![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
185 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The sum of an individual's; behaviors, attitudes, beliefs, and values.
|

Personality
|
|
|
Fairly stable pattern of: thoughts, feelings and actions that are typical of a person
|

Personality
|
|
|
Determines how we react in specific situations
|

Personality
|
|
|
Determines how we adjust to our environment
|
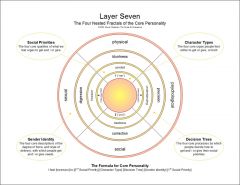
Personality
|
|
|
Personality develops throughout a ___________
|
Lifetime
|
|
|
personality develops fastest during _________
|
Childhood
|
|
|
Personality traits change slower during _______
|
Adulthood
|
|
|
Transmission of genetic characteristics from parents to children
|

Hereditary
|
|
|
Heredity versus environment and social learning
|

Nature versus nurture
|
|
|
The nature versus nurture debate deals with ____
|
Personality development
|
|
|
Heredity (name)
|

nature
|
|
|
Environment and socialization (name)
|
nurture
|
|
|
Advocates of the nature viewpoint believe much human behavior is _________
|
instinctual
|
|
|
Biologically inherited behavior pattern
|
instinct
|
|
|
Sets limits on the socialization process
|
nature/heredity
|
|
|
Nurture advocates attribute personality to _____
|
environmental factors
|
|
|
Capacity for mental achievement
|
intelligence
|
|
|
Most social scientists consider intelligence to be _________.
|
largely learned
|
|
|
Jean Piaget concluded that children learn how to think by passing through _________
|
stages of cognitive development
|
|
|
Swiss Psychologist who dealt with the cognitive development of children
|

Jean Piaget
|
|
|
Cognitive
|
mental intellectual
|
|
|
According to Piaget the human mind has inherent structure that _______.
|
determines what can be learned
|
|
|
Determines rate of cognitive development.
|
social forces
|
|
|
Systematic study of the biological basis for all social behavior
|
sociobiology
|
|
|
Places a strong emphasis on the genetic basis of human behavior
|
sociobiology
|
|
|
Most social scientists believe personality is the result of a blending of __________.
|
heredity and environment/nature & nurture
|
|
|
Most social scientists believe the greatest influence on personality comes from ______.
|
environmental factors/nurture
|
|
|
Birth order, parents, cultural environment and heredity _______.
|
influence personality
|
|
|
How children should feel is ________.
|
learned
|
|
|
How to express or conceal emotions is _______.
|
learned
|
|
|
How to produce or eliminate feelings is _____.
|
learned
|
|
|
Ability to associate emotions with the proper experiences.
|
emotional logic
|
|
|
Emotional logic is _________.
|
learned
|
|
|
Sigmund Freud's system.
|
Psychoanalysis
|
|
|
Freud believed that psychological problems could be traced to _________.
|
repressed childhood experiences
|
|
|
According to Freud personality depends on how the individual's ____________.
|
Id is shaped and controlled during childhood
|
|
|
The irrational part of the personality concerned with seeking pleasure. (Freud)
|
Id
|
|
|
Inborn desire to enjoy ourselves. (Freud)
|
Id
|
|
|
Part of the personality that is rational and deals with the word logically. (Freud)
|
Ego
|
|
|
Part of the psyche that experiences the outside world and reacts to it. (Freud)
|
Ego
|
|
|
The moral part of a personality, the "conscience." (Freud)
|
Superego
|
|
|
Reflects society's ideals and prohibitions. (Freud)
|
Superego
|
|
|
The referee between the Id and the superego.
|
Ego
|
|
|
Believes all behavior is the result of rewards and punishments (perspective)
|
Behavioral Psychology
|
|
|
According to Behavioral Psychology, personality is just the sum total of a persons ______.
|
reinforcements and punishments
|
|
|
According to Behavioral Psychology, the behaviors that become a part of our personality are the ones which are _______.
|
reinforced
|
|
|
Behavioral psychology supports the _________
|
Nurture argument
|
|
|
Two leading Behavioral Psychologists.
|
Watson and Skinner
|
|
|
Wrote Beyond Freedom and Dignity.
|
B.F. Skinner
|
|
|
Are more likely to be achievement-oriented, cooperative, and cautious
|
First Borns
|
|
|
Tend to be; better in social relationships, more affectionate and creative.
|
later-borns
|
|
|
Determines the basic types of personalities that will be found in a society.
|
cultural environment
|
|
|
experience the same "culture" in different ways. (often)
|
males and females
|
|
|
Image of what one is supposed to be and do on the basis of their sex.
|
gender identity
|
|
|
A capacity to learn a particular skill or acquire a particular body of knowledge
|
Aptitude
|
|
|
An aptitude which is a NATURAL talent is the result of _________
|
heredity/nature
|
|
|
Provides us with biological needs.
|
heredity/nature
|
|
|
Determines how we meet biological needs.
|
culture
|
|
|
Places limits on what is possible for an individual.
|
heredity/nature
|
|
|
The importance of culture and social learning on personality development has been shown by _______.
|
cases of isolation
|
|
|
Interactive process through which individuals learn.
|
socialization
|
|
|
Transmitting cultural values to members.
|
socialization
|
|
|
Skills, values, beliefs, and behavior patterns are learned through ________.
|
socialization
|
|
|
Our conscious awareness of possessing a distinct identity.
|
self or sense of self
|
|
|
Tabula Rasa
|
Blank Slate
|
|
|
Believed each newly born individual was a Tabula Rasa. (person) (17th century philosopher)
|
John Locke
|
|
|
According to Locke we are born without a ______.
|
Personality
|
|
|
We develop our sense of being distinct through _____.
|
socialization
|
|
|
John Locke believed he could shape newborns into ______.
|
anything he wanted
|
|
|
Psychologists who agreed with Locke's blanks slate theory. (names)
|
Watson and Skinner
|
|
|
Watson and Skinner's school of Psychology.
|
Behavioralism (Behavioral Psychology)
|
|
|
A process by which we absorb those aspects of culture we encounter.
|
socialization
|
|
|
Believed all children go through three levels of moral development. (person)
|

Lawrence Kohlberg
|
|
|
Define right and wrong according to immediate reward or punishment. (Kohlberg)
|
Preconventional morality
|
|
|
Define right and wrong according to the motive of the action. (Kohlberg)
|
Conventional morality
|
|
|
Judge actions taking into account conflicting norms. (Kohlberg)
|
Postconventional morality
|
|
|
Socialization's most important function. (functionalism)
|
ensuring order
|
|
|
Conflict perspective believes socialization can be harmful because __________.
|
parents are given too much power
|
|
|
Developed the idea of the " looking glass self." (person)
|
Charles Cooley
|
|
|
According to the "looking glass self" our image of ourselves is based on how we imagine we _________.
|
appear to others
|
|
|
I am not who I think I am, I am not who you think I am, I am who I think you think I am.
|
Looking Glass Self
|
|
|
The "looking glass self" comes from the_____.
|
interactionist perspective
|
|
|
A newborn baby has no sense of ________.
|
Self
|
|
|
From the interactive process a child develops a sense of _______.
|
self
|
|
|
Developed the idea of role-taking.
|
George Herbet Mead
|
|
|
Mead's perspective.
|
interactionist (symbolic Interactionist)
|
|
|
Putting ourselves in the place of others. (Mead)
|
role-taking/ taking the role of the other
|
|
|
Taking or pretending to take the role of others.
|
role-taking/ taking the role of the other
|
|
|
According to Mead it forms the basis for the socialization process.
|
role-taking/ taking the role of the other
|
|
|
Role-taking allows us to anticipate what others _______.
|
expect of us
|
|
|
Role-taking allows us to see ourselves through the ________.
|
eyes of others
|
|
|
We first internalize the expectations of ______.
|
significant others
|
|
|
Those closest to us.
|
significant others
|
|
|
Significant others have direct influence on our _______.
|
socialization
|
|
|
The internalized attitudes, expectations, and viewpoints of society.
|
generalized other
|
|
|
As we grow older it takes added importance in guiding our behavior.
|
generalized other
|
|
|
Internalizing the values of society is taking the role of the ___________. (Mead)
|
generalized other
|
|
|
We come to internalize the generalized other through
|
role-taking/ taking the role of the other
|
|
|
Seeing the world through someone else's eyes.
|
role-taking/ taking the role of the other
|
|
|
Imitation, play, and games are Mead's 3 steps of.
|
role-taking/ taking the role of the other
|
|
|
Two related parts of the "self." (Mead)
|
"I" and "Me"
|
|
|
The unsocialized, spontaneous, self-interested component of our personality.
|
"I"
|
|
|
The part of our identity that is aware of society's expectations. (Mead)
|
"Me"
|
|
|
Our socialized self. (Mead)
|
"me"
|
|
|
Stronger component of a child's personality. (Mead)
|
"I"
|
|
|
Gains power through the socialization process.
|
me
|
|
|
Brings our actions in line with society's expectations. (Mead)
|
"me"
|
|
|
The "me" never totally______.
|
dominates the "I"
|
|
|
Part of the personality which makes us look alike. (Mead)
|
"me"
|
|
|
Part of the personality which makes us unique.
|
"I"
|
|
|
When children learn from their parents that they exist and are different. (Wiley)
|
"the we"
|
|
|
Wiley believed the "I" developed from _____.
|
"the we"
|
|
|
Provide situations in which socialization occurs.
|
Agents of Socialization
|
|
|
Family, peer groups, school, and the mass media.
|
agents of socialization
|
|
|
Most important agent of socialization.
|
Family
|
|
|
Principal socializer of young children.
|
Family
|
|
|
Socialization in the family can be both deliberate and _____.
|
unconscious
|
|
|
Deliberate and unconscious socialization sometimes ______ .
|
conflict
|
|
|
A close group of roughly equal age and social characteristics.
|
Peer Group
|
|
|
In peer group socialization the goal is to _____.
|
fit in
|
|
|
Peer group socialization is ______.
|
unstructured
|
|
|
The agent of socialization in which you are now participating.
|
School
|
|
|
TV. Radio, newspapers, books, etc.
|
Mass Media
|
|
|
Reaches large audiences, no personal contact.
|
Mass Media
|
|
|
People are isolated from the rest of society.
|
total institution
|
|
|
Total institutions are primarily concerned with_________.
|
resocialization
|
|
|
Break with past experiences and the learning of new values and norms.
|
resocialization
|
|
|
Dehumanizing of individuals in a total institution.
|
mortification of the self
|
|
|
To resocialize someone it helps to shake their _____.
|
sense of self
|
|
|
Someone who's approval we desire.
|
significant other
|
|
|
To successfully be able to interact with another person you must be able to _______.
|
empathize with them
|
|
|
When you empathize with someone in order to communicate.
|
"taking the role of the other"/Role-taking
|
|
|
Learning roles that one has already acquired.
|
developmental socialization
|
|
|
Prepares a person to assume a role in the future.
|
anticipatory socialization
|
|
|
Erik Erikson believed adult personality develops in response to a _________,
|
series of crisis
|
|
|
According to Dennis Wrong we are NOT puppets of society because we are NOT ______.
|
entirely socialized
|
|
|
Socializing influences are NOT always ______.
|
consistent
|
|
|
Feminist Theory sees gender identities as developed under the influence of ______.
|
Patriarchy
|
|
|
May account for similar socialization practices in different societies.
|
Biological factors
|
|
|
Violating significant social norms.
|
deviance
|
|
|
A mark of social disgrace that sets a deviant apart.
|
stigma
|
|
|
What is considered deviant varies over _____.
|
time
|
|
|
What is considered deviant varies from _______.
|
place to place
|
|
|
What is considered deviant is determined by _____.
|
public consensus or powerful groups/culture
|
|
|
Deviance benefits society by enhancing conformity, strengthening social solidarity, safely releasing discontent, and inducing social change.
|
Durkheim's "Functions" theory
|
|
|
Low levels of deviance actually serve some____.
|
positive functions
|
|
|
Deviance can unify a ______.
|
group
|
|
|
Deviance helps clarity _______.
|
norms
|
|
|
Deviance helps diffuse _______.
|
tension
|
|
|
Deviance provides ______.
|
jobs
|
|
|
Deviance helps induce _______.
|
social change
|
|
|
Views deviance as the natural outgrowth of values, norms and structure of society.
|
Structural-Strain Theory
|
|
|
Deviance is the result of accepting societies goals but not having access to legitimate means.
|
Structural-Strain Theory
|
|
|
The strain of incompatible goals and means results in ______.
|
Anomie
|
|
|
Normlessness
|
Anomie
|
|
|
Norms are unclear and no longer applicable.
|
Anomie
|
|
|
Leaves individuals without sufficient guidelines for behavior.
|
Anomie
|
|
|
He developed the Structural-Strain Theory.
|
Robert Merton
|
|
|
Durkheim developed the idea of anomie to explain why nations undergoing industrialization had high rates of ______.
|
Suicide
|
|
|
To accept both cultural goals and approved means.
|
Conformity
|
|
|
To accept cultural goals but reject approved means.
|
Innovation
|
|
|
Give up on cultural goals but continue to follow rules. (means)
|
Ritualism
|
|
|
Reject both cultural goals and acceptable means.
|
Retreatism
|
|
|
Reject both cultural goals and means but substitute new ones.
|
Rebellion
|
|
|
Views deviance as the result of individuals not having strong enough ties to the community.
|
Hirschi's Control Theory
|
|
|
The wrongdoer is punished in such a way as to be stigmatized, rejected, or ostracized.
|
Disintegrative Shaming
|
|
|
Making wrongdoers feel guilty while showing them understanding, forgiveness, or even respect.
|
Reintegrative Shaming
|
|
|
Disintegrative shaming causes deviance.
|
Braithwaite's Shaming Theory
|
|
|
Views deviance as the result of competition and social inequality.
|
Conflict theory
|
|
|
Deviance is the result of class struggle.
|
Conflict theory
|
|
|
Marxists believe deviance stems from the exploitative nature of _____.
|
capitalism
|
|
|
The powerful have greater; deviant motivation, opportunity and weaker social control.
|
Power Theory
|
|
|
Powerful engage in profitable deviance and the powerless in unprofitable deviance.
|
Power Theory
|
|
|
Views deviance as learned behavior.
|
Cultural-Transmission Theory
|
|
|
Proportion of association a person has with deviant versus non-deviant individuals.
|
Differential Association
|
|
|
According to cultural-transmission theory the reason some learn non-deviance while others learn deviance.
|
Differential Association
|
|
|
If a person interacts mostly with deviants they will learn to be deviant.
|
Cultural-Transmission Theory
|
|
|
Cultural-transmission theory views all individuals as _______.
|
conformists
|
|
|
Being labeled deviant by society leads people to see themselves as deviant and to live up to this self image.
|
Labeling Theory
|
|
|
Nonconformity that goes undetected by those in authority.
|
Primary deviance
|
|
|
Results in the individual being labeled as deviant and accepting the label as true.
|
Secondary Deviance
|
|
|
Being labeled deviant can force an individual into a_____.
|
deviant lifestyle
|
|
|
Social Control is needed because socialization is ______.
|
never complete
|
|
|
As society becomes more heterogeneous and impersonal there is a greater need for _____.
|
formal social controls
|
|
|
Deviant behavior is seen as unwilling and caused by disease.
|
Medicalization of Deviance
|

