in Italy by attacking communists
|

Benito Mussolini
|
|
|
Nickname for Mussolini's private troops he used to take power in Italy
|

Black shirts
|
|
|
Mussolini and his Black shirts marched on Rome in _______ (year)
|
1922
|
|
|
When Mussolini marched on Rome the Italian King asked him to form a government as ______.
|
Prime Minister
|
|
|
After Mussolini was named Prime Minister he used secret police and propaganda to ______-
|
eliminate all opposition
|
|
|
Extreme Nationalism, State supremacy, one party rule, retention of private property
|
Fascism
|
|
|
Want a planned economy with private ownership of the means of production
|
Fascists
|
|
|
Want a planned economy with public ownership of the means of production
|
Communists
|
|
|
Want to maintain the class system with an authoritarian government
|
Fascists
|
|
|
Want to do away with the class system with an authoritarian government.
|
Communists
|
|
|
Fascists believed the state should have an ______ leader
|
authoritarian
|
|
|
Both Fascists and Communists believe in
|
Dictatorial one-party rule
|
|
|
Under Fascism and Communism opposition was _____-
|
outlawed'
|
|
|
In Mussolini's new system loyalty to the state replaced ______.
|
individual goals
|
|
|
Mussolini brought the economy under state control but preserved _____.
|
capitalism
|
|
|
Mussolini's fascist government was the first _________.
|
totalitarian state
|
|
|
A one-party dictatorship attempts to control every aspect of citizens' lives.
|
totalitarian state
|
|
|
Under Joseph Stalin, the Soviet Union developed into a _________.
|
totalitarian state
|
|
|
In the Soviet Union the government made most economic decisions.
|
command economy
|
|
|
Stalin wanted all peasants to farm on state owned farms.
|
collectives
|
|
|
Because farmers resisted collectivization Stalin seized all their grain and left peasants to starve.
|

Terror Famine
|
|
|
Fearing rival party leaders were plotting against him Stalin launched the _________.
|
Great Purge
|
|
|
Resulted in the killing or imprisonment of at least four million people in the Soviet Union.
|
Great Purge
|
|
|
Stalin's attempt to make non-Russian cultures in the Soviet Union more Russian.
|
russification
|
|
|
The communist party in Russia attempted to destroy the religious faith of the people to reinforce the official communist belief of ____.
|
atheism
|
|
|
Soviet leaders had two conflicting _________.
|
foreign policy goals
|
|
|
Soviets worked to spread worldwide communist revolution through the _______.
|

Comintern
|
|
|
At the same time they supported worldwide communist revolution the Soviets also wanted to strengthen their national security through the ______.
|
support of other countries
|
|
|
Did not completely destroy Germany but created a motive for revenge.
|
Versailles Treaty
|
|
|
Germany's solution to war reparations following WWI.
|
Printing money
|
|
|
Just printing money resulted in extremely high _______.
|

inflation
|
|
|
Economic problem in Germany from 1918-23.
|

inflation
|
|
|
Democratic Government set up in Germany after WWI.
|
Weimar Republic
|
|
|
Became a scapegoat for Germany's problems after WWI.
|
Weimar Republic
|
|
|
Germans blamed the Weimar Republic for their __________.
|
defeat in World War I
|
|
|
Was doomed to failure by the harshness of the Versailles Treaty.
|
Weimar Republic
|
|
|
Came out of WWI stronger than before. (countries)
|
U.S. & Japan
|
|
|
World War I resulted in the rise of unstable _________.
|
democracies
|
|
|
When difficulties arise people are often willing to sacrifice democracy in exchange for _________.
|
strong leadership
|
|
|
Avoiding political ties to other countries.
|
isolationism
|
|
|
After World War I Americans became ____.
|
isolationists
|
|
|
By the autumn of 1923 it was worthless
|
German Mark (unit of currency)
|
|
|
Enabled Germany to recover from its tremendous inflation
|
Dawes Plan
|
|
|
$200 million loan from American banks to stabilize German economy.
|
Dawes Plan
|
|
|
National Socialist German Worker's Party
|
Nazi
|
|
|
Became the fuehrer (leader) of the Nazi Party.
|
Adolf Hitler
|
|
|
Attempted a coup in Munich in 1923
|
Adolf Hitler
|
|
|
After the attempted coup in 1923 Hitler was
|
Imprisoned
|
|
|
While in prison Hitler wrote ______-
|
Mein Kampf
|
|
|
Set forth Hitler's objectives for Germany
|
Mein Kampf
|
|
|
Nazism was a form of ______
|
Fascism
|
|
|
Lost popularity during the prosperity of the 1920s
|
Nazis
|
|
|
Results in both Communists and Nazis gaining popularity in the 1930s
|
Great Depression
|
|
|
Because of the depression Germans began to feel they had to choose between _______
|
Communism and Nazism
|
|
|
Nazi private army
|
Storm Troopers
|
|
|
Engaged in terrorism to help the Nazis come to power
|
Storm Troopers
|
|
|
Nickname for the Nazi Storm Troopers
|
Brown Shirts
|
|
|
German initials for Storm Troopers
|
SA
|
|
|
Industrialists, upper class and the middle class backed Hitler because they feared they might lose everything to a ______
|
communist revolution
|
|
|
Ruling body under the Weimar Republic.
|
Reichstag
|
|
|
In 1933 President Hindenburg named Hitler
|
Chancellor
|
|
|
As Chancellor Hitler called for new______
|
Reichstag elections
|
|
|
Enabled the Nazis and their allies to win a majority of seats in the Reichstag.
|
Reichstag Fire
|
|
|
The Nazis blamed the Reichstag fire on the _____
|
Communists
|
|
|
After gaining a two-third majority the Nazi's passed the ______-
|
Enabling Act
|
|
|
The Enabling Act made Hitler the ______
|
Dictator of Germany
|
|
|
Dreaded elite corps of Nazi Germany
|
SS
|
|
|
Hitler's secret police.
|
Gestapo
|
|
|
Used by Hitler to eliminate opposition
|
Gestapo
|
|
|
The Gestapo was part of the ______
|
SS
|
|
|
Nickname for the SS
|
Black shirts
|
|
|
Head of the SS and the Gestapo
|
Heinrich Himmler
|
|
|
Nazi propaganda chief
|
Joseph Goebbels
|
|
|
Deprived Jews of German citizenship and political rights (1935)
|
Nuremburg Laws
|
|
|
Individuals are subordinate to the state but private property is retained
|
Fascism
|
|
|
German Fascism
|
Nazism
|
|
|
Fear of communism, resentment of Jews, resentment of the Treaty of Versailles, and the depression, helped _________
|
Hitler rise
|
|
|
Fascists generally believe in a superior____
|
race
|
|
|
Won support by offering simple solutions to complex problems
|
Dictators
|
|
|
Hoped to solve their nation's economic problems by building a Pacific empire
|
Japanese Militarists
|
|
|
In 1937 Japan went to war against ______
|
China
|
|
|
In 1936 Italy conquered
|
Ethiopia
|
|
|
Making concessions to avoid war.
|
Appeasement
|
|
|
When Hitler first began to violate the Treaty of Versailles, Britain and France followed a policy of _______.
|
Appeasement
|
|
|
Hitler began to violate it provisions step by step.
|
Versailles Treaty
|
|
|
First violation of the Versailles Treaty.
|
German Rearmament
|
|
|
After Hitler rearmed his second violation of the Versailles Treaty was to occupy the demilitarized zone of the _______.
|
Rhineland
|
|
|
Hitler annexed Austria with _______.
|
no resistance
|
|
|
Britain & France give up the Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia to maintain peace.
|
Munich Pact
|
|
|
Germany, Italy, and Japan (1936)
|
Axis Powers
|
|
|
Led revolt against the elected government in Spain.
|
Francisco Franco
|
|
|
Used German and Italian troops against Spain's Republican army.
|
Francisco Franco
|
|
|
During Spain's civil war western democracies _____.
|
remained neutral
|
|
|
The government established by Franco in Spain was _______.
|
Fascist
|
|
|
British Prime Minister famous for appeasement.
|
Neville Chamberlain
|
|
|
Hitler violated the Munich Pact by taking ____.
|
all of Czechoslovakia
|
|
|
Signed a non-aggression pact with Germany in 1939. (shocked the world)
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
Planned to divide Eastern Europe between them.
|
Hitler and Stalin
|
|
|
World War II started when Germany _____.
|
invaded Poland
|
|
|
Date of the beginning of World War II.
|
1939
|
|
|
German "lightning war"
|
Blitzkrieg
|
|
|
Quick surprise strikes by tanks supported by airplanes.
|
Blitzkrieg
|
|
|
After Hitler invaded Poland, Britain and France __________.
|
declared war on Germany
|
|
|
Followed Britain and France declaring war on Germany.
|
Phony War
|
|
|
No fighting on land between the Allies and Germany.
|
Phony War
|
|
|
Those who fought against the Axis Powers.
|
Allies
|
|
|
Hitler's armies simply went around it from the North.
|
Maginot Line
|
|
|
Hitler used the Blitzkrieg to overrun this country in about a month in 1940.
|
France
|
|
|
British rescued 300,000 troops out of France at this port.
|
Dunkirk
|
|
|
Succeeded Neville Chamberlain as Britain's Prime Minister.
|
Winston Churchill
|
|
|
Hitler wanted to crush this country's air force to prepare to invade it.
|
Britain
|
|
|
The British RAF defeated the German Luftwaffe.
|
Battle of Britain
|
|
|
New technology used by Britain in the Battle of Britain.
|
Radar
|
|
|
German Air Force.
|
Luftwaffe
|
|
|
RAF
|
Royal Air Force
|
|
|
Commander of the Luftwaffe
|
Herman Goering
|
|
|
Prevented a German invasion of Britain.
|
Battle of Britain
|
|
|
Head of the Soviet Union during WWII.
|
Joseph Stalin
|
|
|
After Hitler was unable to invade Britain he broke his non-aggression pact and invaded ____.
|
the Soviet Union
|
|
|
Ripped through the Soviet Union at first.
|
Blitzkrieg
|
|
|
Allowed Roosevelt to send war supplies to any country whose defense was vital to the U.S.
|
Lend-lease Act
|
|
|
U.S. President during World War II.
|
Franklin Roosevelt
|
|
|
Official leader of Japan during World War II.
|
Emperor Hirohito
|
|
|
Dominated Japan prior to and during World War II.
|
Militarists
|
|
|
Proposed Japanese Empire. (name)
|
Greater East Asia Co-prosperity Sphere
|
|
|
Japan went to war to obtain an empire for ______.
|
raw materials
|
|
|
Brought the U.S. into World War II.
|
Bombing of Pearl Harbor
|
|
|
Planned and executed the attack on Pearl Harbor.
|
Admiral Yamamoto
|
|
|
The U.S. entered World War II in ________. (year)
|
1941
|
|
|
Critical new naval weapon of WWII.
|
Aircraft Carrier
|
|
|
Turning point in the Pacific War.
|
Battle of Midway
|
|
|
Commander of the American Pacific fleet directed the victory at the Battle of Midway.
|
Admiral Nimitz
|
|
|
The Selective Service Act in 1940 was the first U.S. _________.
|
peacetime draft
|
|
|
Main cause of the loss of civilian lives.
|
bombing by airplanes
|
|
|
Hitler's plan to murder all the Jews.
|
"Final Solution"
|
|
|
Wartime hysteria in the U.S. resulted in the _____.
|
internment of Japanese Americans
|
|
|
Nazi destruction of the Jews. (6 million killed)
|
Holocaust
|
|
|
Nazis sent Jews and political opponents to ____.
|
Concentration camps
|
|
|
Nazis forced Jews, poles, & Soviet Slavs to work as _____.
|
slave labor
|
|
|
Hitler believed they were a master race.
|
Aryans
|
|
|
Carried out Hitler's policy of exterminating the Jews.
|
SS
|
|
|
Americans and British troops first fought together in ______. (place)
|
North Africa
|
|
|
From North Africa the Allies attacked ______. (in 1943)
|
Sicily and Italy
|
|
|
Desert Fox, German General who at first had great success against the Allies in North Africa, eventually his army was driven back and forced to surrender.
|
Erwin Rommel
|
|
|
Beginning of the end of the war in Europe.
|
Invasion of Normandy
|
|
|
The Allied invasion of France forced Hitler to fight a war on _____.
|
two fronts
|
|
|
Beginning of the invasion of Normandy.
|
D-Day
|
|
|
Year of D-Day.
|
1944
|
|
|
Commanding General of the invasion of Normandy.
|
Dwight Eisenhower
|
|
|
Wanted the U.S. & Britain to open a second front in France. (person)
|
Joseph Stalin
|
|
|
Turning point of the war in the Soviet Union.
|
Battle of Stalingrad
|
|
|
Defeated Germany in Russia. (a major factor)
|
Russian Winter
|
|
|
Soviets and Americans met in Germany at the _______.
|
River Elbe
|
|
|
Hitler commits suicide, Germany surrenders.
|
V.E. Day
|
|
|
Roosevelt, Churchill, & Stalin met to plan the end of the war.
|
Yalta Conference
|
|
|
Strategy to defeat Japan in the Pacific.
|
Island hopping
|
|
|
U.S. policy of leap frogging over Islands that were well fortified by the Japanese and attacking less fortified islands that strategically enabled the U.S. to move toward Japan.
|
Island hopping
|
|
|
With the use of blockades islands which were leap frogged were left to _____.
|
"wither on the vine"
|
|
|
Truman ordered the dropping of the Atomic Bomb to avoid _______.
|
invading Japan
|
|
|
Two cities hit by nuclear bombs (in order)
|
Hiroshima & Nagasaki
|
|
|
World War II ended in _______. (year)
|
1945
|
|
|
The number of deaths in World War II was as many as ________.
|
50 million
|
|
|
Created at the end of World War II to keep the peace.
|
United Nations
|
|
|
Nazis tried for war crimes.
|
Nuremburg Trials
|
|
|
World Powers after World War II.
|
U.S. and U.S.S.R.
|
|
|
As soon as World War II was ended distrust and different philosophies led to the _____.
|

Cold War
|
|
|
Tension between the U.S. and the Soviet Union from 1946 to 1990.
|

Cold War
|
|
|
Stalin's threat to Greece and Turkey after the war resulted in the _____.
|

Truman Doctrine
|
|
|
Policy that the U.S. would resist the spread of Communism throughout the world.
|

Truman Doctrine
|
|
|
To strengthen democracies, the U.S. offered food and economic aid to Europe.
|

Marshall Plan
|
|
|
Forced the Soviets to end their blockade of West Berlin.
|

Allied Airlift
|
|
|
New alliance formed by the U.S. and nine other countries in 1949.
|

North Atlantic Treaty Organization
|
|
|
The Soviet Counter to NATO.
|
Warsaw Pact
|

