![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Leukopenia
|
WBC<5k is called leukopenia
Refers to a decreased number of circulating neutrophils. |
|
|
3 Causes of Leukopenia
|
1. Drug toxicity (chemotherapy with alkylating agents). Damage to stem cells results in decreased production of WBCs. Especially neutrophils.
2. Severe infection (e.g. gram-negative sepsis)- increased movement of neutrophils into tissues. 3. GM-CSF or G-CSF may be used pharmacologically to boost granulocyte production, thereby decreasing the risk of infection. |
|
|
Lymphopenia
|
decreased number of circulating lymphocytes
|
|
|
4 causes of lymphopenia
|
1. Immunodeficiency
2. High cortisol state(e.g., exogenous corticosteroids or Cushing Syndrome) 3. Autoimmne destruction (systempic lupus erythmeatosus) 4. Whole body radiation- lymphocytes are highly sensitive to radiation. Lymphopenia is earliest change to emerge. |
|
|
Leukocytosis
|
Increased number of leukocytes (neutrophilic leukocytosis, monocytosis, eosinophilia, basophilia, lymphocytic leukocytosis).
|
|
|
Infectious Mononucleosis (IM)
|
Pathology: Epstein-Barr Virus. Results in lymphocytic leukocytosis comprised of reactive CD8+ T Cells. Transmitted via saliva. Infects oropharynx, liver, B cells.
Clinical Features: 1. Generalized lymphadenopathy (LAD) due to T-cell hyperplasia. 2. Splenomegaly due to T-cell hyperplasia in the PALS. 3. High WBC count with atypical lymphocytes (reactive CD8+ T Cells) in the blood. Populations: Teenager. Detection: Monospot test is used for screening. Complications: Increased risk for splenic rupture; avoid sports 1 yr. Rash if exposed to ampicillin and Dormancy of virus in B cels leads to increase reccurrence. |
|
|
IM
|
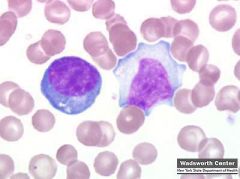
atypical lymphocyte of infectious mononucleosis
|
|
|
Basic Principles: Acute leukemia
|
1. Defined as the accumulation of >20% blasts in the bone marrow.
2. Increased blasts "crowd-out" normal hematopoiesis, resulting in an "acute" presentation with anemia (fatigue), thrombocytopenia (bleeding), or neutropenia (infection). 3. Blasts usually enter the blood stream, resulting in high WBC count. 4. Acute leukemia is subdivided into acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or cute myelogenous leukemia (AML) based on phenotype of the blasts. |

