![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
329 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Momentum (mo) |
U - kilogram meters per second
E - m X v |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Current (i) |
U - coulombs per second or amperes, A
E - charge/time |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Charge (C) |
U - coulombs
E - i X time where 'i' is current |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Density (p) |
U - kilogram per liter
E - m/volume |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Mass (m) |
U - kilogram
E1 - density X volume E2 - F/acceleration |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Distance (x) |
U - meters
E - v X t |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Velocity (v) |
U - meters per second
E1 - x/t E2 - frequency X wavelenth |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Acceleration (a) |
U - meters per second^2
E1 - v/t E2 - F/m |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Pressure (P) |
U - newton per meter^2
E - F/area Paschals! (Pa) |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Speed (s) |
U - meters per second
E - dx/dt |
|
|
Physics: Unit and Eqtn
Force (F) |
U - newtons
E - m * a E - q * v * Bsinϴ E - i * L * Bsinϴ |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Weight (W) |
U - newtons
E1 - density X volume X gravity E2 - m X gravity |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Impulse (I) |
U - newton second
E - F X time |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Work (wr) |
U - newton meters
E1 - F X d E2 - pressure X volume |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Power (pow) |
U - newton meters per second
E1 - F X v E2 - W/t E3 - E/t |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Energy (E) |
U - joules
E1 - pow X t E2 - mv^2 E3 - h(planck) X frequency [CHEM OVERLAP] E4- [h(planck) X v(light)]/wavelength [CHEM OVERLAP] |
|
|
Physics: Unit & Eqtn
Volt (V) |
U - joules per coulomb
E - W/C w= watts c= charge |
|
|
Physics: Units & Eqtn
Angular Momentum |
U - kilogram meter^2 per second
E - m X v X radius |
|
|
Physics: Relationship Game
Keq and Emf (cell) |
Directly related
|
|
|
Physics: Relationship Game
dG (Gibbs) and Emf (cell) |
Inversely related
Opposites? |
|
|
Physics: Deffinitions
Potentiometer |
Voltometer that reads no current but more accurate reading of the difference in potential btwn 2 electrodes
|
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
mass |
E - density X volume
kg/ml^3 X ml^3 |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
weight |
E1 - m X g
E2 - p(Vol)g kg X m/sec^2 kg/ml^3 X ml^3 X m/sec^2 |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
momentum |
E - m X v
kg X m/s |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
speed |
E - distance/time
m/sec |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
distance |
E - velocity X time
m/s X s |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
acceleration |
E - velocity/time
m/s X 1/s |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
force |
E - mass X acceleration
kg X m/s^2 = newton (N) |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
work |
E1 - force X distance
E2 - pressure X volume N X m = joule (J) N/m^2 X m^3 = joule (J) |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
impulse |
E - force X time
N X s |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
viscocity |
E - force/(distance X velocity)
N/m X s/m |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
density |
E - mass/volume
kg/m^3 |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
pressure |
E - force/area
N/m^2 |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
power |
E1 - work/time
E2 - force X velocity J/s N X m/s |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
charge |
E1 - current X time
E2 - joules/volt C/s X s J X C/J |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
dipole moment |
E - coulomb X distance
C X m |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
volt |
E - work/charge
J X 1/C |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
tesla |
E - newton/(distance X current)
N/m X s/C |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis<BR><BR>Capacitance
|
U - Farad
E - area of plate/distance of charges E - charge/volt (Amp/sec) * 1/Volt Volt = Work * 1/Amp * 1/s^2 Amp = (sec/coulomb) |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
period |
E - 1/frequency
s/cycle = 1/hertz (1/Hz) |
|
|
Physics: Unit Analysis
frequency |
E - 1/period
cycle/s = hertz (Hz) |
|
|
Physics: Relationship Game
dG (Gibbs) and Keq |
Inversely related
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Distance |
Scalar
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Speed |
Scalar
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Time |
Scalar
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
ENG |
Scalar
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Mass |
Scalar
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Work |
Scalar
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Displacement |
Vector
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Velocity |
Vector
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Acceleration |
Vector
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Force |
Vector
|
|
|
Physics: Scalar or Vector
Chord |
Vector
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Sin 0 |
0
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Cos 0 |
1
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Sin 30 |
.5
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Cos 30 |
srt3/2
.86 |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Sin 60 |
srt3/2
.86 |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Cos 60 |
.5
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Sin 45 |
srt2/2
.7 |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Cos 45 |
srt2/2
.7 |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Sin 90 |
1
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Cos 90 |
0
|
|
|
Units and Kinetics (KapCH1)
What is a vector? |
Numbers with direciton and magnitude
|
|
|
Units and Kinetics (KapCH1)
What is a scalar? |
Numbers with only magnitude
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Tan 0 |
0
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Tan 30 |
1/srt3
.57 |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Tan 45 |
1
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Tan 60 |
srt3
1.7 |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Tan 90 |
Not Possible
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
What is the difference btwn average speed and average velocity? |
Average speed accounts for actual distance traveled while average velocity does not
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
What is the difference btwn speed and velocity? |
Speed uses distance
Speed is scalar Velocity uses displacement Velocity is a vector |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Mega (M) |
10^6
THINK Million - Mega |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Giga (G/B) |
10^9
THINK Billion - (g/B) |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Tetra (T) |
10^12
THINK Trillion - Tetra |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Angstrom |
10^-10
One unit less than nanometer |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
How can you relate Work with distance? |
Distance and work are baseline units
THINK like a second order distance/velocity/acceleraton |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
How can you relate Power with speed/velocity? |
They are both over time
THINK like a second order distance/velocity/acceleraton |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
How can you relate Energy with acceleration? |
They are both over time^2
THINK like a second order distance/velocity/acceleraton |
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Electron volt (eV) |
1.6 X 10^-19
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
When you hear the words "overall" what do you think? |
Vector or scalar sums!
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
What is the difference distance and displacement? |
Distance is a vector
Displacement is a scalar |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics(KapCH2)
What is the difference mass and weight? |
Weight is a measurement of the body's graviational force
Weight is a vector Mass is a measurement of the body's inertia Mass is a scalar |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics(KapCH2)
What are Newton's Three Laws |
1-A body in rest will stay at rest unless acted upon an external force
F=ma=0 2-There is no acceleartion if the sum of the forces cancels out and there is an acceleration in the resultant net sum of forces SumfF=ma 3-Every action has an equal and opposite reaction Fa=-Fo |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Torque is dependent on what factors? |
1-Magnitude of the force
2-Angle of the force 3-Distance from the fulcrum/lever arm |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
What are the components of circular motion? |
1-Tangential
2-Radial/centripetal |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
What governs the degree of friction? What does it mean? |
Normal Load
The force that squeezes the two surfaces together |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
What is the difference btwn static and kinetic friction? |
Kinetic friction is constant
Static friciton is dependent on the contact points - surface area in contact Max static friction ALWAYS greater than kinetic friction Kinetic friction is independent of surface area and velocity |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
What is translational EQ? |
When the vector sum of all FORCES is 0
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
What are the properties of translational EQ? |
Constant speed
Constant direciton |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
What is rotational EQ? |
When the vector resultant of all TORQUES is 0
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Physics: Relationship Game (pertaining to circular motion) Radial component Speed |
Direct
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Physics: Relationship Game (pertaining to circular motion) Trangential component Speed |
Direct
If it slows it is NEG If it is accelerating it is POS |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Physics: Relationship Game (pertaining to circular motion) Torque clockwise Sign convention |
Indirect
THINK Physics and Organic Organic sounds logical and intuitive Dextro R clockwise is positive Levo S counterclockwise is negative THINK Physics defying logic and time If you have an understanding of physics you can defy time In that clockwise rotation is negative and counterclockwise rotation is positive |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Orbits and Trangential component |
F = (G*m1*m2)/r^2
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Orbits and Radial component |
F = (mv^2)/2
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Physics: Relationship Game Radius of particle's orbit Speed of orbiting particle |
Indirect
THINK (G*m1*m2)/r^2 = F = (mv^2)/2 |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Physics: Relationship Game Angle of slope Frictional Force |
Inverse
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Physics: Relationship Game Angle of slope Frictional Force |
Inverse
|
|
|
Work Energy and Momentum (KapCH3)
Physics: Relationship Game UPe mass |
Direct - linear
|
|
|
Work Energy and Momentum (KapCH3)
Physics: Relationship Game UPe Gravity |
Direct - linear
|
|
|
Work Energy and Momentum (KapCH3)
Physics: Relationship Game UPe Height |
Direct - linear
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Average Acceleration |
dV / dt
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Kinematics Fundamentals Final Velocity (w/o displacement) |
Vf=Vi + at
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Kinematics Fundamentals Displacement (no Vf) |
d(x) = Vi*t + .5(at^2)
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Kinematics Fundamentals Final Velocity (w/o time) |
Vf^2 = Vi^2 + 2a*d(x)
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Average Velocity |
Vave=.5(Vi + Vf)
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Gravitational Force |
F = (G*m1*m2)/r^2
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2
Torque |
τ = r*F*sinθ
THINK WORK W=F*d*cosθ |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Kinetic or Static Friction |
KF= F(friction)= μ * N
SF=F(friction)≤ μ * N |
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Centripetal Acceleration |
Ac=(velocity)^2 / (radius)
|
|
|
Newtonian Mechanics (KapCH2)
Centripital Force |
Fc=Mass * Acceleration
Fc=(mass)(velocity)^2 / (radius) |
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Kinetic ENG |
KE = .5(mass)(velocity)^2
|
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Potential ENG |
UPe = mass * gravity * height
|
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Work |
W=F*d*cosθ
THINK Torque τ = r*F*sinθ |
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Power |
Pow=W/time
Pow=F*velocity Pow=current*Voltage/EMF Pow=current^2*Resistance |
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Momentum |
Mo=mass*velocity
|
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Impulse |
Imp=F*d(time)
Imp=(mass1*velocity1)- (mass2*velocity2) |
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Elastic Collisions |
.5[(m1)*(v1)^2]+.5[(m2)*(v2)^2]=.5[(m1)*(v1)^2]+.5[(m2)*(v2)^2]
|
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Inelastic Collisions |
.5[(m1)*(v1)^2]+.5[(m2)*(v2)^2]>.5[(m1)*(v1)^2]+.5[(m2)*(v2)^2]
|
|
|
Work Energy Momentum (KapCH3)
Completely Inelastic Collisions |
(m1)*(v1)+(m2)*(v2)=[(m1)+(m2)]*(v2)^2
|
|
|
Work Energy and Momentum (KapCH3)
Physics: Relationship Game (momentum is constant) Force Time |
Inverse
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Kinematics Fundamentals Distance (no acceleration) |
d(xf-xi)=[(Vf-Vi)/2]*t
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Range |
(Vi^2)/g
|
|
|
Units and Kinematics (KapCH1)
Time |
sqrt(2h/g)
|
|
|
Work Eneryg and Momentum (KapCH3)
What is the assumption of conservation? Meaning what in terms of forces? |
There are no external forces acting on the system
Vector sum of ext F acting upon system is 0 |
|
|
Work ENG and Momentum (KapCH3)
What are the types of collisions? |
Completely Elastic
Inelastic Collisions Completely Inelastic |
|
|
Work ENG and Momentum (KapCH3)
In completely elastic collisions what happens to the mo and KE? How is the mo calculated? How is the KE calculated? |
mo and KE are conserved
mo(initial)=mo(final) sumKE(initial)=sumKE(final) |
|
|
Work ENG and Momentum (KapCH3)
In inelastic collisions what happens to the mo and KE? How is the mo calculated? How is the KE calcualted? |
mo is conserved NOT KE
mo(initial)=mo(final) sumKE(initial)>sumKE(final) |
|
|
Work ENG and Momentum (KapCH3)
In completely inelastic collisions what happens to the mo and KE? How is the mo calculated? How is the KE calculated? |
mo is conserved NOT KE
mo(initial)=mo(final) m1v1+m2v2=(m1+m2)v3 |
|
|
Work ENG and Momentum (KapCH3)
Physics: Relationship Game (inclined planes, pulleys) Force Distance |
Inverse
|
|
|
Work ENG and Momentum (KapCH3)
How do you calculate efficiency? |
W(out)/W(in)
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Celsius-->K |
C =K -273
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Thermal Expansion |
dL = α*L*(dT)
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Volume Thermal Expansion |
dV = β*V*(dT)
β=3α |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
1st Law of Thermodynamics What is it in words? |
ΔU = Q - W
Change in total internal ENG is equal to the amount of ENG transfered in the form of heat to the system minus the amount of ENG transfered from the system (Work) |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Heat Gained (Q) |
Q = m*c *(dT)
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Heat Gained (Δphase) |
Q = m * (Kphase constant)
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Adiabatic Process What is constant? |
dU = W = P*dV
Q = 0 Q is constant |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Isovolumetric/Isochoric What is constant? |
dU = Q
W = 0 Volume is constant |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Closed Cycle/Isothermal What is constant? |
Q = Q
dU = 0 UPe is constant |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
2nd Law of Thermodynamics What is it in words? |
dS = Q/T
Energy spontaneously disperses from being localized to becoming spread out |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
0th Law of Thermodynamics What is it in words? |
at EQ Q=0 T1=T2
When one object is in thermal eq with another, NO HEAT will flow btwn them |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
What is temperature? |
Average KE of particles
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
How does heat move spontaneously? |
From high temp to low temp
THINK Osmosis-->Heat Osmosis [high H2O]-->[low H2O] |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
What physical properties are affected by changing temperatures? |
Length
Volume Conductivity |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Temp Length |
Direct
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Work done ON system sign notation? |
NEGATIVE
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Work done BY system sign notation? |
POSITIVE
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Heat leaving system? |
NEGATIVE
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Heat entering system? |
POSITIVE
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Heat Work |
Inverse
When work is done by system (+W), heat leaves (-Q) When work is done on system (-W), heat enters (+Q) |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
What are the types of heat transfer? What do they mean? |
Convection - via fluids
*More efficient than convection* Conduction - via solids (direct contact) *Metals are best for conduction* Radiation - via electromagnetic waves *can travel through vacuum* |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
What is specific heat? |
The relationship btwn heat and temperature which is the heat required to raise 1g of a substance by 1 degreeC or K
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Pressure Work |
Indirect
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Volume Work |
Indirect
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game UPe Work |
Indirect
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Volume UPe |
Direct
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Pressure UPe |
Direct
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game ENG Entropy |
Direct
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Work Entropy |
Indirect
THINK Work needed to concentrate ENG = concentration - DEC Entropy |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Heat Entropy |
Direct
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
3rd Law of Thermodynamics What is it in words? |
Suniv = 0 at T = 0 K
You cannot reach absolute 0, but if you do there is no entropy at this temperature |
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Entropy Heat |
Direct
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Physics: Relationship Game Entropy Temperature |
Indirect
|
|
|
Thermodynamics (KapCH4)
Entropy in reversible process |
Q/T=dS=L(heat)*(m/T)
THINK Q=m*L(heat) When the T cross out |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Density |
ρ = mass / volume
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Pressure |
P = Force / Area
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Absolute Pressure |
Pabs= P(surface) + ρgh
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Paschal's Principles |
F1/A1 = F2/A2
A1*d1=A2*d2 THINK Continuity EQTN A1*V1=A2*V2 |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Buoyant Force |
F= ρ*g*V
density of fluid! volume of object |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Continuity EQTN |
Ac1*V1=Ac2*V2
Ac = cross sectional area THINK Pascha's Principles A1*d1=A2*d2 |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Stress |
F/A
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Strain |
ΔL/L - Young
x/h - Shear dV/V - Bulk |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Young's Modulus |
Y= (F/A) / (ΔL/L)
Stress/Strain |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Shear Modulus |
S = (F/A) / (x/h)
Stress/Strain |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Bulk Modulus |
B = (F/A) / (ΔV/V)
Stress/Strain |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Guage Pressure |
Pg=p*g*h
Pg=(Pabs)-Patm Pabs=P(surface) + ρgh |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Total Pressure |
Ptot=Patm+Pg
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Total Pressure |
Ptot=Patm+Pg
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Total Pressure |
Ptot=Patm+Pg
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Critical Velocity |
v=(N*viscocity)/(p*Diameter)
N = Reynold's number |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Linear Velocity |
v(Ac)=(V/dT)
Ac = cross sectional area |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What are characteristics btwn fluids and solids? What are distinct differences? |
Both exert forces perpendicular to their surface
Both can be characterized by density Both have large bulk moduli Fluids conform, impose larger perpendicular forces Solids resist shear |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is specific gravity? |
Ratio of the density of a substance to taht of pure water at 1atm, and 4C
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does spec gravity >1 mean? |
More dense than water
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does spec gravity <1 mean? |
Less dense than water
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is the specifc gravity of water? |
1000kg/L or 1g/ml
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is absolute pressure? |
Total pressure that is exerted on an object that is submerged in a fluid
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Absolute Pressure Depth |
Direct
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Patm Altitude |
Indirect
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is gauge pressure? |
Difference btwn Pabs and Patm
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5
When will an object float? |
p-ave > fluid
specific gravity >/= 1 |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
When will an object sink? |
p-ave < fluid
specifc gravity < 1 |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
How do you determine the percentage of volume submerged? |
Determine the specifc gravity
p-obj/p-water |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is cohesion? |
Attractive force that a moleucle of LIQUID feels toward other molecules
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is adhesion? |
Attractive force that a molecule of LIQUID feels toward another molecule
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is the difference btwn cohesion and adhesion? |
Cohesion occurs with molecules of similar properties
Adhesion occurs with molecules of different properties |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does hydrstatics encompass? |
Paschal
Archimedes Cohesion Adhesion |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does Hydrodynamics encompass? |
Viscocity
Laminar and Turbulent Flow Streamlines Continuity EQTN Bernouli |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is viscocity? |
Resistance of a fluid to flow, a measure of fluid friction
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does thin fluids mean? |
Fluids with low viscocities
They lose less ENG to friction Approximate conservation of ENG Low internal resistance Behave more like ideal fluids |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does thick fluids mean? |
Fluids with high viscocities
They lose more ENG to friciton Dont conserve ENG High internal resistance Don't behave like ideal fluids |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does laminar flow mean? |
Smooth and orderly flow
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does turbulent flow mean? |
Rough and disorderly flow
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does critical velocity depend on? |
Viscocity
Diameter of tube Density of fluid |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What are properties of streamlines? |
Velocity is always tangential to the streamline at any point
Streamlines never cross each other |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is volumetric rate? What are its properties? |
rate of volume passing at a point
1-Must be same for all other points 2-Constant in closed system 3-Independent of chagnes in Ac |
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What is linear velocity? What are its properties? |
Measure of displacement of the fluid particle in a given amoutn of time
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What the continuity EQTN mean? |
fluids will flow more quickly through narrow passages and slowly through wider
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Ac Speed of fluid |
Inverse
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Dynamic pressure Static pressure |
Inverse
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Static pressure Velocity |
Inverse
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does Young's Modulus mean? |
Stretching or pushing force changing the length
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
What does Shear Modulus mean? |
Parallele force leading to shear - change in shape
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)<BR><BR>What does Bulk Modulus mean?
|
Compressibility: degree to which a material will experience a dV in relation to applied pressure
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Yield Strength |
Shape change beyond which material will not return to normal
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Ultimate Strenght |
Point beyond which the object will rupture
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Shear |
shape change due to the lateral shift in the direction of the force
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Bulk moduli Compressibility |
Indirect
|
|
|
Fluids and Solids (KapCH5)
Physics: Relationship Game Bulk moduli Speed of sound |
Direct
Sound travels greatest in a solids because IMFs and close proximity of molecules |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What is the fundamental unit of charge |
1.60X10^(-19) C = eV
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Fundamental Coulomb's Law |
F = (k*q1*q2) / r^2
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Fundamental Electric Field |
E = (k*q)/ r^2
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Force of E Field on a charge |
F = q * E
Can be set = ma |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Fundamental Electric potential |
V = (k*q) / r
V = W/q |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Fundamental Electric Potential ENG |
UPe = q*V
UPe = k(q*Q/r) (charge * voltage) |
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
Force of B Field on charge |
F = q*v*B(sinθ)
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
Current |
i= Δq / Δt
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
Force of Wire with Current |
F = i*L*B(sinθ)
(current*length*Bfield) |
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
B field created by long straight wire |
B = (μo*I) / (2πr)
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
B field created by loop wire |
B = (μo * I) / (2r)
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Voltage (Ohms Law) |
V = iR
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Potential Difference |
Va-Vb=Wa-b/qo
Wa-b: work necessary to make it from point a to point b |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game Felec Charges |
Direct
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game Felec Distance |
Indirect
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game eV Distance |
Inverse
THINK Felec |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What does a positive charge mean? |
Radiates outward
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What does a negative charge mean? |
Radiates inward
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What does close electrical lines field mean? |
Weaker
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What does far electrical field lines mean? |
Stronger
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What are the four different potential energies? |
Gravitational
Chemical Mechanical Electrical Potential Energy |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Electric dipole |
Coulombs*meter
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH3)
Calculate Efield with a test charge at a point within |
F/q
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH3)
Calculate Efield with a charge and distance btwn charges |
(k*q)/r^2
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What direction is the Efield when the test charge is POS? |
Same direction
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What direction is the Efield when the test charge is NEG? |
Opposite direction
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game Efield direction POS test charge |
Direct
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game Efield direction NEG test charge |
Indirect
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6
Physics: Relationship Game UPele INC close Like charges (+) |
INC POS
Direct |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
UPele INC far Like charges (+) |
INC NEG
Indirect |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
UPele INC far Unlike charges (-) |
INC POS
Indirect |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
UPele INC close Unike charges (-) |
INC NEG
Direct |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What is UPele? |
The amount of work/ENG to bring a charge a set point
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What is eV? |
Ratio of UPele over the charge magnitude
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game Felec Distance |
Inverse
THINK eV |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game Felec (Coulomb) Charge magnitude |
Direct
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game POS q (spont) eV |
Direct (DEC)
DEC UPele |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physics: Relationship Game NEG q (spont) eV |
Indirect (INC)
DEC UPele |
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
What is the equipotential line mean? |
The eV at every point on the line is the same
|
|
|
Electrostatics (KapCH6)
Physcis: Relatioship Game Efield Dipole moment |
Inverse - Opposites
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
What are the conditiosn for the generation of Mfields |
Charge
Movement |
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7
What is the SI unit for Mfield? |
Tesla
10^4 gauss = 1 T |
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
What is the Curie Temp? |
Critial temperature for ferromagnetic materials in which above the temp the material is paramagnetic, below the temp, the material is magnetized and is permanently magnetized
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
What is the SI unit for current? |
Amps
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
Physics: Relationship Game Mfield Distance |
Inverse
|
|
|
Magnetism (KapCH7)
What is the RHrule? |
Thumb is the direction of v
Palm is the magnetic force Fingers are the magnetic field |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What is a conductor? |
Materials that allow the electric charge to move freely within the material
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What is an insulator? |
Materials that hold on to electrons to slow the electric charge
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Current (+) eV |
Inverse
(current goes from higher to lower eV) |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Electrons (-) eV |
Direct
(electrons goes from lower to higher eV) |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What is Kirchoff's Junciton Rule? |
At any point or juction, the sum of the currents directed into that point equals the sum of currents directed away from that point
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What is Kirchoff's Loop Rule? |
Sum of voltage equals the sum of voltage drops around a closed circuit loop
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Conductor Resistance |
Inverse
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Insulator Resistance |
Direct
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What are the characteristics that determine resistance? |
Resistivity
Lenght Cross Sectional Area *Temperature |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Resistivity |
(rho)=(Resistance*Acsc)/length
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Lenght Resistance |
Direct
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Resistance Resistivity |
Direct
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Cross Sectional Area Resistance |
Indirect
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Physics: Relationship Game Tempterature Resistance |
Direct
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Ohm's Law |
Voltage drop=i*resistance
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What does ohms law mean? |
Voltage changes while the current is constant
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Voltage drop including the internal resistance |
V=emf-i*(Resistance internal)
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Power |
P=i*V
P=ENG/time P=i^2*Resistance P=V^2/Resistance |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Resistors in Series |
R=R1 + R2... + Rn
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Resistors in Parallel |
1/R=1/R1 + 1/R2... + 1/Rn
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Voltage in Series |
V=V1 + V2... + Vn
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Current |
i=Voltage/Resistance
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
n Identical Resistance in Parallel |
R/n
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Capacitance |
C=charge/V
C=[(permitivity of free space)*area]/distance btwn plates |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Potential ENG stored in Capacitor |
UPe=.5CV^2
THINK kinematics and KE |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
What is a dielectric material? What does it do? |
Material that shields the opposite carhges from each other
DEC voltage, augments the capacitance based on dielectric constant (Cf=KCi) |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Capacitors in Series |
1/C=1/C1 + 1/C2... + 1/Cn
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Capacitors in Parallel |
C=C1 + C2... + Cn
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Instantaneous Current in AC |
i=imax*sin(2*pi*f*t)
i=imax*sin(angvel*t) |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Average Current in AC |
0!
|
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Average Power in one cycle at AC |
iRMS=imax/(sqrt2)
sqrt2 = 1.41! |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Average Voltage in one cycle at AC |
VRMS=Vmax/(sqrt2)
sqrt2 = 1.41! |
|
|
DC and AC Circuits (KapCH8)
Average Voltage in AC |
0!
|
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Snell's Law |
n1(sinϴ1)=n2(sinϴ2)
|
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
What does Snell's Law mean? |
It means that if there is a smaller n initially, that the light will bend towards the normal(perpendicular).
However if there is a larger n initially, the light will bend away from normal(parallel) |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Speed of light taking into account index of refreaction (n) |
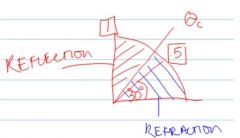
v=c/n
The speed of light in VACUUM is the largest and the rest WILL BE LESS |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
What is total internal reflection? |
When the indicent ϴ is greater than the ϴcrit.
|
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Physics: Relationship Game Ratio of indeceis of refraction Critical angle |
Direct
The smaller the ratio the smaller the critical angle |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
What is the take home message of dispersion? |
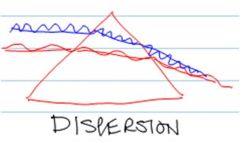
Higher wavelenghts mean (low freq and n) IR closer to the incident light
Lower wavelenghts (high freq and n) UV farther to the indicent light |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Pavlov High feq low wvLth |
VIOLET!
UV Higher n Think cancer |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Pavlov Low feq High wvLth |
RED!
IR Lower n Think organic chemistry |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Physics: Relationship Game Freq Index of refraction |
Direct
Higher freq refracts more light becaus there are more chances as it turns more |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Physics: Relationship Game ENG Freq |
Direct
E=h*f |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Physics: Relationship Game ENG WvLnth |
Indirect
E=h(v/wavelength) |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Physics: Relationship Game Resulting dispersion Ratio of indeices of refraction |
Inverse
The LOWER the ratio, the LOWER the angle towards the normal which means a greater dispersion |
|
|
Light and Optics (K,BP:10)
Physics: Relationship Game Resulting angle Ratio of indeices of refraction |
Direct
The LOWER the ratio, the LOWER the angle towards the normal |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Speed of waves |
v= (sqrt[Ftension*length/mass]
TRANSVERSE WAVE ONLY v=(wavelength/Period) v=(wavelength*freq) |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Physics: Relationship Game Wave speed Lenght of string |
Direct
THINK v=freq*wavelength OR v=sqrt[(tension*length)/mass] |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Physics: Relationship Game Wave speed Mass |
Indirect
THINK v=sqrt[(tension*length)/mass] |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Physics: Relationship Game Wave speed Tension |
Direct
THINK v=sqrt[(tension*length)/mass] |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Frequency (general) |
f=.5sqrt(constant/change)
Spring f=.5sqrt(k/m) Pendulum f=.5sqrt(g/L) |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Period (general) |
f=1/T
so... T=.5sqrat(change/constant) Spring T=.5sqrt(m/k) Pendulum T=.5sqrt(L/g) |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Wavelength Harmonics and Standing Waves |
1) wvLnth=2L/n
n is 1,2,3... Open Pipes and Strings 2) wvLnth=4L/n n is 1,2,3 Closed Pipes |
|
|
Waves and Periodic Motion (K9, BP5)
Frequency Harmonics and Standing Waves |
1) f=n/2L
n is 1,2,3... Open Pipes and Strings 2) f=n/4L n is 1,2,3... Closed Pipes |
|
|
Periodic Motion (K BP)
Pavlov wavelength |
2L!
Consider it |
|
|
Electrics
Movement of opposites |
Accelerate towards each other
Likes attract! |
|
|
Optics (K10)
What does the focal legnth depend on? |
Radius of curvature
|
|
|
Optics (K10)
Pavlov Focal point of Diverging What does that mean? Vex/Cave? |
NEGATIVE!
THINK it is negative when things move away Virtual and Behind THINK Negative things are fake(virtual) and [talk] behind you Convex! THINK Vexing is negative |
|
|
Optics (K10)
Pavlov Focal point of Converging What does that mean? Vex/Cave? |
POSITIVE!
THINK it is positive when things get closer Real and Front THINK Positve things are real and infront of you Concave THINK Light is comming together in a cave |
|
|
Optics (K10)
Pavlov Negative Magnification |
INVERTED!
THINK You are negative in the upside down view when reality is right side up |
|
|
Optics (K10)
Pavlov Positive Magnification |
Upright!
THINK You are positive in the reality of things upright |
|
|
Why is the sin and cos of 45 the same?
|
They are the same because the two legs are equal in length when both angles are 45.
(45-45-90 rule) |

