![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
|
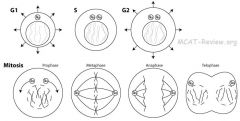
PMAT
Prophase = Prepare (condense chromatin into chromosomes, break down nuclear membrane, assemble mitotic spindle, centriole pairs move toward opposite poles of the cell) Metaphase = Middle (Chromosomes line up in the middle) Anaphase = Apart (Sister chromatids pulled apart to opposite sides of cell) Telophase = Prophase in reverse. de-condense chromosomes, re-form nuclear membrane, break down mitotic spindle. |
|
|
DNA Replication
|
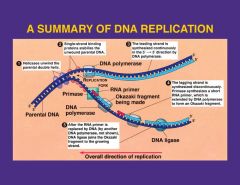
DNA replicates 5' to 3'
|
|
|
Cellular Respiration
|
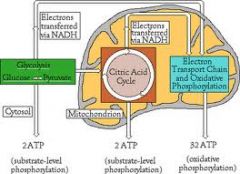
Net gain per glucose.
Glycolysis: 2 ATP, 2 NADH PDC: 2 pyruvate > 2 acteylCoA + 2 NADH Krebs: 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 GTP each NADH > 2.5 ATP each FADH2 > 1.5 ATP overall theoretical: 32 ATP actual: 36 ATP |
|
|
Electron Transport Chain
|
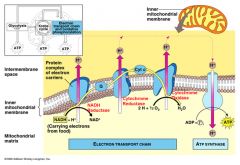
oxides NADH to NAD+, intermembrane increases in [H+] = low pH, this drives ATP synthase
Oxygen is final e- acceptor, gets reduces to H2O |
|
|
Fat Metabolism: Beta Oxidation
|
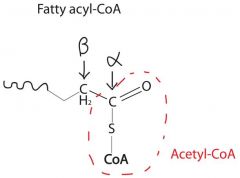
occurs in mitochondria matrix. Acetyl-CoA goes to Krebs cycle
Ester hydrolysis occurs in cytosol More energy per gram than any other food. |
|
|
Oxidation
|
attachment of Oxygen or increase bonds to Oxygen.
Remove H's, loose e- OIL RIG LEO GIR |
|
|
Reduction
|
Remove Oxygen or decrease bonds to Oxygen.
Add H's, gain e- |
|
|
Prokaryote Polymerases
|
3 types of DNApol
DNApol III: fast 5'-3' replication, 3'-5' exonuclease (proof reading) DNApol II: unknown DNApol I: slower, 5'-3' exonuclease to remove primer single RNApol for transcription |
|
|
Eukaryote Polymerases
|
single DNApol
RNApol I: rRNA RNApol II: mRNA RNApol III: tRNA |
|
|
lac Operon (prokaryotes regulation of transcription)
|
Absence of lactose: repressor binds to operator, preventing production of catabolic enzymes wich would break down lactose for energy
Presence of lactose: lactose binds to repressor, pulling it off operator thereby allowing transcription and production of catabolic enzymes |
|
|
Tryp Operon
|
opposite to lac operon.
in presence of excess tryptophan, enzyme transcription is prevented |
|
|
Prokaryotes
|
no membrane bond organelles
has nucleoid which has no membrane. 1 ds circular DNA translation occurs before transcription is complete |
|
|
Gram-negative
|
Stains red.
thicker, outer layer |
|
|
Fungus
|
mushrooms: multi-celled
yeast: uni-cellular chitin in cell wall asexual or sexual |
|
|
Telomeres
|
In Eukaryotes
extended portions of DNA. each replication cycle part of the end is lost. Involved in aging. |
|
|
Simple Diffusion (passive transport)
|
easily pass thru membrane e.g. steroid
or glucose in RBC. don't need help from protein channels |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion (passive transport)
|
Integral membrane protein channels: very selective e.g. voltage or ligand-gated
Carriers: uniport, symport, anti-port |
|
|
Primary Active Transport (active = against gradient)
|
coupled to ATP hydrolysis e.g. NaK ATPase.
3Na+ out, 2K+ in (since life evolved from ocean Na+Cl- is high outside the cell) |
|
|
Secondary Active Transport
|
indirectly coupled to ATP.
e.g. ATPase pump is used to create Na+ gradient, then glucose is pumped against its gradient |
|
|
Signal Transduction
|
converts chemical into cellular response.
ligand binds to receptor....then can create cascade of events |
|
|
G-protein coupled receptor
|
e.g. epinephrine binds to receptor, GDP > GTP, alpha subunit releases, adenyl cyclase > cAMP (second messenger)
|
|
|
Meiosis I
|
Prophase I: longest step, homologous chromosomes (2n) pair up (XX), recombination occurs
Metaphase I: tetrads align in middle Anaphase I: homologs separate, X on each side Telophase I: considered haploid (n) still have replicated sister chromatids (46 total copies) |
|
|
Meiosis II
|
movement of chromosomes as in Mitosis.
end up with 4 gametes (n) |
|
|
Non-disjunction
|
homologous chromosomes fail to separate in Meiosis I (2 cells, 1 w/ 4 copies, other with Zero)
or sister chromatids fail to separate in Meiosis II |
|
|
Hardy-Weinberg
|
p + q = 1
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 |
|
|
Human Taxonomy
|
Dear King Philip Came Over For Green Soup
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Mammalia, Primates, Hominidae |
|
|
Sympathetic (Autonomic PNS)
|
increase heart rate, increase BP
increase blood to muscles, decrease to digestion Pupil Dilation increase glucose by breaking down glycogen |
|
|
Myopia (nearsightedness)
|
too much curve in lense or long eye-ball, focal length is shorter
corrected with divergent lense |
|
|
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
|
lens is too flat or short eye-ball, focal length goes passed eye-ball.
corrected with converging lens |
|
|
Ear
|
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
Cochlea: detects sound Semi-circular canal: detects orientation and movement |
|
|
Vagus Nerve
|
decreases HR
increase GI activity - parasympathetic |
|
|
Chirality of amino acids and sugars
|
amino acids: L
sugars: D |
|
|
Glucose anomers
|
alpha: OH group is opposite of methyl
beta: OH group is on same side as methyl humans can only metabolize alpha. cellulose has beta linkages. |
|
|
amphipathic
|
e.g. phospholipid
hydrophilic (polar) on one side and hyrdophobic (non-polar) on the other side |
|
|
Michaelis constant
|
Km = 1/2Vmax
enzyme saturation kinetics |
|
|
zymogen
|
inactive form of enzyme.
once cleaved, become irreversibly activated. |
|
|
substrate level phosphorylation
|
formation of ATP from ADP and Pi using energy from highly favorable rxn
occurs in cytoplasm - glycolysiss also in mitochondra - Krebs cycle |
|
|
Fermentation
|
recycles NADH to NAD+
|
|
|
transposons
|
section of DNA that can excise itself from chromosome and reinsert itself
|
|
|
Crossing over > Genetic Recombination
|
homologous chromosomes form tetrad, after (if) they cross over its called a chiasma
|
|
|
Viral Life Cycles
|
lytic: virus takes over cell, reproduces inside cell than eventually causes the cell to lyse (burst)...*virulent virus*
lysogenic: virus incorporates its genes into hosts. (HIV, reverse transcribes RNA to DNA then incorporates into cell) *temperate virus* becomes dormant or latent called provirus/prophage/lysogen. Becomes virulent after stress e.g. herpes simplex virus |
|
|
+ strand RNA
|
unenveloped RNA. + means proteins can be directly translated from RNA.
e.g. common cold, HIV |
|
|
- strand RNA
|
must be transcribed to +RNA before translation can occur.
e.g. measles, rabies, flu |
|
|
Bacteriophage
|
virus targeted to bacteria
capsid/head, tail, tail fiber |
|
|
3 major shapes of bacteria
|
cocci: round
bacilli: rod spirilla/spirochetes: spiral |
|
|
Bacteria Nutrition
|
troph = eat
Carbon auto: CO2 hetero: organic e.g. glucose Energy chemo: chemical photo: light |
|
|
Tonicity
|
measure of osmotic pressure (water) and defined by the SOLUTION. solutes can't cross the membrane
hypertonic: solution has higher conc. of solutes, therefore water goes down conc. gradient, cell shrivels isotonic: iso = same hypotonic: lower conc. of solutes in solution, therefore water goes into cell, cell bursts |
|
|
vertical sagittal plane
|
divides body cavity into right and left portions
|
|
|
Eukaryotic organelles
|
rER: (r = ribosomes) translate proteins that will be exported, pushed into ER lumen
Golgi: receive proteins from rER lumen to process them, glycosylate etc. lysosomes: come from golgi, hydrolyze endocytic stuff, can rupture to cause autolysis sER: synthesize and store fats |
|
|
Microtubules
|
(contain tubulin) larger than microfilaments. e.g. flagella, cilia, spindle apparatus
cilia: fallopian tubes, respiratory tract MTOC (microtubule organizing center), centrosome, centriole |
|
|
Microfilaments
|
(contain actin) squeeze membrane in phagocytosis and cytokinesis
contraction in microvilli, muscle |
|
|
Flagella and cilia
|
9 + 2 microtubules in eukaryotes
axoneme is the major portion dynein connects microtubules |
|
|
Cellular Junctions
|
tight junctions: watertight fluid barrier, e.g. kidney, intestines, bladder....waste materials can't escape into the body
desmosome: attach two cells at single point, e.g. skin gap junction: small tunnels connecting cells, e.g. cardiac muscle....spread action potential from cell to cell |
|
|
Hypothalamus hormones
|
Releasing hormones for the pituitary
PACTOGG PRH = Prolactin Releasing Hormone. ADH = Antidiuretic Hormone = Vasopressin, increase water reabsorption in kidney = conserve water, increase blood pressure. CRF = Corticotropin Releasing Factor. TRH = Thyroid Releasing Hormone. Oxytocin = stimulates uterine contractions during labor, also milk secretion during suckling. GnRH = Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone, stimulates pituitary to release FSH and LH. GHRH = Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone. Posterior Pituitary: Oxytocin, ADH |
|
|
Pituitary hormones
|
FLAT PiG
FSH = Follicle Stimulating Hormone, Stimulate ovary follicles to mature, testis to produce sperm. LH = Luteinizing Hormone, LH surge triggers ovulation, stimulates testis to produce testosterone. ACTH = AdrenoCorticoTropic Hormone, Stimulates adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. TSH = Thyroid Stimulation Hormone = Stimulate thyroid to release thyroid hormones. PRL = Prolactin, Stimulates breast to produce milk. GH = Growth Hormone, Stimulates growth of muscle, bone, burns fat. |
|
|
Endocrine Gland products:
Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Gonads |
Adrenals: steroids, glucocorticoid - cortisol. mineral corticoid - aldosterone.
(tyrosine derivatives - catecholamines -- epi and norepinephrine) Pancreas: insulin, glucagon Thyroid: (tyrosine derivatives) T3, T4, parathyroid Gonads: testosterone, estrogen, progesterone |
|
|
oxidative phosphorylation
|
process in ETC that produces ATP, oxidizes NADH
|

