![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
470 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
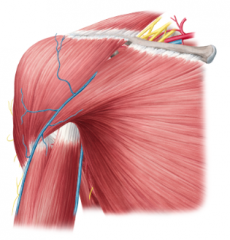
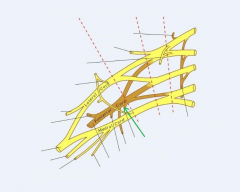
Shoulder Girdle:
Girdle - from circle: the shoulder (pectoral) girdle is an incomplete circle including the scapula and clavicle bones. Here, we can see the cephalic vein in the deltopectoral groove, as well as the basilic vein on the medial side of the arm. Petoralis major and deltoid cover the anterior surface superficially; biceps brachii is visible on the anterior surface of the arm. |
Shoulder Girdle
|
|
|
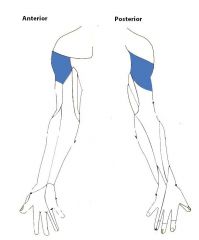
Axillary Nerve:
A branch from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from C5, c6. Sensory Innervation: "Regimental badge" area Motor Innervation: Teres minor Deltoid (Abductors of arm) Passes through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery. Injury to the Axillary Nerve: Anterior dislocation of the humerus at the glenohumeral joint, or a fracture of the humerus at the surgical neck. Motor deficit: paralysis of deltoid and teres minor - inability to abduct arm. In long-standing cases, the paralysed deltoid rapidly atrophies, and the greater tubercle can be palpated in that area. |
Axillary Nerve
|
|
|
Dorsal Scapular Nerve:
A supraclavicular branch from the C5 root of the brachial plexus. Motor Innervation: Levator scapulae Rhomboid minor Rhomboid major |
Dorsal Scapular Nerve
|
|
|
Lateral Pectoral Nerve:
A branch from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c5, C6 and c7 Motor Innervation: Pectoralis major's clavicular head |
Lateral Pectoral Nerve
|
|
|
Long Thoracic Nerve [of Bell]:
A supraclavicular branch from the C5, C6 and c7 [Bells of heaven] roots of the brachial plexus. Motor Innervation: Serratus anterior Injury to the Long Thoracic Nerve: Since the serratus anterior's function is to hold the scapula against the thoracic wall, injury to the long thoracic nerve will result in "winging" of the scapula. |
Long Thoracic Nerve [of Bell]
|
|
|
Lower Subscapular Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with a contribution from C6. Motor Innervation: Subscapularis (lower fibres) Teres major |
Lower Subscapular Nerve
|
|
|
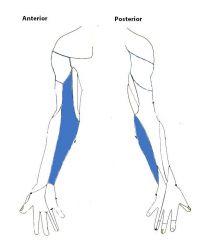
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c8, t1 Sensory Innervation: Medial half of the forearm, with a greater influence on the anterior surface - here, it innervates skin higher up, towards the axilla. |
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
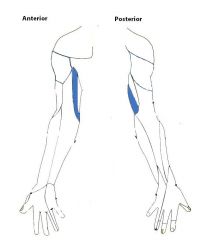
Medial Brachial Cutaneous Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c8, t1. Sensory Innervation: A thin strip of skin just superior to the dermatome of the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve, on the medial surface of the arm. |
Medial Brachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
Medial Pectoral Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch from the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c8, t1. Motor Innervation: Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor |
Medial Pectoral Nerve
|
|
|
Median Nerve:
A terminal branch of the brachial plexus, with contributions from the lateral (c6, c6) and medial (c8, t1) cords of the brachial plexus. Sensory Innervation: Anterior surface and posterior tips of the first three-and-a-half digits. Motor Innervation - Anterior Forearm: Flexor forearms: Palmaris longus Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor digitorum profundus (lateral half) Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Hand: (Meat LOAF - Median) Thenar muscles: Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Intermediate Volar: Lumbrical I Lumbrical II Injury to Median Nerve: Since the median nerve travels through the carpal tunnel (formed by the flexor retinaculum bridging the hamate and pisiform to the scaphoid and trapexium), injury may occur as a result of compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel (carpal tunnel syndrome). |
Median Nerve
Meat LOAF |
|
|
Musculocutaneous Nerve:
A terminal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, with contributionsfrom c5, c6, c7. Sensory Innervation: Lateral half of the forearm, with a greater influence on the anterior surface of the forearm. Motor Innervation - Anterior Arm: Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii Brachialis |
Musculocutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
Radial Nerve:
A terminal branch of the brachial plexus, formed by the continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c5 - t1 Sensory Innervation: A long, thin strip of skin immediately inferolateral to the "Regimental badge" area, travelling down the centre of the posterior surface of the forearm. Also includes the dorsal surface of the first three-and-a-half digits, excluding the tips. Motor Innervation - Posterior Arm and Posterior Forearm: Extensor Arm: Triceps brachii Anconeus Flexor Arm: Brachioradialis Extensor Forearm: Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Supinator Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis longus Extensor indicis The radial nerve travels through the lower triangular space with the deep brachial artery. They both travel in the radial sulcus, close to the surface of the humerus. Injury to the Radial Nerve: A mid-shaft fracture of the humerus may damage the radial nerve, causing "wrist-drop". |
Radial Nerve
|
|
|
Subclavian Nerve:
A supraclavicular branch of the superior trunk of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c5, C6 and c7. Motor Innervation: Subclavius |
Subclavian Nerve
|
|
|
Suprascapular Nerve:
A supraclavicular branch of the superior trunk of the brachial plexus, with contributions from C5 and c6. Motor Innervation: Supraspinatus Infraspinatus The suprascapular nerve travels through the foramen created by the superior transverse scapular ligament and the suprascapular notch, innervates supraspinatus, then travels to infraspinatus via the spinoglenoid notch. Injury to the Suprascapular Nerve: Ossification of the superior transverse scapular ligament may cause compressive damage to the suprascapular nerve, paralysing supraspinatus and infraspinatus. |
Suprascapular Nerve
|
|
|
Thoracodorsal Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c6, C7, c8. Motor Innervation: Latissimus dorsi |
Thoracodorsal Nerve
|
|
|
Ulnar Nerve:
A terminal branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c8, t1 Sensory Innervation: Final one-and-a-half digits of the hand. Motor Innervation - Hand muscles: Medial Volar: Palmaris brevis Hypothenar muscles: Abductor digiti minimi of the hand Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Intermediate Volar: Palmar interossei Dorsal interossei Lumbrical III Lumbrical IV Lateral Volar: Adductor pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis (deep head) Flexor forearms: Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum profundus (medial half) Injury to the Ulnar Nerve: Entrapment, e.g. by cubital tunnel syndrome causes tingling in the last one-and-a-half digits, and in severe cases can present as ulnar claw. |
Ulnar Nerve
AbOF |
|
|
Upper Subscapular Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with a contribution from C5. Motor Innervation: Subscapularis (upper fibres) |
Upper Subscapular Nerve
|
|
|
Axillary Nerve
|
Axillary Nerve
|
|
|
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
Medial Brachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
Medial Brachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
Median Nerve
|
Median Nerve
|
|
|
Musculocutaneous Nerve
|
Musculocutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
Radial Nerve
|
Radial Nerve
|
|
|
Ulnar Nerve
|
Ulnar Nerve
|
|
|
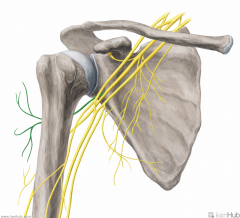
Axillary Nerve:
A branch from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from C5, c6. Sensory Innervation: "Regimental badge" area Motor Innervation: Teres minor Deltoid (Abductors of arm) Passes through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery. Injury to the Axillary Nerve: Anterior dislocation of the humerus at the glenohumeral joint, or a fracture of the humerus at the surgical neck. Motor deficit: paralysis of deltoid and teres minor - inability to abduct arm. In long-standing cases, the paralysed deltoid rapidly atrophies, and the greater tubercle can be palpated in that area. |
Axillary Nerve
|
|
|
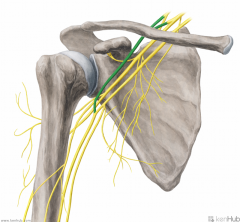
Lateral Cord:
A cord formed by the convergence of the anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunks of the brachial plexus. Gives rise to the lateral pectoral nerve and musculocutaneous nerves. Contributes to the median nerve. |
Lateral Cord
|
|
|
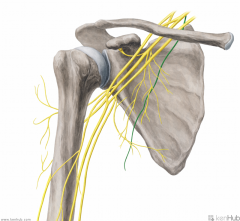
Long Thoracic Nerve [of Bell]:
A supraclavicular branch from the C5, C6 and c7 [Bells of heaven] roots of the brachial plexus. Motor Innervation: Serratus anterior Injury to the Long Thoracic Nerve: Since the serratus anterior's function is to hold the scapula against the thoracic wall, injury to the long thoracic nerve will result in "winging" of the scapula. |
Long Thoracic Nerve [of Bell]
|
|
|
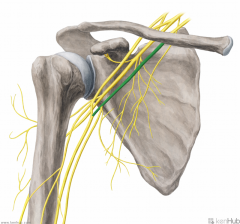
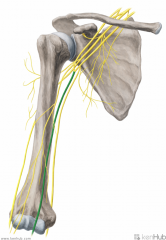
Medial Cord:
A cord of the brachial plexus formed by the continuation of the anterior division of the inferior trunk. Gives rise to the medial pectoral, medial brachial cutaneous, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerves and ulnar nerves. Contributes to the median nerve. |
Medial Cord
|
|
|
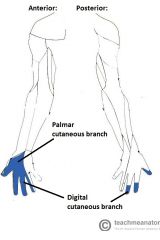
Median Nerve:
A terminal branch of the brachial plexus, with contributions from the lateral (c6, c6) and medial (c8, t1) cords of the brachial plexus. Sensory Innervation: Anterior surface and posterior tips of the first three-and-a-half digits. Motor Innervation - Anterior Forearm: Flexor forearms: Palmaris longus Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor digitorum profundus (lateral half) Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Hand: (Meat LOAF - Median) Thenar muscles: Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Intermediate Volar: Lumbrical I Lumbrical II Injury to Median Nerve: Since the median nerve travels through the carpal tunnel (formed by the flexor retinaculum bridging the hamate and pisiform to the scaphoid and trapexium), injury may occur as a result of compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel (carpal tunnel syndrome). |
Median Nerve
Meat LOAF |
|
|
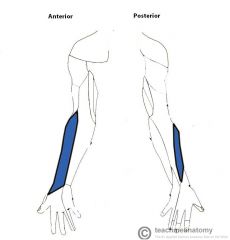
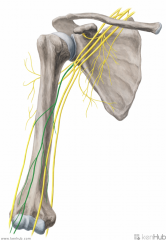
Musculocutaneous Nerve:
A terminal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, with contributionsfrom c5, c6, c7. Sensory Innervation: Lateral half of the forearm, with a greater influence on the anterior surface of the forearm. Motor Innervation - Anterior Arm: Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii Brachialis |
Musculocutaneous Nerve
|
|
|
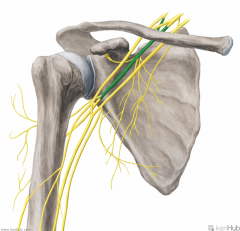
Posterior Cord:
A cord of the brachial plexus formed by the convergence of the posterior divisions of the superior, middle and inferior trunks of the brachial plexus. Gives rise to the upper subscapular, thoracodorsal, lower subscapular and axillary nerves. Continues to become the radial nerve. |
Posterior Cord
|
|
|
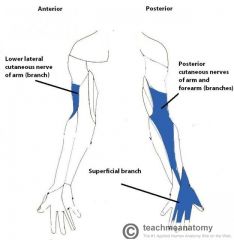
Radial Nerve:
A terminal branch of the brachial plexus, formed by the continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c5 - t1 Sensory Innervation: A long, thin strip of skin immediately inferolateral to the "Regimental badge" area, travelling down the centre of the posterior surface of the forearm. Also includes the dorsal surface of the first three-and-a-half digits, excluding the tips. Motor Innervation - Posterior Arm and Posterior Forearm: Extensor Arm: Triceps brachii Anconeus Flexor Arm: Brachioradialis Extensor Forearm: Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Supinator Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis longus Extensor indicis The radial nerve travels through the lower triangular space with the deep brachial artery. They both travel in the radial sulcus, close to the surface of the humerus. Injury to the Radial Nerve: A mid-shaft fracture of the humerus may damage the radial nerve, causing "wrist-drop". |
Radial Nerve
|
|
|
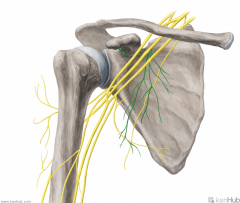
Subscapular Nerve:
(Upper and Lower Subscapular Nerves combined) Infraclavicular branches of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from C5, C6. Motor Innervation: Subscapularis (upper fibres) Subscapularis (lower fibres) Teres major |
Subscapular Nerve
|
|
|
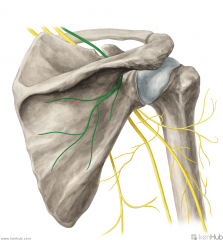
Suprascapular Nerve:
A supraclavicular branch of the superior trunk of the brachial plexus, with contributions from C5 and c6. Motor Innervation: Supraspinatus Infraspinatus The suprascapular nerve travels through the foramen created by the superior transverse scapular ligament and the suprascapular notch, innervates supraspinatus, then travels to infraspinatus via the spinoglenoid notch. Injury to the Suprascapular Nerve: Ossification of the superior transverse scapular ligament may cause compressive damage to the suprascapular nerve, paralysing supraspinatus and infraspinatus. |
Suprascapular Nerve
|
|
|
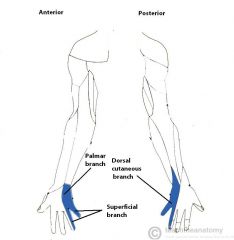
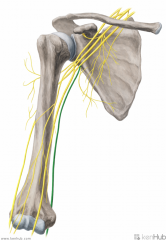
Ulnar Nerve:
A terminal branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c8, t1 Sensory Innervation: Final one-and-a-half digits of the hand. Motor Innervation - Hand muscles: Medial Volar: Palmaris brevis Hypothenar muscles: Abductor digiti minimi of the hand Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Intermediate Volar: Palmar interossei Dorsal interossei Lumbrical III Lumbrical IV Lateral Volar: Adductor pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis (deep head) Flexor forearms: Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum profundus (medial half) Injury to the Ulnar Nerve: Entrapment, e.g. by cubital tunnel syndrome causes tingling in the last one-and-a-half digits, and in severe cases can present as ulnar claw. |
Ulnar Nerve
AbOF |
|
|
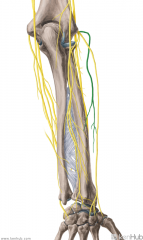
Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve:
The continuation of the musculocutaneous nerve which supplies sensor innervation to the lateral half of the forearm, with a greater influence on the anterior surface of the forearm. |
Lateral Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
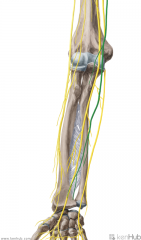
|
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve:
An infraclavicular branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus, with contributions from c8, t1 Sensory Innervation: Medial half of the forearm, with a greater influence on the anterior surface - here, it innervates skin higher up, towards the axilla. |
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
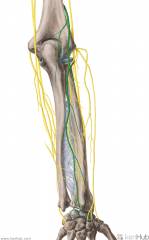
|
Posterior Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve:
The branch of the radial nerve which supplies sensory innervation to the long, thin strip of skin immediately inferolateral to the "Regimental badge" area, travelling down the centre of the posterior surface of the forearm. |
Posterior Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve
|
|
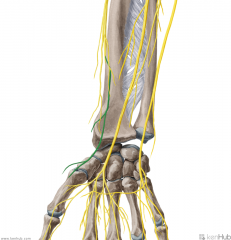
|
Superficial Branch of the Radial Nerve:
The branch of the radial nerve which supplies sensory innervation to the dorsal surface of the first three-and-a-half digits, excluding the tips. |
Superficial Branch of the Radial Nerve
|
|
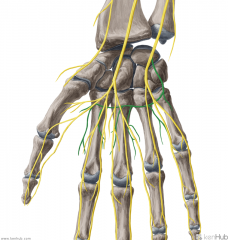
|
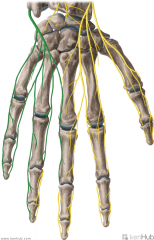
Deep Branch of the Ulnar Nerve:
The terminal (motor) branch of the ulnar nerve, accompanied by the deep palmar branch of the ulnar artery. Motor Innervation: Hypothenar muscles: Abductor digiti minimi of the hand Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Intermediate Volar: Palmar interossei Dorsal interossei Lumbrical III Lumbrical IV Lateral Volar: Adductor pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis (deep head) |
Deep Branch of the Ulnar Nerve
|
|
|
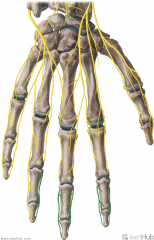
Dorsal Branch of the Ulnar Nerve:
The branch of the ulnar nerve which supplies sensory innervation to the final one-and-a-half digits of the hand. |
Dorsal Branch of the Ulnar Nerve
|
|
|
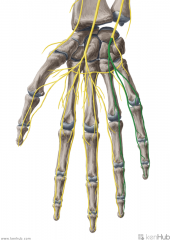
Proper Palmar Digital Nerves of the Median Nerve:
A continuation of the common palmar nerves of the median nerve. Sensory Innervation: Tips of the second, third and lateral half of the fourth digit. Motor Innervation: Lumbrical I |
Proper Palmar Digital Nerves of the Median Nerve
|
|
|
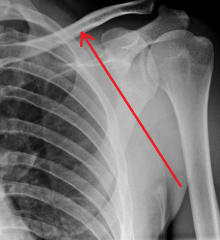
Superficial Branch of the Ulnar Nerve:
A terminal branch of the ulnar nerve. Sensory Innervation: Skin on the medial side of the hand. Motor Innervation: Palmaris brevis The nerve then divides into a common palmar digital nerve and a proper palmar digital nerve. |
Superficial Branch of the Ulnar Nerve
|
|
|
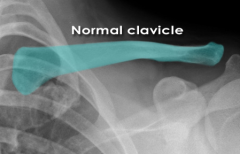
|
Normal Clavicle
|
|
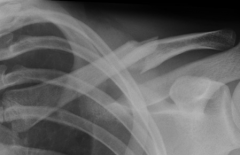
|
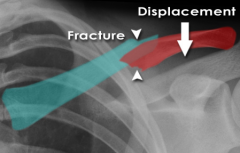
|
Fractured Clavicle
|
|
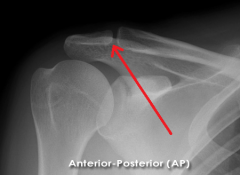
|
|
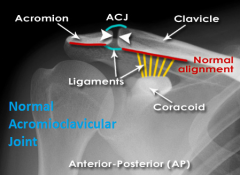
Normal Acromioclavicular Joint
|
|
|
|
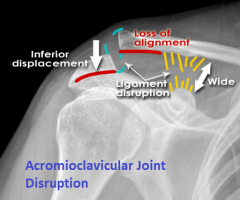
Acromioclavicular Joint Disruption
|
|
|
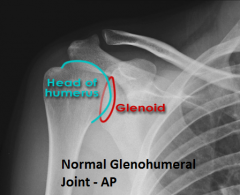
|
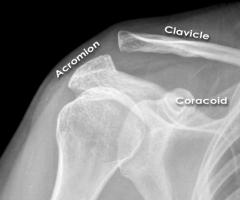
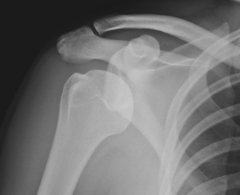
Normal Glenohumeral Joint, AP view
|
|
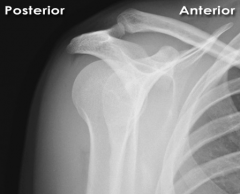
|
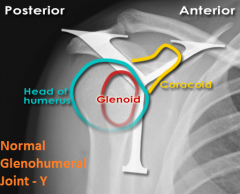
|
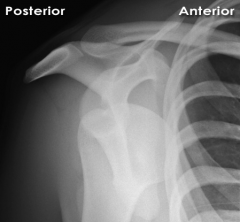
Normal Glenohumeral Joint, Y view
|
|
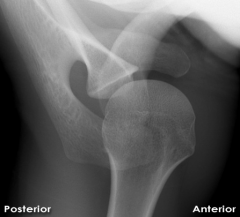
|
|
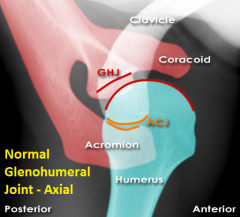
Normal Glenohumeral Joint, Axial view
|
|
|
|
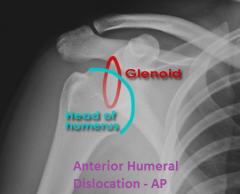
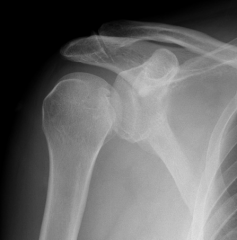
Anterior Dislocation of Humerus, AP view
|
|
|
|
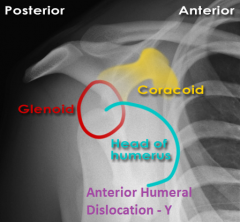
Anterior Dislocation of Humerus, Y view
|
|
|
|
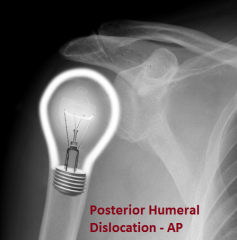
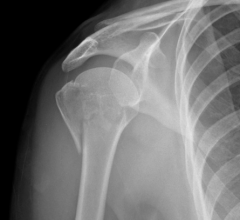
Posterior Dislocation of Humerus, AP view
|
|
|
|
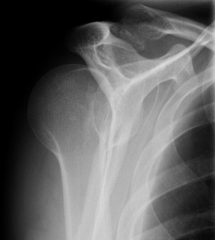
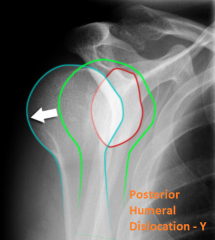
Posterior Dislocation of the Humerus, Y view
|
|
|
|
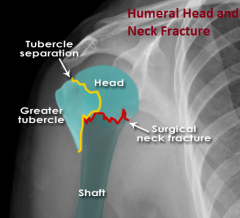
Head and Neck Fracture of the Humerus
|
|
|
|
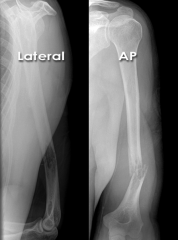
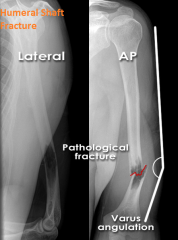
Humerus Shaft Fracture
|
|
|
|
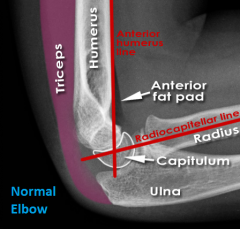
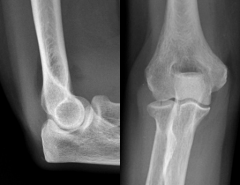
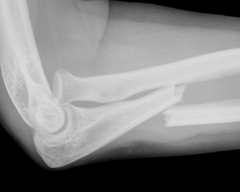
Normal Elbow
|
|
|
|
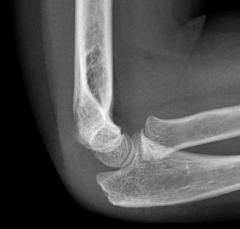
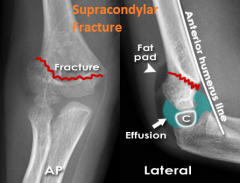
Supracondylar Fracture
|
|
|
|
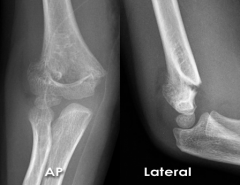
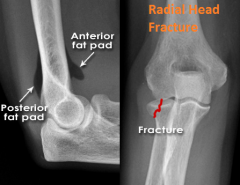
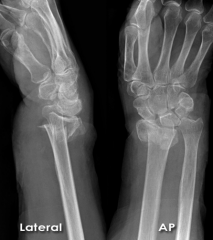
Radial Head Fracture
|
|
|
|
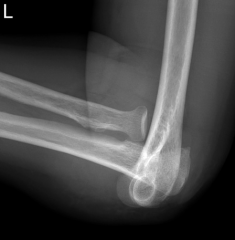
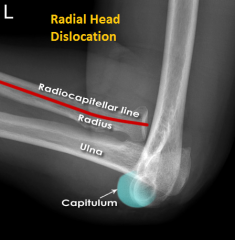
Radial Head Dislocation
|
|
|
|
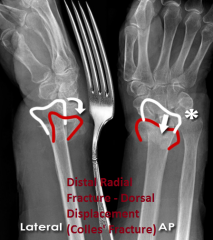
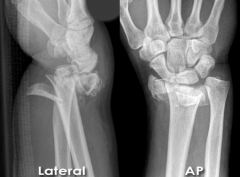
Distal Radius Fracture - Dorsal Displacement (Colles' Fracture)
|
|
|
|
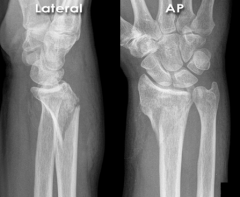
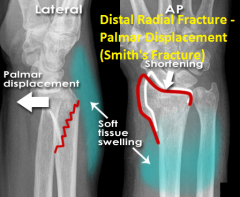
Distal Radius Fracture - Palmar Displacement (Smith's Fracture)
|
|
|
|
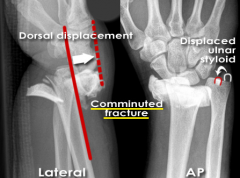
Distal Radius Fracture - Comminuted
|
|
|
|
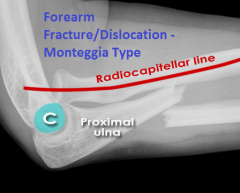
Forearm Fracture/Dislocation - Monteggia Type
|
|
|
|
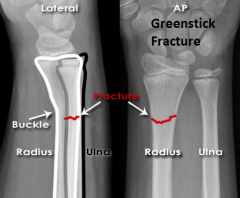
Greenstick Fracture
|
|
|
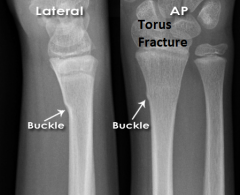
|
Torus Fracture
|
|
|
|
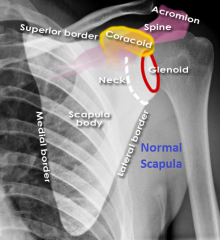
Normal Scapula
|
|
|
|
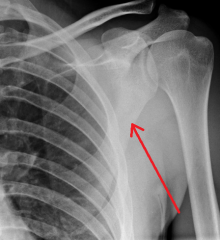
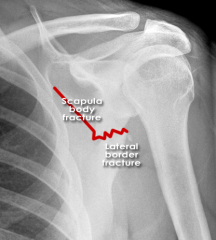
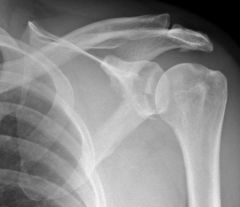
Fractured Scapula
|
|
|
|
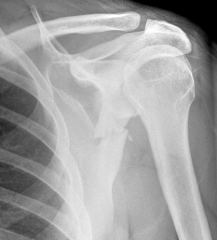
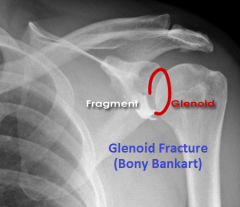
Glenoid Fracture (Bony Bankart)
|
|
|
|
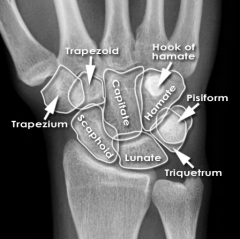
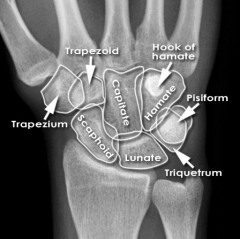
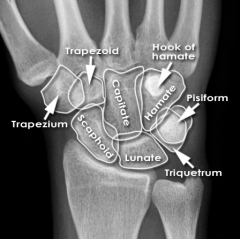
Trapezium
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
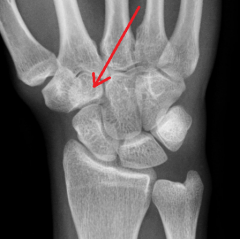
|
|
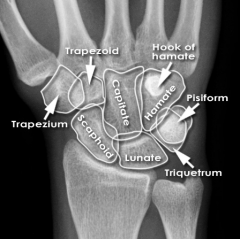
Trapezoid
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
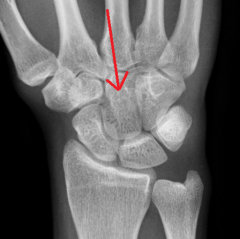
|
|
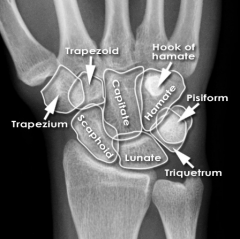
Capitate
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
|
|
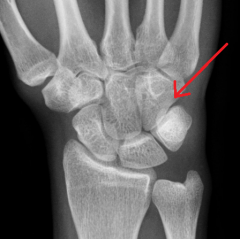
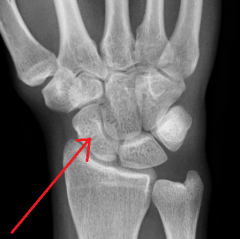
Hamate
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
|
|
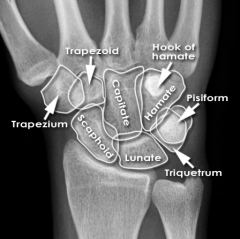
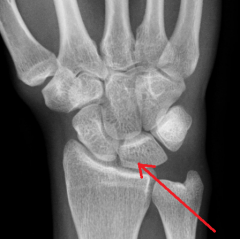
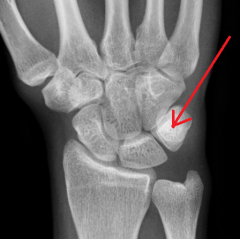
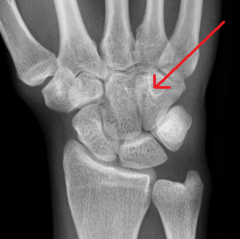
Scaphoid
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
|
|
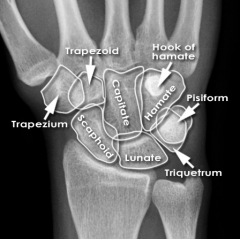
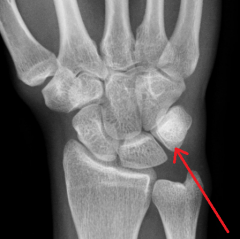
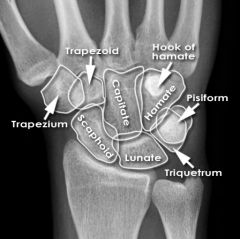
Lunate
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
|
|
Triquetrum
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
|
|
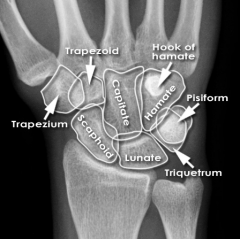
Pisiform
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate |
|
|
|
Hook of Hamate
|
|
|
|
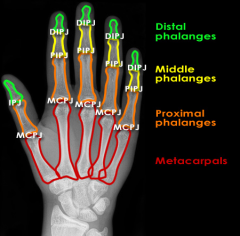
Metacarpals and Phalanges
|
|
|
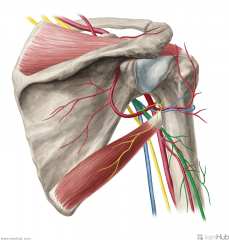
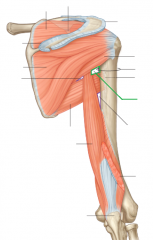
Upper Triangular Space (Triangular Space):
Boundaries: Superior: Teres minor Inferior: Teres major Lateral: Triceps brachii's long head Contents: Circumflex scapular artery |
Upper Triangular Space (Triangular Space)
|
|
|
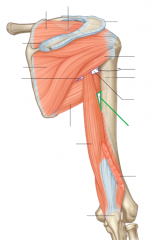
Quadrangular Space:
Boundaries: Superior: Teres minor Inferior: Teres major Lateral: Humerus' surgical neck Medial: Triceps brachii's long head Contents: Axillary nerve Posterior circumflex humeral artery |
Quadrangular Space
|
|
|
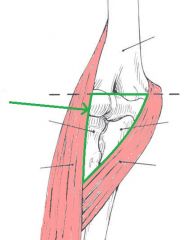
Lower Triangular Space (Triangular Interval):
Borders: Superior: Teres major Lateral: Humerus Medial: Triceps brachii's long head Contents: Radial nerve Deep brachial artery |
Lower Triangular Space (Triangular Interval)
|
|
|
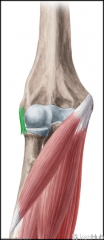
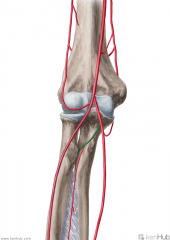
Cubital Fossa (Antecubital Fossa):
Boundaries: Superior: The imaginary line joining the medial and lateral epicondyles Lateral: Brachioradialis Medial: Pronator Teres Contents: Biceps brachii tendon Median nerve Brachial artery, which bifurcates near the apex into the radial artery (superficial), and ulnar artery (deeper). Superficial to the cubital fossa: Cephalic vein runs laterally. Basilic vein runs medially. Median cubital vein runs between the two - a common site of venepuncture. |
Cubital Fossa (Antecubital Fossa)
|
|

|
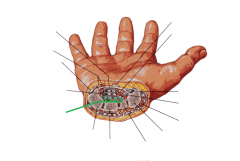
Anatomical Snuffbox:
Borders: Posterior/medial: Extensor pollicis longus Posterolateral: Extensor pollicis brevis Lateral: Abductor pollicis longus Floor: Scaphoid (and Trapezuim) Contents: Radial artery travels along the floor of the anatomical snuffbox, over the scaphoid. |
Anatomical Snuffbox
|
|
|
Carpal Tunnel:
Flexor digitorum profundus tendons |
Carpal Tunnel
|
|
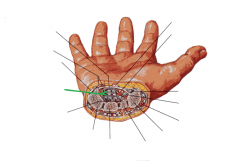
|
Carpal Tunnel:
Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons |
Carpal Tunnel
|
|
|
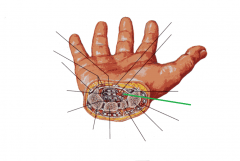
Carpal Tunnel:
Flexor pollicis longus tendons |
Carpal Tunnel
|
|
|
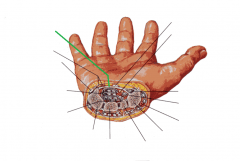
Carpal Tunnel:
Flexor retinaculum |
Carpal Tunnel
|
|
|
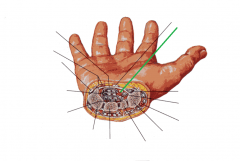
Carpal Tunnel:
Median nerve |
Carpal Tunnel
|
|
|
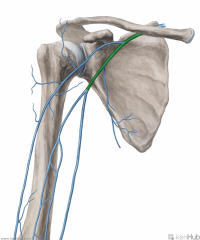
Axillary Vein:
Source: Cephalic vein Basilic vein Brachial veins Drains to: Subclavian vein Complementary Artery: Axillary Artery |
Axillary Vein
|
|
|
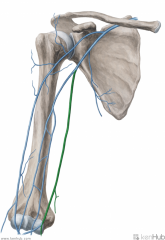
Basilic Vein:
Source: Dorsal venous network of the hand Drains to: Axillary vein |
Basilic vein
|
|
|
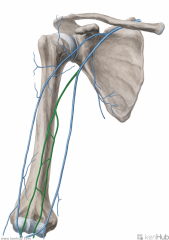
Brachial Vein:
Source: Radial veins Ulnar veins Drains to: Axillary vein Complementary Artery: Brachial artery |
Brachial Vein
|
|
|
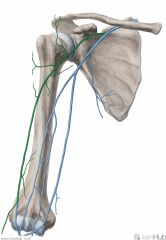
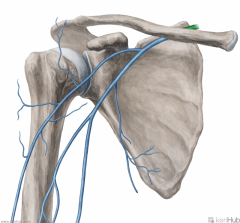
Cephalic Vein (of the arm):
Source: Cephalic vein of the forearm Drains to: Axillary vein Complementary Artery: Thoracoacromial artery's deltoid branch Course: Travels between the deltoid and pectoralis major, in the deltopectoral groove |
Cephalic Vein (of the arm)
|
|
|
Subclavian Vein:
Source: Axillary vein External jugular vein Drains to: Brachiocephalic vein Complementary Artery: Subclavian Artery |
Subclavian Vein
|
|
|
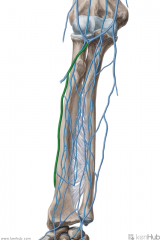
Cephalic Vein of the Forearm:
Source: Dorsal venous network of the hand Drains to: Cephalic vein (of the arm) Median cubital vein |
Cephalic Vein of the Forearm
|
|
|
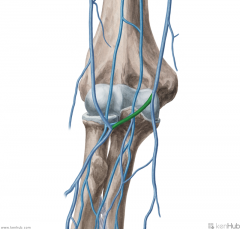
Median Cubital Vein:
Source: Cephalic vein of the forearm Drains to: Basilic vein |
Median Cubital Vein
|
|
|
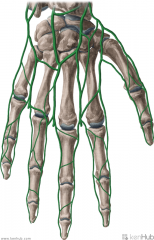
Dorsal Venous Network of the Hand:
Source: Dorsal metacarpal veins Drains to: Cephalic vein of the forearm Basilic vein |
Dorsal Venous Network of the Hand
|
|
|
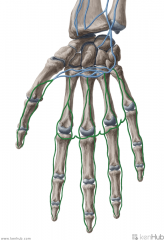
Palmar Metacarpal and Digital Veins:
Source: Metacarpal and Digital regions of the hand Drains to: Deep palmar venous arch (venae comitantes) Superficial palmar venous arch (venae comitantes) Complementary Artery: Deep metacarpal arteries Palmar digital arteries |
Palmar Metacarpal and Digital Veins
|
|
|
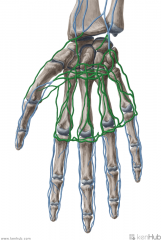
Superficial and Deep Palmar Venous Arches:
Venae comitantes which accompany the superficial and deep palmar arches Source: Palmar digital veins Palmar metacarpal veins Drains to: Ulnar vein Complementary arteries: Superficial palmar arch Deep palmar arch |
Superficial and Deep Palmar Venous Arches
|
|
|
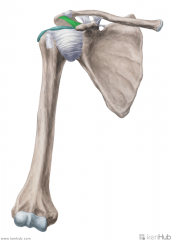
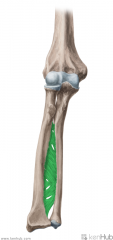
Annular Ligament of the Radius:
(Annular: ring-shaped) Attachments: Anterior margin of the radial notch on the ulna Posterior margin of the radial notch on the ulna Function: Embraces the head of the radius, preventing distal displacement of the radius. Allows the head of the radius to rotate on its axis during supination and pronation. |
Annular Ligament of the Radius
|
|
|
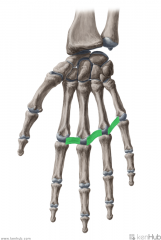
Annular Ligaments of the Hand:
(Annular: ring-shaped) Attachments: Metacarpal and Carpal bones Function: Form the annular parts of the fibrous sheaths of the fingers. The form ring-shaped tunnels for the tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus to travel through. |
Annular Ligaments of the Hand
|
|
|
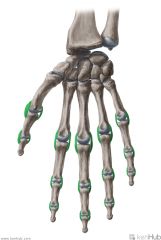
Collateral Ligaments of the Hand:
Attachments: Either: successive phalanges of the fingers Or: One metacarpal and one phalanx of the fingers Function: Stabilise the interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints in flexion, allowing spreading of the fingers in extension, but not in flexion. |
Collateral Ligaments of the Hand
|
|
|
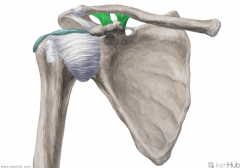
Coracoacromial Ligament:
Attachments: Superolateral surface of the coracoid process Summit (lateral margin) of the acromion Function: Protects the head of the humerus. |
Coracoacromial Ligament
|
|
|
Coracoclavicular Ligaments:
Attachments: The conoid ligament attaches to the conoid tubercle. It is the medial part of the coracoclavicular ligament. The trapezoid ligament attaches to the trapezoid line. It is the lateral part of the coracoclavicular ligament. Function: The conoid ligament limits anterior movement of the scapula with respect to the clavicle. The trapezoid ligament limits posterior movement between these two bones. Both ligaments prevent the clavicle from overriding the lateral end of the clavicle. |
Coracoclavicular Ligaments
|
|
|
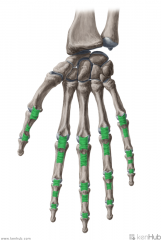
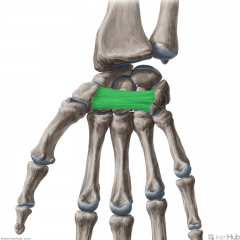
Deep Transverse Metacarpal Ligaments:
Attachments: Palmar surface of the heads of metacarpals II to V Function: Runs across the palmar surfaces of the heads of metacarpals II to V, connecting them together. The palmar surface is concave where the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus pass over it. |
Deep Transverse Metacarpal Ligaments
|
|
|
Flexor Retinaculum:
Attachments: Medially: Hook of Hamate Pisiform Laterally: Scaphoid Trapezium Function: Forms a tunnel with the carpal bones - the carpal tunnel. Flexor tendons and the median nerve travel through the carpal tunnel. Clinical Relevance: Inflammation of one of the tendons in the carpal tunnel may compress the median nerve, causing carpal tunnel syndrome. |
Flexor Retinaculum
|
|
|
Glenohumeral Ligament:
Attachments: Superior: Superior glenoid labrum (12 o'clock position) Superior to lesser tubercle Middle: Superior glenoid labrum, just below the insertion of the superior glenohumeral ligament Medial to lesser tubercle Inferior: Glenoid labrum - 3 o'clock to 9 o'clock positions Inferior part of lesser tubercle Function: Stabilises the head of the humerus during movement of the arm. |
Glenohumeral Ligament:
|
|
|
Interosseous Membrane of the Forearm:
Attachments: Radius' medial margin Ulna's lateral margin Function: Connects the radius and ulna, stabilising the radioulnar joints. Provides a surface for muscular attachment. Muscles Attached: Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicis longus |
Interosseous Membrane of the Forearm
|
|
|
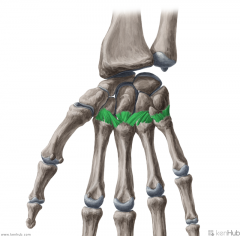
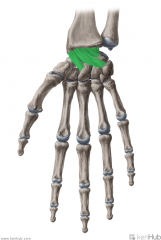
Palmar Carpometacarpal Ligament:
Attachments: Metacarpal II to Trapezium Metacarpal III to Trapezium, Capitate and Hamate Metacarpal IV to Hamate Metacarpal V to Hamate Function: Attaches the palmar surface of the distal carpal bones to metacarpals II to V. |
Palmar Carpometacarpal Ligament
|
|
|
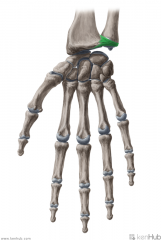
Palmar Radiocarpal Ligament:
Attachments: Radius' distal end Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum Function: Fibres angle across from the distal end of the radius to the medial side of the wrist. The ligament stabilises the wrist joint and limits radial deviation of the wrist. |
Palmar Radiocarpal Ligament
|
|
|
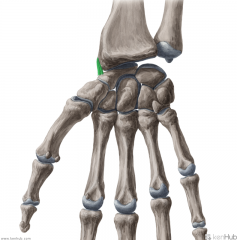
Palmar Radioulnar Ligament:
Attachments: Anterior margin of ulnar notch Anterior margin of the head of the ulnar Function: Stabilises the distal radioulnar joint. |
Palmar Radioulnar Ligament
|
|
|
Radial Collateral Ligament of the Wrist:
Attachments: Tip of the styloid process of the radius Radial surface of the scaphoid Function: Limits ulnar deviation of the wrist. |
Radial Collateral Ligament of the Wrist
|
|
|
Radial Collateral Ligament:
Attachments: Lateral epicondyle Annular ligament of the radius Function: Stabilises the elbow during flexion. Prevents medial flexion and lateral translation of the elbow joint. |
Radial Collateral Ligament
|
|
|
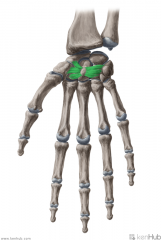
Radiate Carpal Ligaments:
Attachments: Capitate Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetral Function: Stabilises the carpal bones. |
Radiate Carpal Ligaments
|
|
|
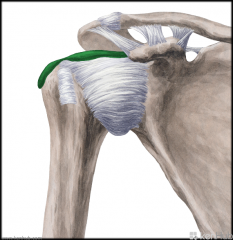
Subacromial-Subdeltoid Bursa (SSB):
Location: Superior to the glenohumeral joint capsule Inferior to the deep surface of the deltoid muscle and coracoacromial arch. Function: Decreases friction and allows free motion of the rotator cuff relative to the coracoacromial arch and the deltoid muscle. |
Subacromial-Subdeltoid Bursa (SSB)
|
|
|
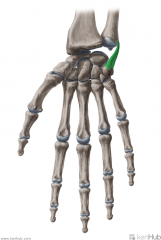
Ulnar Collateral Ligament of the Wrist:
Attachments: Tip of the styloid process of the ulna Pisiform, medial surface of the triquetral Function: Stabilises the medial aspect of the wrist joint. |
Ulnar Collateral Ligament of the Wrist
|
|
|
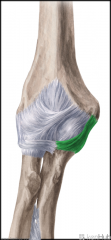
Ulnar Collateral Ligament:
Attachments: Medial epicondyle Coronoid process, olecranon Function: Resists valgus force and supports the ulnohumeral joint. |
Ulnar Collateral Ligament
|
|
|
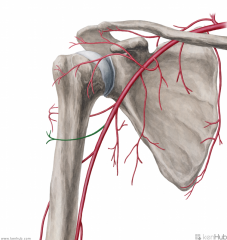
Anterior Circumflex Humeral Artery:
Source: Axillary Artery Branches from the axillary artery's lateral aspect. Course: Runs across the anterior surface of the surgical neck of the humerus Muscles Supplied: (Deltoid) Continuation: Anastomoses with the posterior circumflex humeral artery |
Anterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
|
|
|
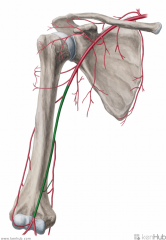
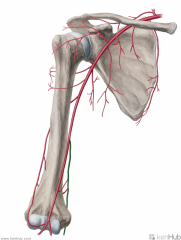
Axillary Artery:
Source: Subclavian Artery Becomes the axillary artery at the lateral margin of the first rib Branches: (from proximal to distal) (Screw The Lawyers Save A Patient) Superior thoracic artery Thoracoacromial artery Lateral thoracic artery Subscapular artery Anterior circumflex humeral artery Posterior circumflex humeral artery Muscles Supplied: Axilla Complementary Vein: Axillary vein Continuation: Brachial artery Once past the inferior border of teres major |
Axillary Artery
Screw The Lawyers Save A Patient |
|
|
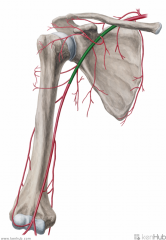
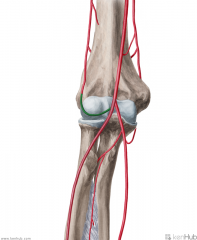
Brachial Artery:
Source: Axillary artery Becomes the brachial artery once past the inferior border of teres major Branches: Deep brachial artery Superior ulnar collateral artery Inferior ulnar collateral artery Muscles Supplied: Biceps brachii Triceps brachii Complementary Vein: Brachial vein(s) - venae comitantes Continuation: Bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries near the apex of the cubital fossa |
Brachial Artery
|
|
|
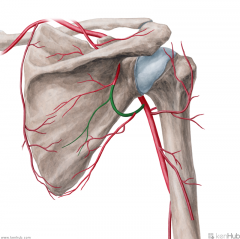
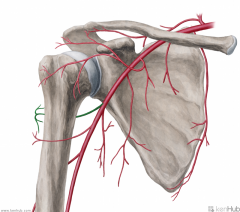
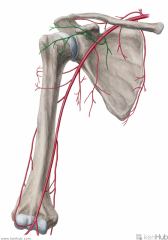
Circumflex Scapular Artery:
Source: Subscapular Artery Branches from the subscapular artery Muscles Supplied: Infraspinatus Teres major Teres minor Course: Travels through the upper triangular space, then runs across the dorsum of the scapula Muscles Supplied: Subscapularis Continuation: Anastomoses with the dorsal scapular artery and the suprapular artery |
Circumflex Scapular Artery
|
|
|
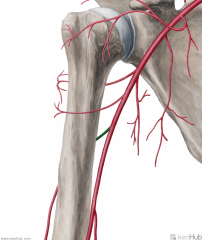
Deep Brachial Artery (Profunda Brachii):
Source: Brachial artery Branches from the brachial artery's posterolateral surface, just below teres minor Course: Closely follows the radial nerve in the radial sulcus of the humerus. Branches: Gives off a branch which anastomoses with the posterior circumflex humeral artery Radial collateral Medial collateral Muscles Supplied: Triceps brachii (Deltoid) Continuation: Anastomoses with the radial recurrent artery |
Deep Brachial Artery (Profunda Brachii)
|
|
|
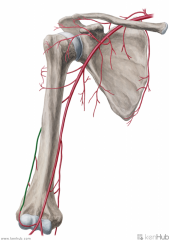
Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery:
Source: Axillary artery Branches from the axillary artery at the inferior border of subscapularis Course: Travels through the quadrangular space with the axillary nerve, then wraps around the posterior surface of the surgical neck of the humerus Muscles Supplied: Deltoid Teres minor Continuation: Anastomoses with the anterior circumflex humeral artery and deep brachial artery |
Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
|
|
|
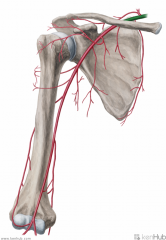
Radial Collateral Artery:
Source: Deep brachial artery Branches from the deep brachial artery in the arm Continuation: Anastomoses with the radial recurrent artery |
Radial Collateral Artery
|
|
|
Subclavian Artery:
Source: (left side) Third branch from the aortic arch (right side) One half of the bifurcation of the brachiocephalic artery Branches: (VITamin C & D) Vertebral artery Internal thoracic artery Thyrocervical trunk Costocervical trunk Dorsal scapular artery Complementary Vein: Subclavian vein Continuation: Brachial artery Becomes the brachial artery at the lateral margin of the first rib |
Subclavian Artery
|
|
|
Superior Ulnar Collateral Artery:
Source: Brachial artery Branches from the brachial artery just distal to the middle of the arm Continuation: Anastomoses with the posterior ulnar recurrent artery and inferior ulnar recurrent artery |
Superior Ulnar Collateral Artery
|
|
|
Thoracoacromial Artery:
Source: Axillary artery Branches from the axillary artery at the upper edge of pectoralis major Branches: Pectoral Acromial Clavicular Deltoid (humeral) Muscles Supplied: Pectoral: Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Acromial: (Deltoid) Clavicular: Subclavius Deltoid: (Pectoralis major) (Deltoid) Continuation: Pectoral: Anastomoses with the lateral thoracic artery and intercostal branches of the internal thoracic artery Acromial: Ends on the acromion, in a network formed by branches of the suprascapular nerve, thoracoacromial nerve, and posterior circumflex humeral artery |
Thoracoacromial Artery
|
|
|
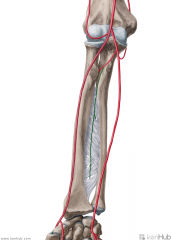
Anterior Interosseous Artery:
Source: Common interosseous artery One half of the bifurcation of the interosseous artery Branches: Muscular branches Nutrient branches to radius and ulna Palmar carpal network Muscles Supplied: Flexor forearms: Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Continuation: Sends a branch to join the palmar carpal network. Anastomoses with dorsal interosseous artery, and continues to join the dorsal carpal network. |
Anterior Interosseous Artery
|
|
|
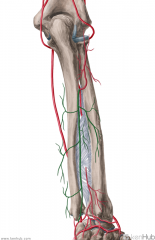
Common Interosseous Artery:
Source: Ulnar artery Branches from the ulnar artery immediately inferior to the ulnar tuberosity Continuation: Bifurcates into the anterior interosseous artery and the posterior interosseous artery after about 1cm |
Common Interosseous Artery
|
|
|
Posterior Interosseous Artery:
Source: Common interosseous artery One half of the birfurcation of the common interosseous artery Branches: Interosseous recurrent artery Muscles Supplied: Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor indicis Continuation: Anastomoses with the anterior interosseous artery and the dorsal carpal network |
Posterior Interosseous Artery
|
|
|
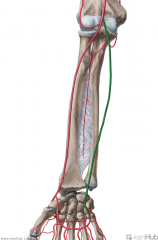
Radial Artery:
Source: Brachial artery One half of the bifurcation of the brachial artery Branches: Forearm: Radial recurrent artery Palmar carpal branch of the radial artery Dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery Superficial palmar branch of the radial artery Wrist: Dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery First dorsal metacarpal artery Hand: Princeps pollicis artery Radialis indicis Complementary Vein: Radial vein(s) - venae comitantes Continuation: Becomes the deep palmar arch (raDial -> Deep; Ulnar -> sUperficial) |
Radial Artery
(raDial -> Deep; Ulnar -> sUperficial) |
|
|
Radial Recurrent Artery:
Source: Radial artery Branches from the radial artery immediately inferior to the bifurcation of the brachial artery near the apex of the cubital fossa Muscles Supplied: Supinator Brachioradialis Brachialis Continuation: Anastomoses with the terminal part of the deep brachial artery |
Radial Recurrent Artery
|
|
|
Ulnar Artery:
Source: Brachial artery One half of the bifurcation of the brachial artery Branches: Anterior ulnar recurrent artery Posterior ulnar recurrent artery Common interosseous artery Muscular artery Palmar carpal Dorsal carpal Deep volar Superficial volar arch Muscles Supplied: (Superficial flexors of forearm) Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum superficialis Extensor carpi ulnaris Complementary Vein: Ulnar vein(s) - venae comitantes Continuation: Becomes the superficial palmar arch (Ulnar -> sUperficial; raDial -> Deep) |
Ulnar Artery
|
|
|
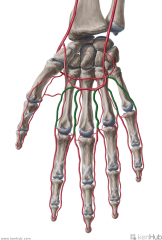
Common Palmar Digital Arteries:
Source: Superficial palmar arch Branches from the convexity of the superficial palmar arch Muscles Supplied: Lumbricals I to IV Complementary Vein: Palmar digital veins Continuation: Each of the outer arteries become the proper palmar digital arteries past the metacarpophalangeal joint; Each of the three inner arteries bifurcates into two adjacent proper palmar digital arteries, supplying adjacent digits, past the metacarpophalangeal joint |
Common Palmar Digital Arteries
|
|
|
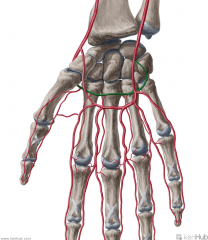
Deep Palmar Arch:
Source: Radial artery (Deep -> raDial; sUperficial -> Ulnar) The terminal part of the radial artery (Also from the deep branch of the ulnar artery) Branches: Palmar metacarpal arteries Muscles Supplied: Lumbricals I to IV Complementary Vein: Deep palmar venous arch (venae comitantes) Course: The deep palmar arch lies slightly proximal to the superficial palmar arch |
Deep Palmar Arch
|
|
|
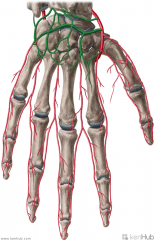
Dorsal Carpal Arch:
Source: Dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery Dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery Anterior interosseous artery Posterior interosseous artery An arterial network spanning the dorsal surface of the carpal bones, formed by anastomoses of branches of the dorsal carpal branch of the radial and ulnar arteries, and the dorsal and palmar interosseous arteries. Branches: Three dorsal metacarpal arteries are given off by the arch |
Dorsal Carpal Arch
|
|
|
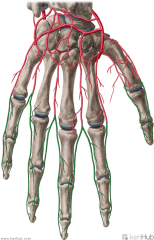
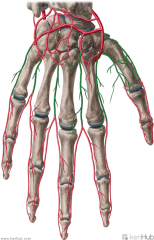
Dorsal Digital Arteries:
Source: Dorsal metacarpal arteries Muscles Supplied: Lumbricals I to IV Complementary Vein: Dorsal digital vein Course: Travel along the sides and dorsal surface of the phalanges of the digits |
Dorsal Digital Arteries
|
|
|
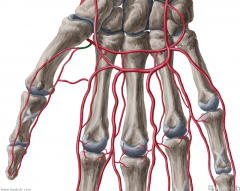
Dorsal Metacarpal Arteries:
Source: Dorsal carpal arch Muscles Supplied: Dorsal interosseous muscles I to IV Complementary Vein: Dorsal metacarpal veins Continuation: Each of the three arteries lying between digits II to V bifurcates into two adjacent dorsal digital arteries at the metacarpophalangeal joint, supplying adjacent digits; Each of the arteries supplying the outside of the first digit (thumb) and the outside of the second and fifth digits becomes a dorsal digital artery at the metacarpophalangeal joint. |
Dorsal Metacarpal Arteries
|
|
|
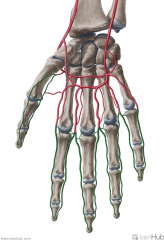
Principal Artery of the Thumb:
Source: Radial artery Branches from the radial artery just as it turns medially towards the deep part of the hand Continuation: Bifurcates at the carpometacarpal joint, and is then distributed to the palmar surface and sides of the thumb |
Principal Artery of the Thumb
|
|
|
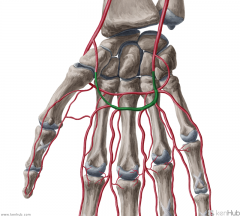
Proper Palmar Digital Arteries:
Source: Common palmar digital arteries The terminal part of the common palmar digital arteries; the middle three common palmar digital arteries bifurcate into two proper palmar digital arteries each Muscles Supplied: Supply the side of each finger Complementary Vein: Palmar digital veins |
Proper Palmar Digital Arteries
|
|
|
Superficial Palmar Arch:
Source: Ulnar artery (sUperficial -> Ulnar; Deep -> raDial) The terminal part of the ulnar artery (also from the superficial branch of the radial artery) Branches: Common palmar digital arteries Muscles Supplied: Lumbricals I to IV Complementary Vein: Superficial palmar venous arch (venae comitantes) |
Superficial Palmar Arch
|
|
|
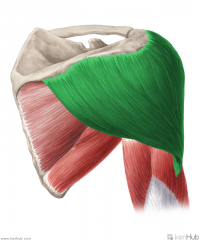
Deltoid:
Origin: Clavicular (anterior) head: deltoid tubercle of the clavicle Acromial (lateral) head: superior (lateral) surface of the acromion Spinal (posterior) head: originates from the inferior lip of the spine of the scapula Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Action: Clavicular (anterior) head: flexion and medial rotation (adduction <60 degrees; abduction >60 degrees) Acromial (lateral) head: abduction Spinal (posterior) head: extension and lateral rotation (adduction <60 degrees; abduction >60 degrees) Innervation: Axillary nerve (C5, c6) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior circumflex humeral artery |
Deltoid
|
|
|
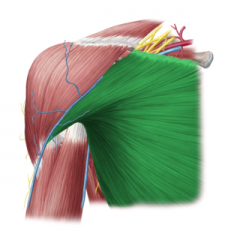
Pectoralis major:
Origin: Clavicular head: medial half of the anterior surface of the clavicle Sternocostal head: manubrium and body of the sternum; first six costal cartilages; aponeurosis of external obliques Insertion: Crest of the greater tubercle Action: Clavicular head: adduction, medial rotation and flexion Sternocostal head: extension Innervation: Clavicular head: lateral pectoral nerve (c5, C6) Sternocostal head: medial pectoral nerve (C7, C8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Thoracoacromial trunk's pectoral branch |
Pectoralis major
|
|
|
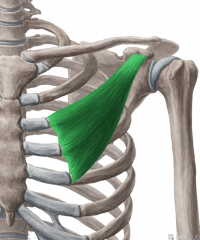
Pectoralis minor:
Origin: Ribs III-V, near their costal cartilages Insertion: Anterior surface of the coracoid process Action: Stabilises scapula, pulling it inferiorly and anteriorly against the thoracic wall (Also accessory muscle in respiration, with a fixed scapula) Innervation: Medial pectoral nerve (c8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Thoracoacromial trunk's pectoral branch |
Pectoralis minor
|
|
|
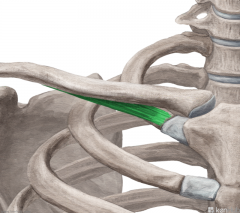
Subclavius:
Origin: First rib (and its cartilage) Insertion: Subclavian groove Action: Depresses clavicle (maintaining sternoclavicular joint) Innervation: Subclavian nerve (C5, c6) Primary Arterial Supply: Thoracoacromial artery's clavicular branch |
Subclavius
|
|
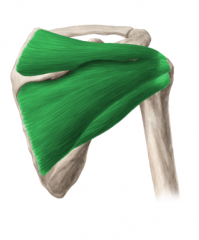
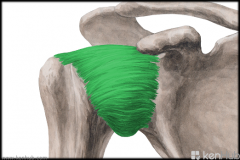
Rotator Cuff
|
Rotator Cuff:
Muscles: (SITS) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis Origin: Scapula Insertion: Humerus Function: Stabilises the glenohumeral joint Abduction, (adduction), medial rotation, lateral rotation (and assists extension) of the humerus |
Rotator Cuff
SITS |
|
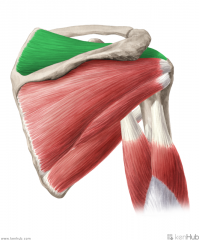
|
Supraspinatus:
Origin: Supraspinous fossa Insertion: Greater tubercle's superior facet Action: Initiates abduction Innervation: Suprascapular nerve (c4, C5, c6) Primary Arterial Supply: Suprascapular artery |
Supraspinatus
|
|
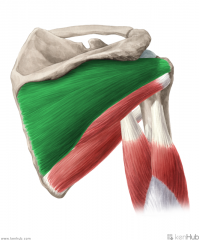
|
Infraspinatus:
Origin: Infraspinous fossa Insertion: Greater tubercle's middle facet Action: External rotation (Adduction) Innervation: Suprascapular nerve (C5, c6) Primary Arterial Supply: Suprascapular artery Circumflex scapular artery |
Infraspinatus
|
|
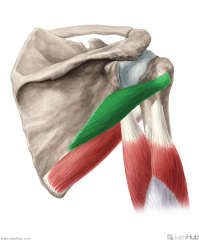
|
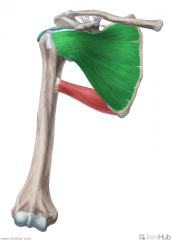
Teres Minor:
Origin: Upper two thirds of the lateral border of the scapula Insertion: Greater tubercle's inferior facet Action: Lateral rotation (Adduction) Innervation: Axillary nerve (C5, c6) Primary Arterial Supply: Circumflex scapular artery Posterior circumflex humeral artery Note: Teres minor forms the superior border of the quadrangular space and the upper triangular space |
Teres Minor
|
|
|
Subscapularis:
Origin: Subscapular fossa Insertion: Lesser tubercle of the humerus Action: Medial rotation (Assists extension) Innervation: (c5, C6, c7) Upper subscapular nerve (upper fibres) Lower subscapular nerve (lower fibres) Primary Arterial Supply: Subscapular artery |
Subscapularis
|
|
|
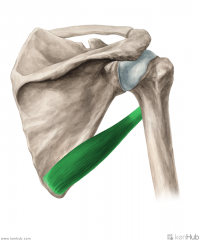
Teres Major:
Origin: Inferior angle of the scapula's posterior surface Insertion: Crest of lesser tubercle Action: Medial rotation Adduction (Assist in extension) Innervation: Lower subscapular nerve (c5, C6) Primary Arterial Supply: Subscapular artery Circumflex scapular artery Note: Teres major forms the inferior border of the quadrangular space and upper triangular space; Teres major forms the superior border of the lower triangular space |
Teres Major
|
|
|
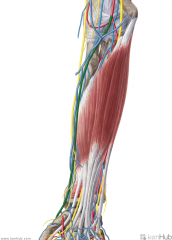
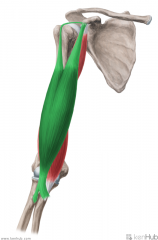
Biceps Brachii:
Origin: Short head: Lateral tip of the coracoid process Long head: Supraglenoid tubercle Insertion: Posterior (rough) surface of the radial tuberosity Action: Supination Short head: Flexion of forearm Long head: Flexion of arm Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (c5, C6) Primary Arterial Supply: Brachial artery |
Biceps Brachii
|
|
|
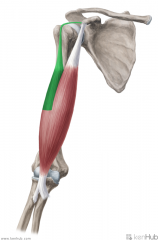
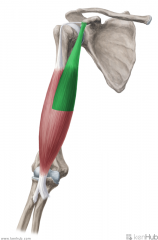
Long Head of Biceps Brachii:
Origin: Supraglenoid tubercle Insertion: Posterior (rough) surface of the radial tuberosity Action: Supination, flexion of arm Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (c5, C6) Primary Arterial Supply: Brachial artery |
Long Head of Biceps Brachii
|
|
|
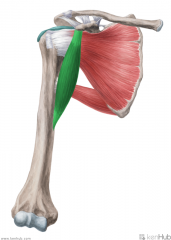
Short Head of Biceps Brachii:
Origin: Lateral tip of the coracoid process Insertion: Posterior (rough) surface of the radial tuberosity Action: Supination, flexion of forearm Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (c5, C6) Primary Arterial Supply: Brachial artery |
Short Head of Biceps Brachii
|
|
|
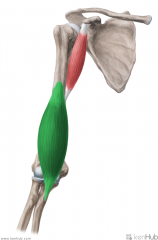
Coracobrachialis:
Origin: Lateral tip of the coracoid process Insertion: Medial surface of mid-shaft humerus Action: Flexion and adduction of arm Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (c5, C6, c7) Primary Arterial Supply: Brachial artery |
Coracobrachialis
|
|
|
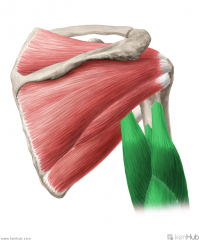
Brachialis:
Origin: Anterior surface of the distal half of the humeral shaft Intermuscular septa Insertion: Coronoid process and ulnar tuberosity Action: Flexion of forearm Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (c5, C6) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial recurrent artery |
Brachialis
|
|
|
Triceps Brachii:
Origin: Long head: Infraglenoid tubercle Lateral head: Posterior surface of proximal third of the humerus; lateral intermuscular septum Medial head: Posterior surface of distal half of the humerus; intermuscular septa Insertion: Superoposterior surface of the olecranon Action: Extension of forearm Long head: extension and adduction of arm Innervation: Radial nerve (c6, C7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep brachial artery Note: Long head of triceps brachii forms the medial border of the quadranguar space; Long head of triceps brachii forms the lateral border of the lower triangular space |
Triceps Brachii
|
|
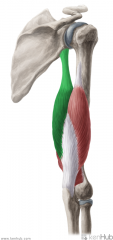
|
Long Head of Triceps Brachii:
Origin: Infraglenoid tubercle Insertion: Superoposterior surface of the olecranon Action: Extension of forearm, extension and adduction of arm Innervation: Radial nerve (c6, C7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep brachial artery Note: Long head of triceps brachii forms the medial border of the quadranguar space; Long head of triceps brachii forms the lateral border of the lower triangular space |
Long Head of Triceps Brachii
|
|
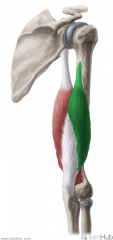
|
Lateral Head of Triceps Brachii:
Origin: Posterior surface of proximal third of the humerus Lateral intermuscular septum Insertion: Superoposterior surface of the olecranon Action: Extension of forearm Innervation: Radial nerve (c6, C7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep brachial artery |
Lateral Head of Triceps Brachii
|
|
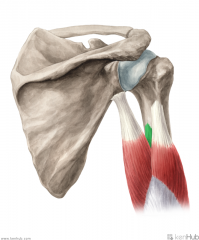
|
Medial Head of Triceps Brachii:
Origin: Medial head: Posterior surface of distal half of the humerus; intermuscular septa Insertion: Superoposterior surface of the olecranon Action: Extension of forearm Innervation: Radial nerve (c6, C7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep brachial artery |
Medial Head of Triceps Brachii
|
|
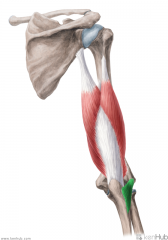
|
Anconeus:
Origin: Lateral epicondyle Insertion: Lateral surface of the olecranon Action: Extension of forearm Stabilises elbow and abducts ulna during pronation Innervation: Radial nerve (c7, c8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Interosseous recurrent artery, a branch of the posterior interosseous artery Note: The anconeus is partially blended with the triceps brachii; some consider it to be the fourth head of the triceps brachii, making it homologous to the quadriceps femoris in the lower limb. |
Anconeus
|
|
|
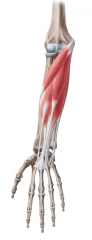
Superficial Flexors of the Forearm:
(Layers 1 and 2) Muscles: Layer 1: Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Layer 2: Flexor digitorum superficialis Origin: Common flexor origin on medial epicondyle Innervation: Median nerve Flexor carpi radialis: Ulnar nerve Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Superficial Flexors of the Forearm
|
|
|
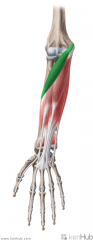
Pronator Teres:
Origin: Humeral head: Common flexor origin on medial epicondyle Ulnar head: Medial surface of the coronoid process Insertion: Midpoint of the lateral surface of the shaft of the radius Action: Pronation (Flexion) Innervation: Median nerve (c6, C7) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery Note: Pronator Teres forms the medial border of the cubital fossa |
Pronator Teres
|
|

|
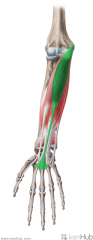
Flexor Carpi Radialis:
Origin: Common flexor origin on medial epicondyle Insertion: Base of metacarpals II to III Action: Flexion and abduction (radial deviation) Innervation: Median nerve (c6, C7) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Flexor Carpi Radialis
|
|
|
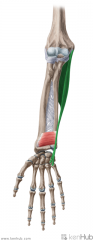
Palmaris Longus:
Origin: Common flexor origin on medial epicondyle Insertion: Palmar aponeurosis Action: Flexion Innervation: Median nerve (c7, c8) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery Absent in ~13% of forearms |
Palmaris Longus
|
|
|
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris:
Origin: Humeral head: Common flexor origin on medial epicondyle Ulnar head: Proximal two thirds of posterior surface of ulna, including olecranon Insertion: Pisiform Hook of Hamate Base of metacarpal V Action: Flexion, adduction (ulnar deviation) Innervation: Ulnar nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery Note: Pisiform is a sesamoid bone of the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris |
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
|
|
|
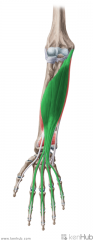
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Origin: Humeral head: Common flexor origin on medial epicondyle Humeroulnar head: Medial aspect of coronoid process Radial head: Middle third of anterior surface of the radius Insertion: Sides of the base of the middle phalanges (i.e. digits II to V) Tenons bifurcate and insert on the sides of the middle phalanges, to allow flexor digitorm profundus' tendons to pass through to reach the distal phalanges. Action: Flexion of the fingers (at proximal interphalangeal joint) Innervation: Median nerve (c7, c8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
|
|
|
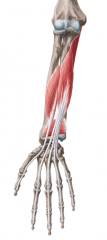
Deep Flexors of the Forearm:
(Layers 3 and 4) Muscles: Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Origin: Anterior surface of the radius and ulna Innervation: Median nerve Lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus: Ulnar nerve Primary arterial supply: Anterior interosseous artery |
Deep Flexors of the Forearm
|
|
|
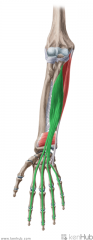
Flexor Digitorum Profundus:
Origin: Medial and anterior surfaces of proximal two thirds of the ulna, and adjacent interosseous membrane Insertion: Base of distal phalanges II to V Action: Flexion of distal interphalangeal joints of digits II to V Innervation: Median nerve (digits II-III) (c8, T1) Ulnar nerve (digits IV-V) (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery Anterior interosseous artery |
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
|
|
|
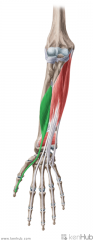
Flexor Pollicis Longus:
Origin: Middle two quarters of anterior surface of the radius, and adjacent interosseous membrane Insertion: Base of the distal phalanx of the thumb Action: Flexion of interphalangeal joints of the thumb Innervation: Anterior interosseous nerve, from Median nerve (C8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Anterior interosseous artery |
Flexor Pollicis Longus
|
|
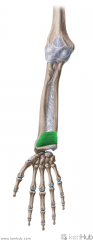
|
Pronator Quadratus:
Origin: Medial surface of the distal quarter of the ulna Insertion: Anterior surface of the distal quarter of the radius Action: Pronation Innervation: Anterior interosseous nerve, from Median nerve (C8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Anterior interosseous artery |
Pronator Quadratus
|
|
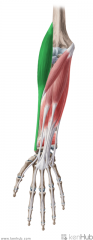
|
Brachioradialis:
Origin: Proximal half of lateral supracondylar ridge Insertion: Base of radial styloid process Action: Flexes forearm (Assists in pronation and supination) Innervation: Radial nerve (c5, C6, c7) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial recurrent artery Note: Brachioradialis forms the lateral border of the cubital fosssa |
Brachioradialis
|
|
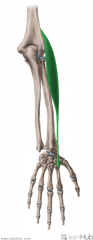
|
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus:
Origin: Distal half of lateral supracondylar ridge Insertion: Base of dorsal surface of metacarpal II Action: Extension and abduction (radial deviation) of the wrist Innervation: Radial nerve (c6, c7) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial artery |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
|
|
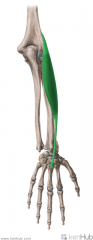
|
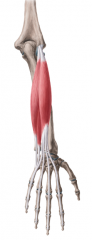
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis:
Origin: Common extensor origin on lateral epicondyle Insertion: Base of dorsal surface of metacarpal III Action: Extension and abduction (radial deviation) of the wrist; clenching of the fist Innervation: Deep branch of radial nerve (C7, c8) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial artery |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
|
|
|
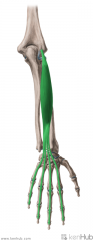
Superficial Extensors of the Forearm:
Muscles: Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Origin: Common extensor origin on lateral epicondyle Innervation: Radial nerve |
Superficial Extensors of the Forearm
|
|
|
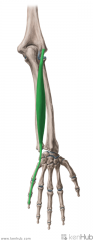
Extensor Digitorum:
Origin: Common extensor origin on lateral epicondyle Insertion: Extensor expansion of middle and distal phalanges II to V Central bands insert on the base of the middle phalanges; lateral bands insert on the base of the distal phalanges Action: Extension of digits II to V Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve (continuation of deep branch of radial nerve) (C7, c8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous artery |
Extensor Digitorum
|
|
|
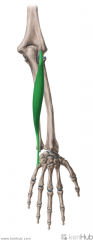
Extensor Digiti Minimi:
Origin: Common extensor origin on lateral epicondyle Insertion: Extensor expansion of digit V Joins the tendon of extensor digitorum in inserting at the base of the middle and distal phalanges of digit V Action: Extension of digit V Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve (continuation of deep branch of radial nerve) (C7, c8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous artery |
Extensor Digiti Minimi
|
|
|
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris:
Origin: Common flexor origin on lateral epicondyle Distal half of the lateral supracondylar ridge Ulnar head: middle third of the posterior surface of the ulna Insertion: Medial surface of the base of metacarpal V Action: Extension and adduction (ulnar deviation) of the wrist; clenching of the fist Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve (continuation of deep branch of radial nerve) (C7, c8) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
|
|
|
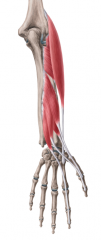
Deep Extensors of the Forearm:
Muscles: Supinator Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis longus Extesor indicis Origin: Posterior surface of the radius and ulna Innervation: Radial nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous artery |
Deep Extensors of the Forearm
|
|
|
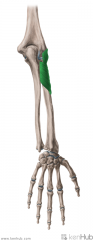
Supinator:
Origin: Common extensor origin on lateral epicondyle Lateral surface of the ulna, just distal to the radial notch (supinator fossa) Radial collateral ligament Annular collateral ligament Insertion: Lateral surface of the proximal third of the shaft of the radius Action: Supination Innervation: Deep branch of Radial nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial recurrent artery |
Supinator
|
|
|
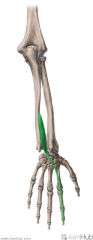
Extensor Indicis
Origin: Posterolateral surface of distal ulna and adjacent interosseous membrane Insertion: Extensor expansion of digit II Joins the flexor digitorum tendon in inserting at the base of the middle and distal phalanges of digit II Action: Extension of digit II Innervation: Posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous artery |
Extensor Indicis
|
|
|
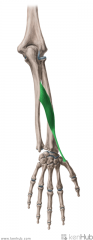
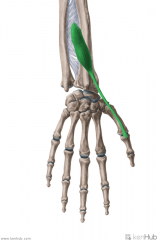
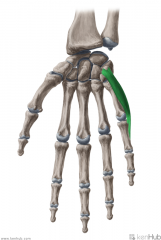
Abductor Pollicis Longus:
Origin: Posterolateral surface of the second quarter of the shaft of the ulna, posteromedial surface of the third quarter of the shaft of the radius, and the intervening interosseous membrane Insertion: Radial side of the base of metacarpal I Action: Abduction of the thumb (Extension of the thumb) Innervation: Posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous artery Note: Radial styloid process' dorsal surface has a groove for abductor pollicis longus' tendon Abductor pollicis longus forms the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox |
Abductor Pollicis Longus
|
|
|
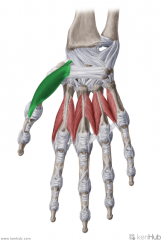
Extensor Pollicis Brevis:
Origin: Posterior distal radial shaft and adjacent interosseous membrane Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx I Action: Extension of thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint Innervation: Posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous Artery Note: Radial styloid process' dorsal surface has a groove for extensor pollicis brevis' tendon Extensor pollicis brevis forms the posterolateral border of the anatomical snuffbox |
Extensor Pollicis Brevis
|
|
|
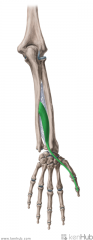
Extensor Pollicis Longus:
Origin: Posterolateral mid-shaft ulna and adjacent interosseous membrane Insertion: Base of distal phalanx I Action: Extension of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint Innervation: Posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve (c7, C8) Primary Arterial Supply: Posterior interosseous artery Note: Extensor pollicis longus forms the posterior/medial border of the anatomical snuffbox |
Extensor Pollicis Longus
|
|
|
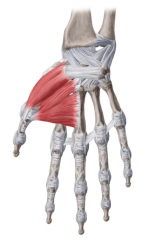
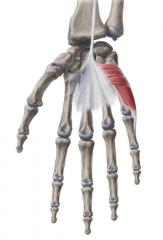
Thenar Eminence:
Muscles: (AbOF) Abductor Pollicis Brevis Opponens Pollicis Flexor Pollicis Brevis Innervation: Recurrent branch of Median Nerve Deep branch of Ulnar nerve Primary Arterial Supply: Radial Artery (Superficial palmar branch) Note: The thenar eminence is a mirror image of the hypothenar eminence |
Thenar Eminence
AbOF |
|
|
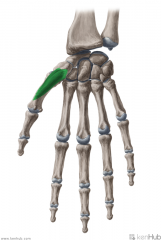
Abductor Pollicis Brevis:
Origin: Flexor retinaculum; scaphoid and trapezium Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx I Action: Abduction of thumb Innervation: Recurrent branch of Median Nerve (C8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial Artery (Superficial palmar branch) |
Abductor Pollicis Brevis
|
|
|
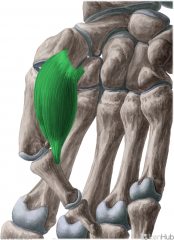
Opponens Pollicis:
Origin: Flexor retinaculum; trapezium Insertion: Radial surface of the shaft of metacarpal I Action: Opposition of the thumb Innervation: Recurrent branch of Median Nerve (C8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial Artery (Superficial palmar branch) |
Opponens Pollicis
|
|
|
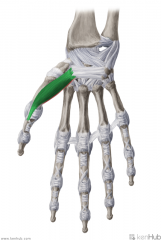
Flexor Pollicis Brevis:
Origin: Superficial head: Flexor retinaculum; trapezium Deep head: Trapezoid and capitate Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx I Action: Flexion of thumb (Assists adduction and opposition) Innervation: Superficial head: Recurrent branch of Median Nerve (C8, t1) Deep head: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial Artery (Superficial palmar branch) |
Flexor Pollicis Brevis
|
|
|
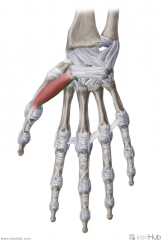
Superficial Head of Flexor Pollicis Brevis:
Origin: Flexor retinaculum; trapezium Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx I Action: Flexion of thumb (Assists adduction and opposition) Innervation: Recurrent branch of Median Nerve (C8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial Artery (Superficial palmar branch) |
Superficial Head of Flexor Pollicis Brevis
|
|
|
Deep Head of Flexor Pollicis Brevis:
Origin: Trapezoid and capitate Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx I Action: Flexion of thumb (Assists adduction and opposition) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Radial Artery (Superficial palmar branch) |
Deep Head of Flexor Pollicis Brevis
|
|
|
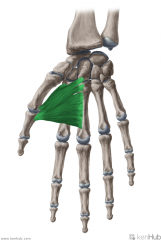
Adductor Pollicis:
Origin: Oblique head: Base of metacarpals II and III; adjacent Capitate Transverse head: Anterior body of metacarpal III Insertion: Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx I Action: Adduction of the thumb (Flexion of the thumb) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch |
Adductor Pollicis
|
|
|
Oblique Head of Adductor Pollicis:
Origin: Base of metacarpals II and III; adjacent Capitate Insertion: Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx I Action: Adduction of the thumb (Flexion of the thumb) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch |
Oblique Head of Adductor Pollicis
|
|

|
Transverse Head of Adductor Pollicis:
Origin: Anterior body of metacarpal III Insertion: Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx I Action: Adduction of the thumb (Flexion of the thumb) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch |
Transverse Head of Adductor Pollicis
|
|
|
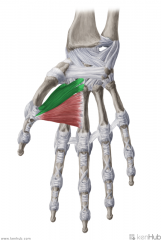
Hypothenar Eminence
Muscles: (AbOF) Abductor digiti minimi of the hand Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Hypothenar Eminence
AbOF |
|
|
Abductor Digiti Minimi of the Hand:
Origin: Pisiform Insertion: Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx V Action: Abduction of digit V Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Abductor Digiti Minimi of the Hand
|
|
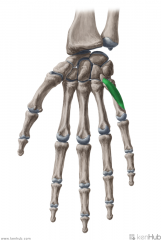
|
Opponens Digiti Minimi:
Origin: Flexor retinaculum; Hook of Hamate Insertion: Medial surface of the shaft of metacarpal V Action: Opposition of digit V to thumb Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Opponens Digiti Minimi
|
|
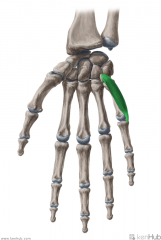
|
Flexor Digiti Minimi (Brevis):
Origin: Flexor retinaculum; Hook of Hamate Insertion: Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx V Action: Flexion of digit V Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery |
Flexor Digiti Minimi (Brevis)
|
|
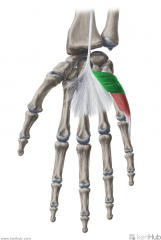
|
Palmaris Brevis:
Origin: Flexor retinaculum; medial border of the palmar aponeurosis Insertion: Skin of medial border of hand Action: Assists in grasping actions Innervation: Superficial branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, t1) Primary Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery (Superficial branch) |
Palmaris Brevis
|
|
|
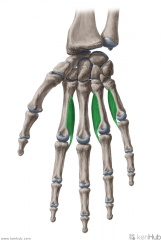
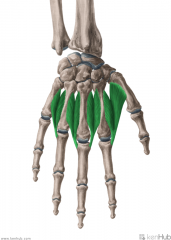
Palmar Interossei:
3 muscles Origin: Medial surface of the shaft of metacarpal II; Lateral surfaces of the shafts of metacarpals IV and V Insertion: Extensor expansions Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx II; Lateral surfaces of the shafts of proximal phalanges IV and V Action: (PAd) Adduction of the fingers (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch (Palmar metacarpal artery) |
Palmar Interossei
PAd |
|
|
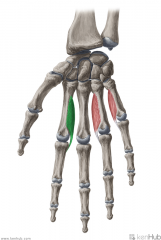
Palmar Interosseous I:
Origin: Medial surface of the shaft of metacarpal II Insertion: Extensor expansion Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx II Action: (PAd) Adduction of digit II (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch (Palmar metacarpal artery) |
Palmar Interosseous I
|
|
|
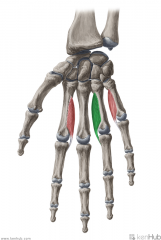
Palmar Interosseous II:
Origin: Lateral surface of the shaft of metacarpal IV Insertion: Extensor expansion Lateral surface of the shaft of proximal phalanx IV Action: (PAd) Adduction of digit IV (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch (Palmar metacarpal artery) |
Palmar Interosseous II
|
|
|
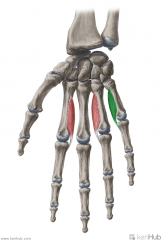
Palmar Interosseous III:
Origin: Lateral surface of the shaft of metacarpal V Insertion: Extensor expansion Lateral surface of the shaft of proximal phalanx V Action: (PAd) Adduction of digit V (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arch (Palmar metacarpal artery) |
Palmar Interosseous III
|
|
|
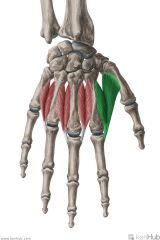
Dorsal Interossei:
4 muscles Origin: Adjacent metacarpal shafts Insertion: Extensor expansions Radial surfaces of the bases of proximal phalanges II and III; Medial surfaces ot the bases of proximal phalanges III and IV Action: DAb Abduction of the fingers (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Dorsal and Palmar metacarpal arteries |
Dorsal Interossei
DAb |
|
|
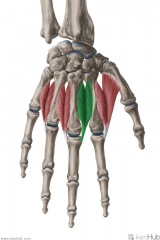
Dorsal Interosseous I:
Origin: Adjacent shafts of metacarpals I and II Insertion: Extensor expansion Radial surface of the base of proximal phalanx II Action: DAb Abduction of digit II (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Dorsal and Palmar metacarpal arteries |
Dorsal Interosseous I
|
|
|
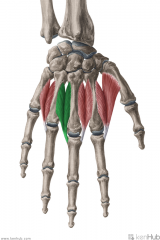
Dorsal Interosseous II:
Origin: Adjacent shafts of metacarpals II and III Insertion: Extensor expansion Radial surface of the base of proximal phalanx III Action: DAb Abduction of digit III (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Dorsal and Palmar metacarpal arteries |
Dorsal Interosseous II
|
|
|
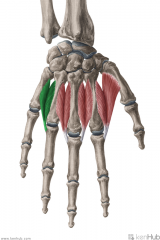
Dorsal Interosseous III:
Origin: Adjacent shafts of metacarpals III and IV Insertion: Extensor expansion Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx III Action: DAb Abduction of digit III (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Dorsal and Palmar metacarpal arteries |
Dorsal Interosseous III
|
|
|
Dorsal Interosseous IV:
Origin: Adjacent shafts of metacarpals IV and V Insertion: Extensor expansion Medial surface of the base of proximal phalanx IV Action: DAb Abduction of digit IV (with respect to the midline of digit III) Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Dorsal and Palmar metacarpal arteries |
Dorsal Interosseous IV
|
|
|
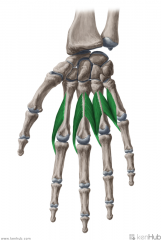
Lumbricals:
(Lumbrical -> Earthworm: looks like an earthworm) 4 muscles Origin: Tendons of flexor digitorum profundus Insertion: Extensor expansions Radial surfaces of the bases of middle phalanges II to V Action: Extension of interphalangeal joints II to V Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joints II to V Innervation: (c8, T1) Lumbricals I to II: Median nerve (Palmar digital branches) Lumbricals III to IV: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve Primary Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery |
Lumbricals
|
|
|
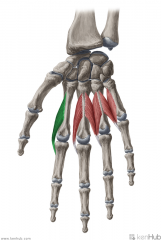
Lumbrical I:
Origin: (Unipennate) Radial margin of flexor digitorum profundus' tendon to digit II Insertion: Extensor expansion Radial surfaces of the base of middle phalanx II Action: Extension of interphalangeal joint II Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joint II Innervation: Median nerve (Palmar digital branches) (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery |
Lumbrical I
|
|
|
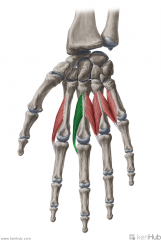
Lumbrical II:
Origin: (Unipennate) Radial margin of flexor digitorum profundus' tendon to digit III Insertion: Extensor expansion Radial surfaces of the base of middle phalanx III Action: Extension of interphalangeal joint III Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joint III Innervation: Median nerve (Palmar digital branches) (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery |
Lumbrical II
|
|
|
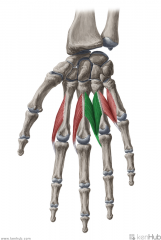
Lumbrical III:
Origin: (Bipennate) Flexor digitorum profundus' tendons to digits III (medial margin) and IV (radial margin) Insertion: Extensor expansion Radial surface of the base of middle phalanx IV Action: Extension of interphalangeal joint IV Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joint IV Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery |
Lumbrical III
|
|
|
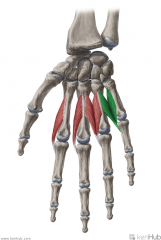
Lumbrical IV:
Origin: (Bipennate) Flexor digitorum profundus' tendons to digits IV (medial margin) and V (radial margin) Insertion: Extensor expansion Radial surface of the base of middle phalanx V Action: Extension of interphalangeal joint V Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joint V Innervation: Deep branch of Ulnar nerve (c8, T1) Primary Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery |
Lumbrical IV
|
|
|
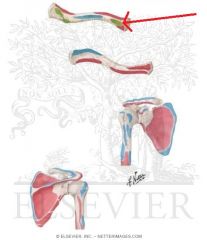
Costoclavicular Ligament
|
|
|
|
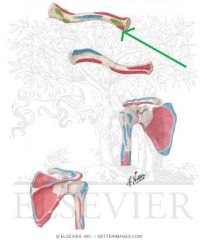
Sternohyoid Origin
|
|
|
|
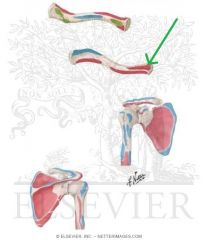
Sternocleidomastoid Origin
|
|
|
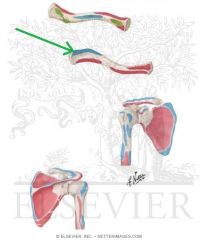
|
Trapezius Insertion
|
|
|
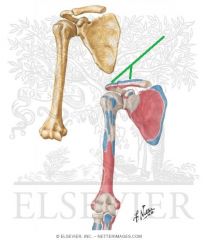
|
Trapezius Insertion
|
|
|
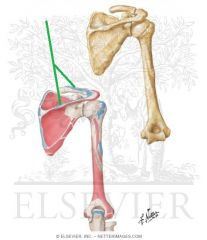
|
Trapezius Insertion
|
|
|
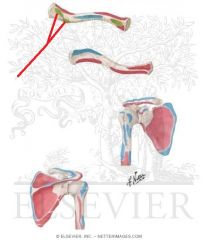
|
Coracoclavicular Ligament
|
|
|
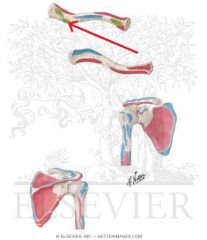
|
Conoid Ligament
|
|
|
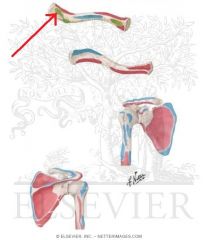
|
Trapezoid Ligament
|
|
|
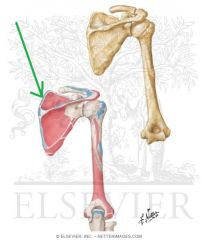
|
Levator Scapulae Insertion
|
|
|
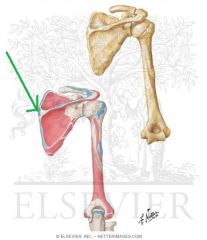
|
Rhomboid Minor Insertion
|
|
|
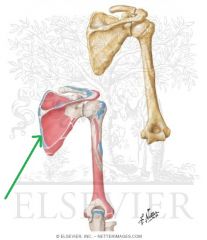
|
Rhomboid Major Insertion
|
|
|
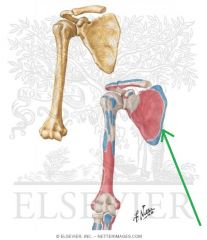
|
Serratus Anterior Insertion
|
|
|
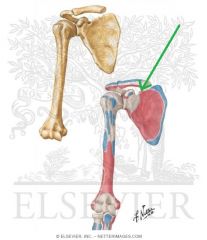
|
Omohyoid Origin
|
|
|
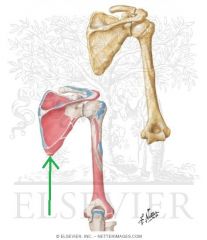
|
Latissimus Dorsi Origin - very small slip on inferior angle of scapula
|
|
|
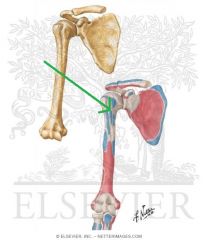
|
Latissimus Dorsi Insertion
|
|
|
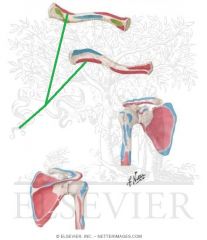
|
Deltoid Origin - Clavicular Head
|
|
|
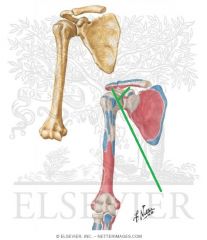
|
Deltoid Origin - Clavicular and Acromial Heads
|
|
|
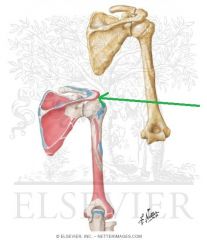
|
Deltoid Origin - Acromial Head
|
|
|
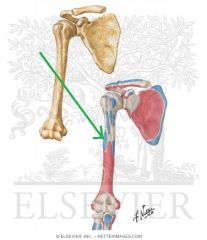
|
Deltoid Insertion
|
|
|
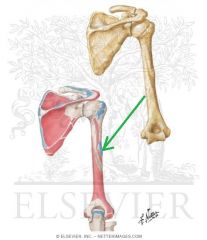
|
Deltoid Insertion
|
|
|
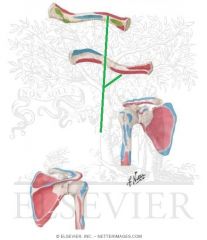
|
Pectoralis Major Origin - Clavicular Head
|
|
|
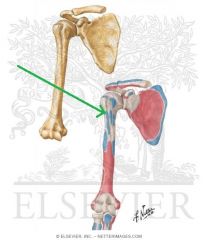
|
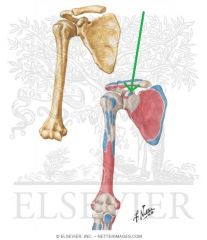
Pectoralis Major Insertion
|
|
|
|
Pectoralis Minor Insertion
|
|
|
|
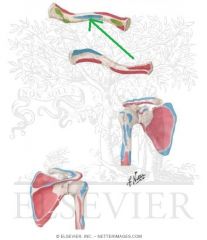
Subclavius Insertion
|
|
|
|
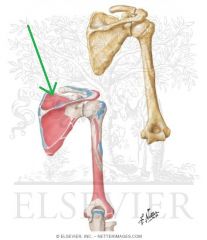
Supraspinatus Origin
|
|
|
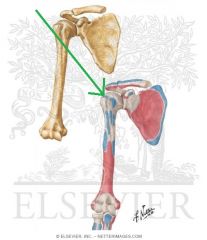
|
Supraspinatus Insertion
|
|
|
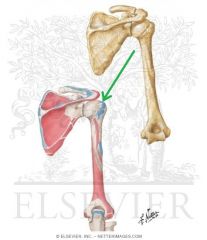
|
Supraspinatus Insertion
|
|
|
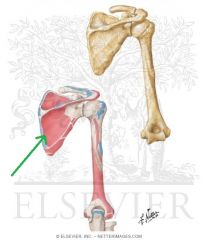
|
Infraspinatus Origin
|
|
|
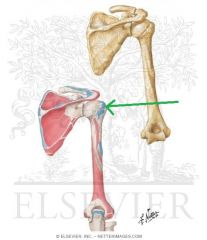
|
Infraspinatus Insertion
|
|
|
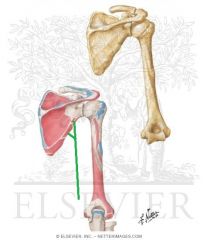
|
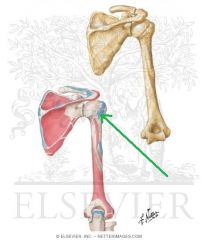
Teres Minor Origin
|
|
|
|
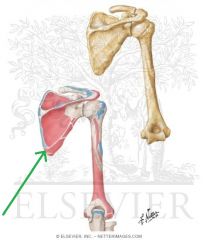
Teres Minor Insertion
|
|
|
|
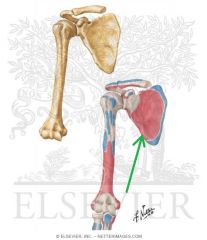
Subscapularis Origin
|
|
|
|
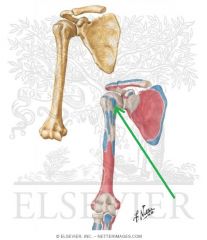
Subscapularis Insertion
|
|
|
|
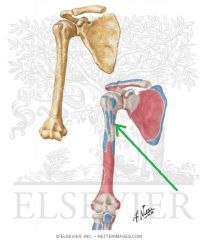
Teres Major Origin
|
|
|
|
Teres Major Insertion
|
|
|
|
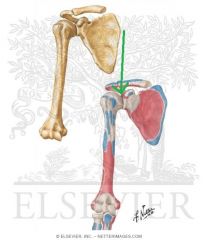
Biceps Brachii Origin - Long Head
|
|
|
|
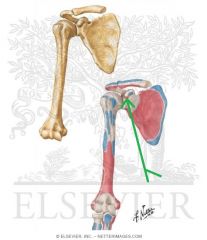
Biceps Brachii Origin - Short Head
Coracobrachialis Origin |
|
|
|
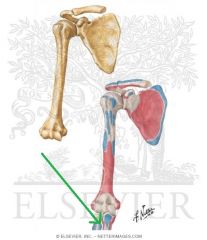
Biceps Brachii Insertion
|
|
|
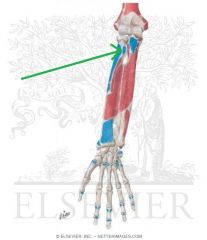
|
Biceps Brachii Insertion
|
|
|
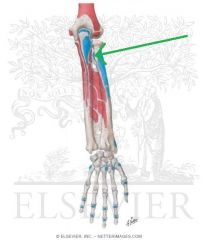
|
Biceps Brachii Insertion
|
|
|
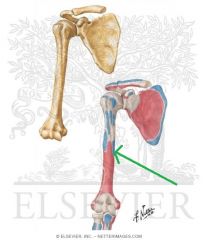
|
Coracobrachialis Insertion
|
|
|
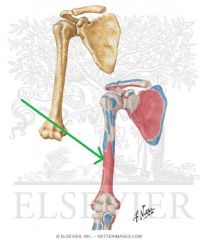
|
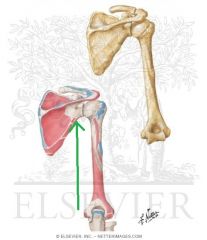
Brachialis Origin
|
|
|
|
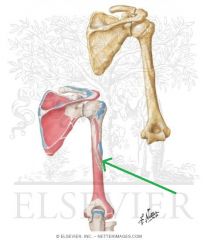
Brachialis Origin
|
|
|
|
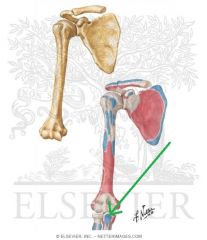
Brachialis Insertion
|
|
|
|
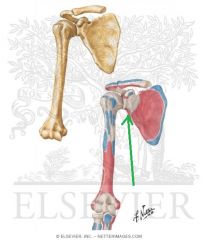
Triceps Brachii Origin - Long Head
|
|
|
|
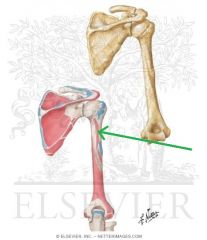
Triceps Brachii Origin - Long Head
|
|
|
|
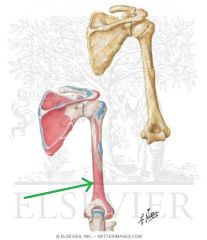
Triceps Brachii Origin - Lateral Head
|
|
|
|
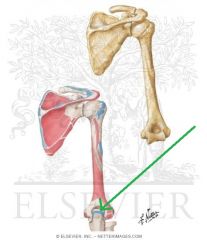
Triceps Brachii Origin - Medial Head
|
|
|
|
Triceps Brachii Insertion
|
|
|
|
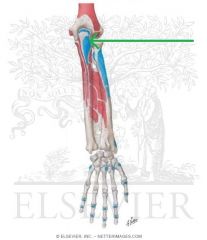
Anconeus Origin
|
|
|
|
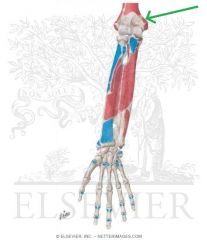
Anconeus Insertion
|
|
|
|
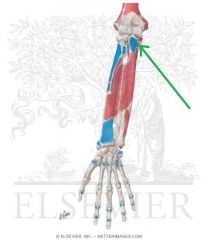
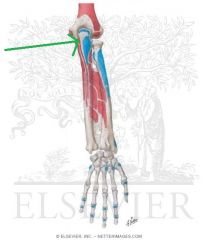
Pronator Teres Origin - Humeral Head
|
|
|
|
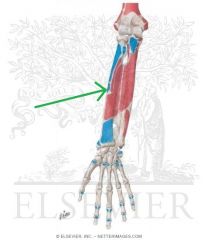
Pronator Teres Origin - Ulnar head
|
|
|
|
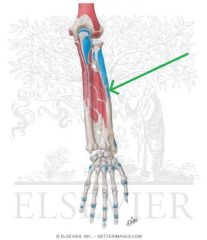
Pronator Teres Insertion
|
|
|
|
Pronator Teres Insertion
|
|
|
|
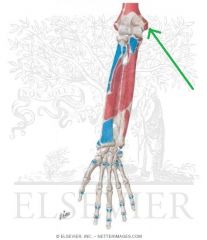
Common Flexor Origin
Muscles: Pronator Teres Flexor Carpi Radialis Palmaris Longus Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Digitorum (humeral head) |
|
|
|
Flexor Carpi Radialis Insertion
|
|
|
|
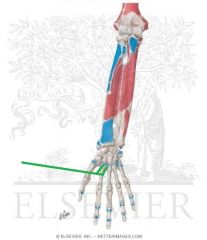
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Origin - Ulnar Head
|
|
|
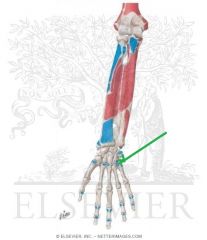
|
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Insertion
|
|
|
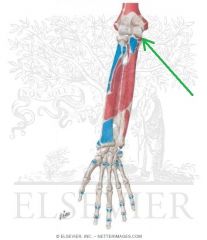
|
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Origin - Humeroulnar Head
|
|
|
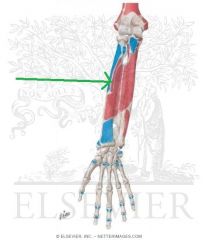
|
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Origin - Radial Head
|
|
|
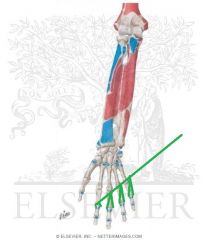
|
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Insertion
|
|
|
|
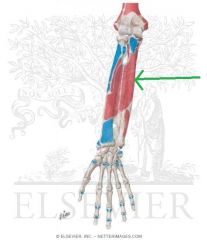
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Origin
|
|
|
|
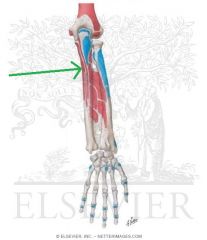
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Origin
|
|
|
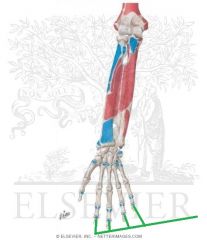
|
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Insertion
|
|
|
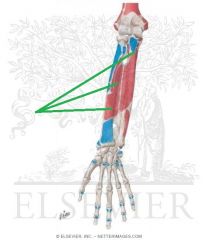
|
Flexor Pollicis Longus Origin
|
|
|
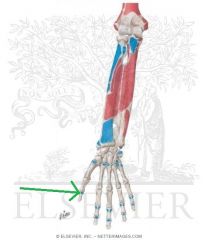
|
Flexor Pollicis Longus Insertion
|
|
|
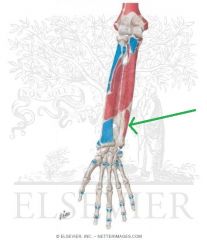
|
Pronator Quadratus Origin
|
|
|
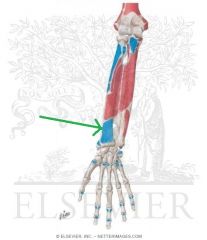
|
Pronator Quadratus Insertion
|
|
|
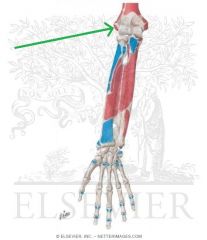
|
Common Extensor Origin
Muscles: Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Extensor Digitorum Extensor Digiti Extensor Carpi Ulnaris |
|
|
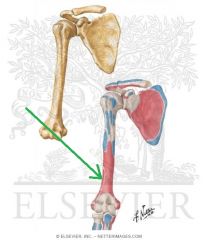
|
Brachioradialis Origin
|
|
|
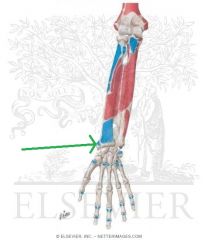
|
Brachioradialis Insertion
|
|
|
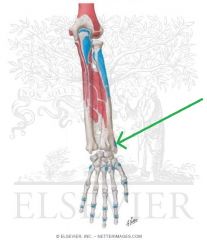
|
Brachioradialis Insertion
|
|
|
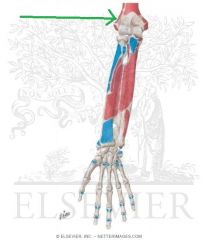
|
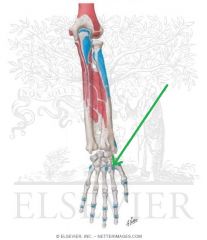
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Origin
|
|
|
|
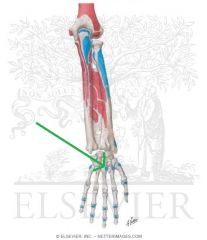
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Insertion
|
|
|
|
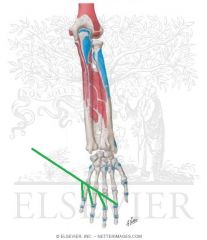
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Insertion
|
|
|
|
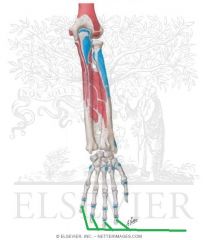
Extensor Digitorum Insertion - Central Bands
|
|
|
|
Extensor Digitorum Insertion - Lateral Bands
|
|
|
|
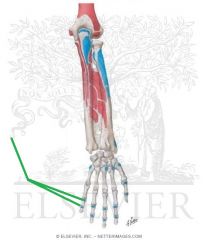
Extensor Digiti Minimi Insertion
|
|
|
|
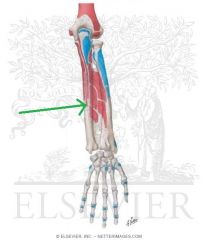
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Origin - Humeral Head
|
|
|
|
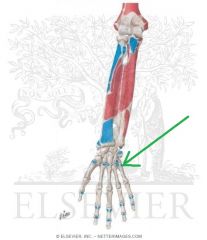
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Insertion
|
|
|
|
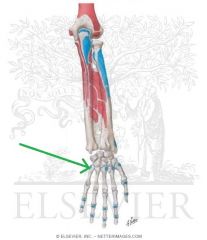
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Insertion
|
|
|
|
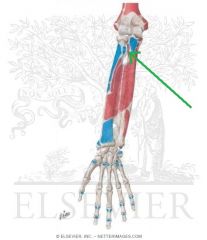
Supinator Origin
|
|
|
|
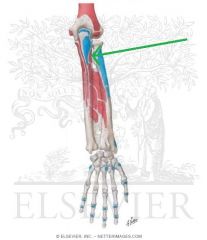
Supinator Origin
|
|
|
|
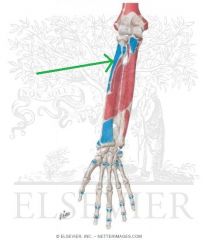
Supinator Insertion
|
|
|
|
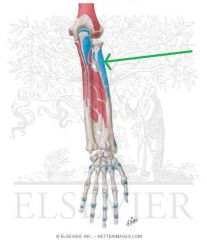
Supinator Insertion
|
|
|
|
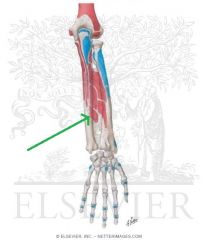
Extensor Indicis Origin
|
|
|
|
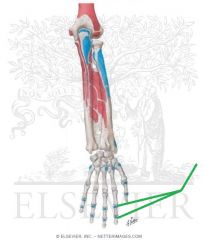
Extensor Indicis Insertion
|
|
|
|
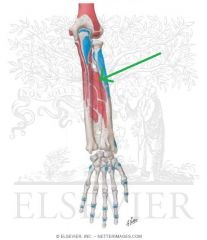
Abductor Pollicis Longus Origin
|
|
|
|
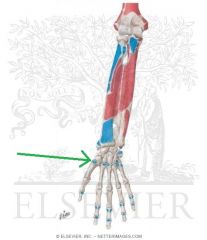
Abductor Pollicis Longus Insertion
|
|
|
|
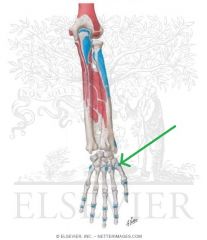
Abductor Pollicis Longus Insertion
|
|
|
|
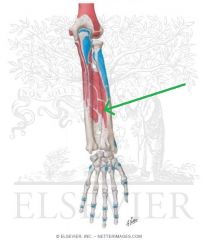
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Origin
|
|
|
|
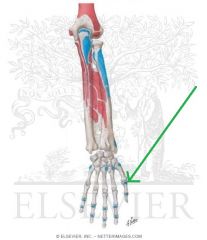
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Insertion
|
|
|
|
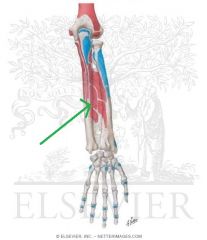
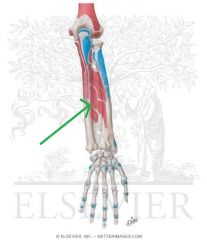
Extensor Pollicis Longus Origin
|
|
|
|
Extensor Pollicis Longus Origin
|
|
|
|
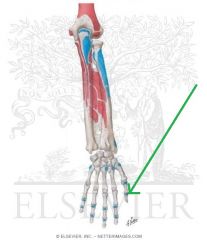
Extensor Pollicis Longus Insertion
|
|
|
|
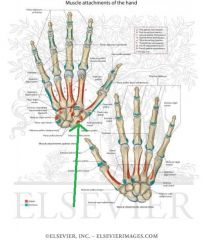
Abductor Pollicis Brevis Origin
|
|
|
|
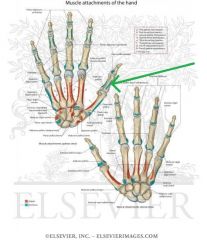
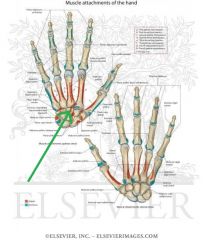
Abductor Pollicis Brevis Insertion
Flexor Pollicis Brevis Insertion |
|
|
|
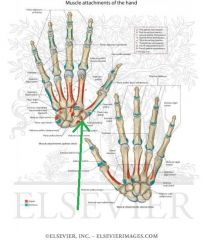
Opponens Pollicis Origin
|
|
|
|
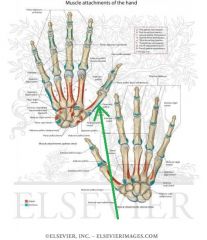
Opponens Pollicis Insertion
|
|
|
|
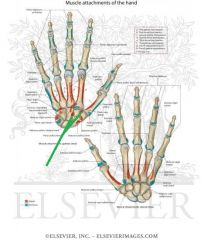
Flexor Pollicis Brevis Origin
|
|
|
|
Adductor Pollicis Origin - Oblique Head
|
|
|
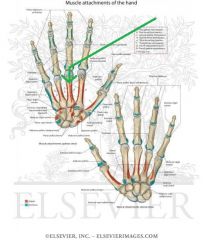
|
Adductor Pollicis Origin - Transverse Head
|
|
|
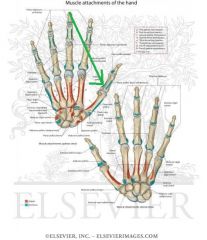
|
Adductor Pollicis Insertion
|
|
|
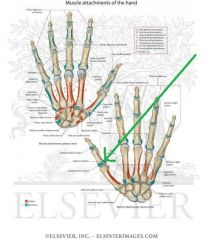
|
Adductor Pollicis Insertion
|
|
|
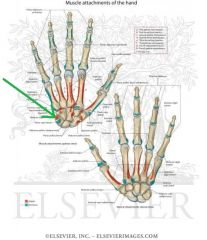
|
Abductor Digiti Minimi Origin
|
|
|
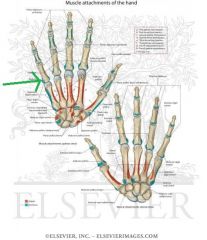
|
Abductor Digiti Minimi Insertion
|
|
|
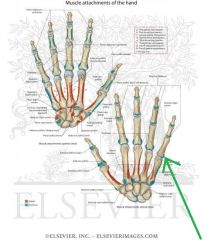
|
Abductor Digiti Minimi Insertion
|
|
|
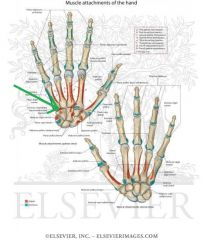
|
Opponens Digiti Minimi Origin
|
|
|
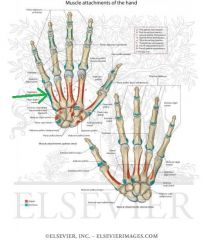
|
Opponens Digiti Minimi Insertion
|
|
|
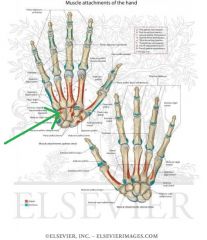
|
Flexor Digiti Minimi Origin
|
|
|
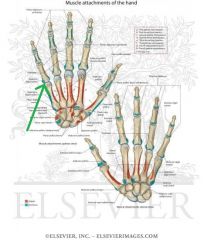
|
Flexor Digiti Minimi Insertion
|
|
|
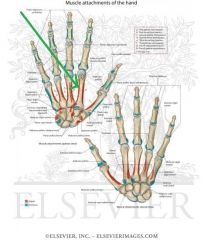
|
Palmar Interosseous I Origin
|
|
|
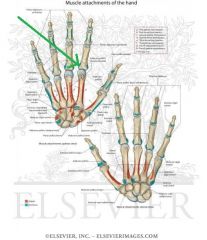
|
Palmar Interosseous I Insertion
|
|
|
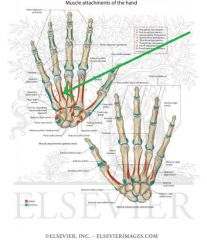
|
Palmar Interosseous II Origin
|
|
|
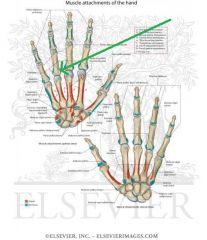
|
Palmar Interosseous II Insertion
Lumbrical III Insertion |
|
|
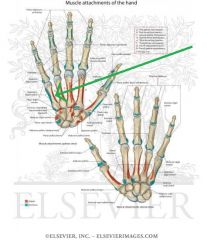
|
Palmar Interosseous III Origin
|
|
|
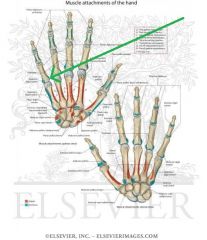
|
Palmar Interosseous III Insertion
Lumbrical IV Insertion |
|
|
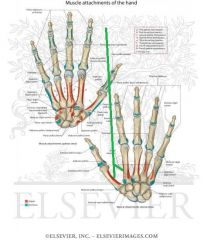
|
Dorsal Interosseous I Origin
|
|
|
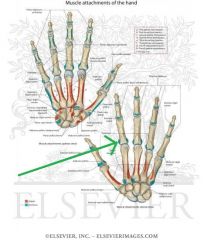
|
Dorsal Interosseous I Insertion
Lumbrical I Insertion |
|
|
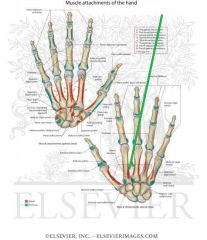
|
Dorsal Interosseous II Origin
|
|
|
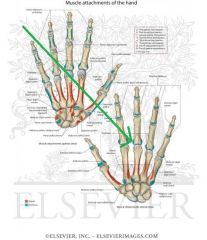
|
Dorsal Interosseous II Insertion
Lumbrical II Insertion |
|
|
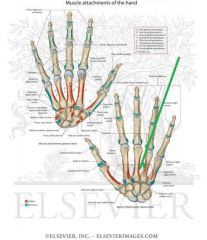
|
Dorsal Interosseous III Origin
|
|
|
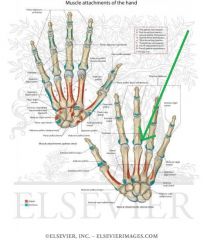
|
Dorsal Interosseous III Insertion
|
|
|
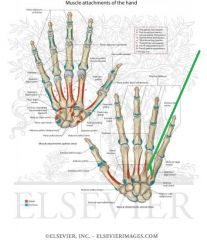
|
Dorsal Interosseous IV Origin
|
|
|
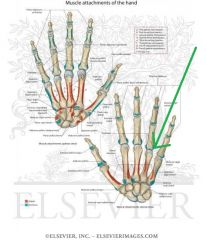
|
Dorsal Interosseous IV Insertion
|
|
|
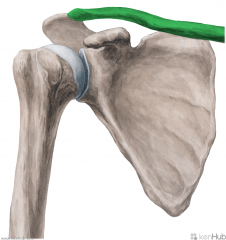
|
Clavicle:
(Clavicula -> Little Key: rotates on its axis like a key when the arm abducts) Long bone. The clavicle attaches the upper limb to the trunk; protects the underlying neurovascular structures supplying the upper limb; transmits force from the upper limb to the axial skeleton. This makes it the most commonly fractured bone in the body. Fractures commonly result from a fall onto the shoulder, or onto an outstretched hand. The most common point of fracture is the junction of the medial two thirds and lateral third. After fracture, the lateral end of the clavicle is displaced inferiorly by the weight of the arm, and medially, by the pectoralis major. The medial end is pulled superiorly, by the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The suprascapular nerves may be damaged by the upwards movement of the medial part of the fracture. These nerves innervate the lateral rotators of the upper limb at the shoulder – so damage results in unopposed medial rotation of the upper limb – the ‘waiters tip’ position. |
Clavicle
|
|
|
Scapula:
(Skatein -> To dig: has the appearance of a trowel) Flat bone. "Winging" of the scapula can accompany any weakness of the serratus anterior, especially damage to the long thoracic nerve. Movements: Elevation, Depression Protraction (abduction), Retraction (adduction) Upward (lateral) rotation, Downward (medial) rotation Anterior Tipping, Posterior Tipping |
Scapula
|
|

|
Humerus:
(Umerus -> Shoulder -> Is a bone of the shoulder) Long bone. Movements: Flexion, extenstion Abduction, adduction Circumduction Medial rotation, lateral rotation |
Humerus
|
|

|
Radius:
(Radius -> Ray/Rod/Spoke of a Wheel) Long bone. Movements: (together with ulna) Flexion, extension Pronation, supination |
Radius
|
|

|
Ulna:
(Ulna -> elbow) Long bone. Movements: (together with the radius) Flexion, extension Pronation, supination |
Ulna
|
|
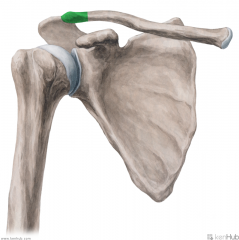
|
Acromial (Lateral) End of the Clavicle:
The acromial (lateral) end of the clavicle articulates with the acromion of the scapula to form the acromioclavicular joint. |
Acromial (Lateral) End of the Clavicle
|
|
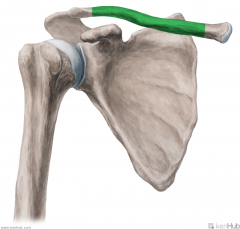
|
Shaft of the Clavicle:
Trapezius' superior head inserts onto the lateral third of the posterior border of the clavicle. Pectoralis major's clavicular head originates from the medial half of the anterior surface of the clavicle. Sternocleidomastoid's clavicular head originates from the medial third of the superior surface of the clavicle. Sternohyoid originates from the medial end of the posterior border of the inferior surface of the clavicle, medial to the costoclavicular ligament. |
Shaft of the Clavicle
|
|

|
Conoid Tubercle:
The conoid ligament attaches to the conoid tubercle. It is the medial part of the coracoclavicular ligament. |
Conoid Tubercle
|
|

|
Trapezoid Line:
The trapezoid ligament attaches to the trapezoid line. It is the lateral part of the coracoclavicular ligament. |
Trapezoid Line
|
|

|
Deltoid Tubercle:
Deltoid's clavicular (anterior) head originates from the deltoid tubercle of the clavicle. |
Deltoid Tubercle
|
|
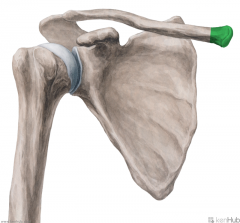
|
Sternal (Medial) End of the Clavicle:
The sternal end of the clavicle articulates with the sternal notch of the manubrium of the sternum to form the sternoclavicular joint. |
Sternal (Medial) End of the Clavicle
|
|

|
Subclavian Groove:
Subclavius inserts onto the subclavian groove of the clavicle. |
Subclavian Groove
|
|
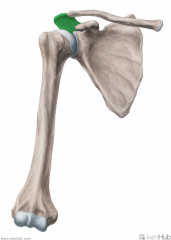
|
Acromion:
The acromion is a continuation of the spine of the scapula. Deltoid's acromial (lateral) head originates from the superior (lateral) surface of the acromion. Trapezius' middle head inserts onto the medial border of the acromion. The coracoacromial ligament attaches to the summit (lateral margin) of the acromion. |
Acromion
|
|
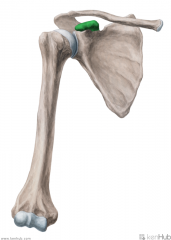
|
Coracoid Process:
Coracobrachialis originates from the lateral tip of the coracoid process. Biceps brachii's short head originates from the lateral tip of the coracoid process. Pectoralis minor inserts onto the anterior surface of the coracoid process. The coracoclavicular ligament attaches to the superior border of the coracoid process, with the conoid ligament medial to the trapezoid ligament. The coracoacromial ligament attaches to the superolateral surface of the coracoid process. The coracohumeral ligament attaches to the lateral border of the coracoid process. The superior transverse scapular ligament attaches to the base of the coracoid process, and bridges the suprascapular notch. |
Coracoid Process
|
|
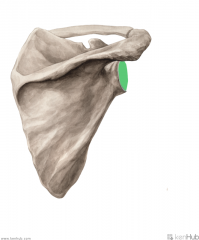
|
Glenoid Cavity (Fossa):
The glenoid cavity articulates with the head of the humerus to form the glenohumeral joint (synovial, ball-and-socket). The glenoid cavity is very shallow, allowing for the widest range of movement of all joints. The glenoid cavity's margins give rise to the fibrocatilagenous glenoid labrum, deepening the cavity. |
Glenoid Cavity (Fossa)
|
|
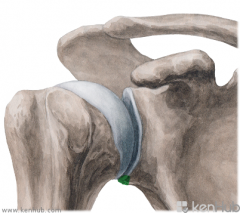
|
Infraglenoid Tubercle:
Triceps brachii's long head originates from the infraglenoid tubercle. |
Infraglenoid Tubercle
|
|
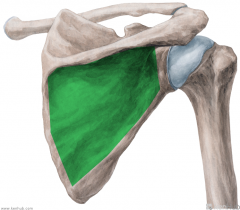
|
Infraspinous Fossa:
Infraspinatus originates from the infraspinous fossa. |
Infraspinous Fossa
|
|
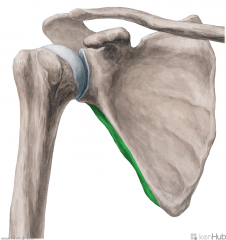
|
Lateral (Axillary) Border of the Scalupa:
Teres minor originates from the lateral (axillary) border of the scapula (from the superior two thirds). Teres major originates from the lateral (axillary) border of the scapula (from the posterior surface of the inferior angle). |
Lateral (Axillary) Border of the Scapula
|
|
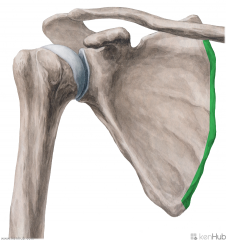
|
Medial Border of the Scapula:
Extends from the superior to the inferior angle. Serratus anterior inserts onto the anterior lip of the medial border of the scapula. Levator scapulae inserts onto the posterior lip of the medial border, superior to the level of the spine of the scapula. Rhomboid minor inserts onto the posterior lip of the medial border, at the level of the spine of the scapula. Rhomboid major inserts onto the posterior lip of the medial border, inferior to the level of the spine of the scapula. |
Medial Border of the Scapula
|
|
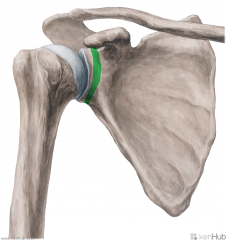
|
Anatomical Neck of the Scapula:
Fractures to this site are less common than fractures to the surgical neck of the scapula (exits medial to the coracoid process). This is a sign of severe chest trauma. It is most commonly seen in high-speed collisions, crushing injuries, or sports injuries. A fractured scapula does not require much intervention, as the tone of the surrounding muscles holds the pieces in place for healing to occur. The spinoglenoid notch is found on the dorsal surface of the neck of the scapula. |
Anatomical Neck of the Scapula
|
|
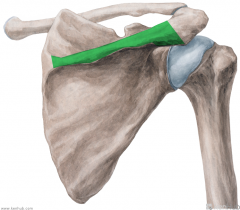
|
Spine of the Scapula:
Most prominent feature of the posterior of the scapula, it runs transversely, dividing the surface in two. Trapezius' middle head inserts onto the superior lip of the spine of the scapula. Deltoid's spinal (posterior) head originates from the inferior lip of the spine of the scapula. |
Spine of the Scapula
|
|
|
Spinoglenoid Notch:
Connects the supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa. The suprascapular nerve and suprascapular artery run through the spinoglenoid notch. |
Spinoglenoid Notch
|
|
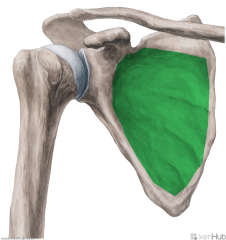
|
Subscapular Fossa:
Subscapularis originates from the subscapular fossa. |
Subscapular Fossa
|
|
|
Superior Border of the Scapula:
Runs from the superior angle to the base of the coracoid process. Its lateral end contains the suprascapular notch, which is transformed into a foramen by the superior transverse scapular ligament, and serves for the passage of the suprascapular nerve. If the ligament becomes ossified, it may cause paralysis of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. |
Superior Border of the Scapula
|
|
|
Supraglenoid Tubercle:
Biceps brachii's long head originates from the supraglenoid tubercle. |
Supraglenoid Tubercle
|
|
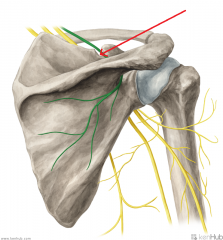
|
Suprascapular Notch:
The suprascapular nerve travels through the foramen created by the suprascapular notch and the superior transverse scapular ligament. If the ligament becomes ossified, it may cause paralysis of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. |
Suprascapular Notch
|
|
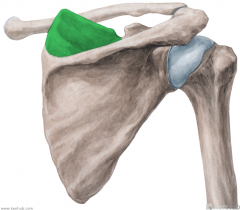
|
Supraspinous Fossa:
Supraspinatus originates from the supraspinous fossa. |
Supraspinous Fossa
|
|
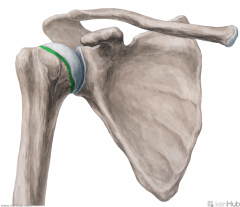
|
Anatomical Neck of the Humerus:
Attaches the head of the humerus to the tubercles. Attachment site for the articular capsule of the glenohumeral joint (synovial, ball-and-socket). |
Anatomical Neck of the Humerus
|
|
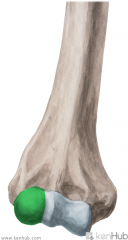
|
Capitulum of Humerus:
Articulates with the head of the radius. |
Capitulum of Humerus
|
|
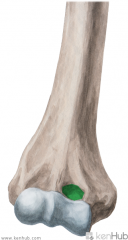
|
Coronoid Fossa:
Receives the coronoid process of the ulna during flexion of the forearm. |
Coronoid Fossa
|
|
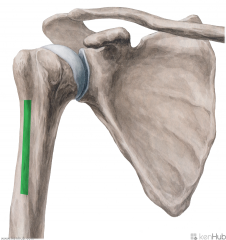
|
Crest of the Greater Tubercle or Lateral Lip of the Bicipital Groove:
Pectoralis major inserts into the crest of the greater tubercle. |
Crest of the Greater Tubercle or Lateral Lip of the Bicipital Groove
|
|
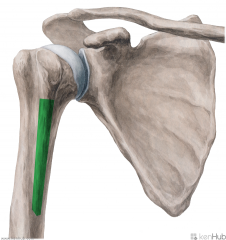
|
Crest of the Lesser Tubercle or Medial Lip of Bicipital Groove:
Teres major inserts onto the crest of the lesser tubercle. Latissimus dorsi inserts onto the crest of the lesser tubercle, between pectoralis major and teres major. |
Crest of the Lesser Tubercle or Medial Lip of Bicipital Groove
|
|
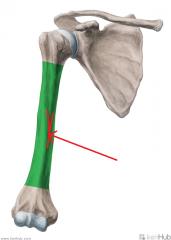
|
Deltoid Tuberosity:
Deltoid inserts onto the deltoid tuberosity. |
Deltoid Tuberosity
|
|
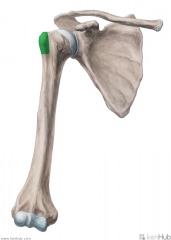
|
Greater Tubercle:
Supraspinatus inserts onto the superior facet of the greater tubercle. Infraspinatus inserts onto the middle facet of the greater tubercle. Teres minor inserts onto the inferior facet of the greater tubercle. |
Greater Tubercle
|
|
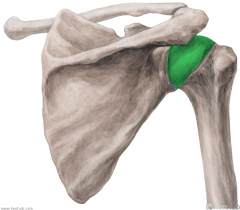
|
Head of the Humerus:
Articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the glenohumeral joint (synovial, ball-and-socket). |
Head of the Humerus
|
|
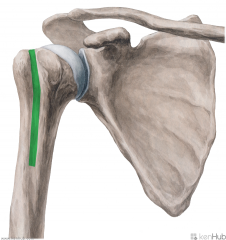
|
Intertubercular Sulcus or Bicipital Groove:
Biceps brachii's long head's tendon runs through this groove, between the tendons for pectoralis major and teres minor. |
Intertubercular Sulcus or Bicipital Groove
|
|
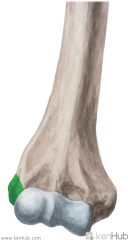
|
Lateral Epicondyle of the Humerus:
Site of the common extensor origin. Radial collateral ligament attaches to the lateral epicondyle. |
Lateral Epicondyle of the Humerus
|
|
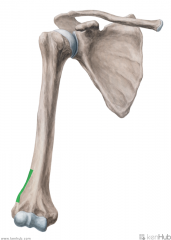
|
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge:
Brachioradialis originates from the anterior lip of the lateral supracondylar ridge. Extensor carpi radialis longus originates from the anterior lip of the lateral supracondylar ridge. Triceps brachii's medial head inserts partially onto the posterior lip of the lateral supracondylar ridge. A supracondylar fracture occurs by falling on a flexed elbow. It is a transverse fracture, spanning between the two epicondyles. Direct damage, or swelling, can cause interference to the blood supply of the forearm from the brachial artery. The resulting ischaemia can cause Volkmann’s ischaemic contracture – uncontrolled flexion of the hand, as flexors muscles become fibrotic and short. There also can be damage to the medial, ulnar or radial nerves. |
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge
|
|
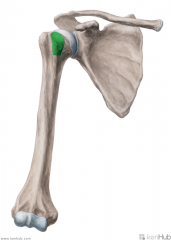
|
Lesser Tubercle:
Subscapularis inserts onto the lesser tubercle. |
Lesser Tubercle
|
|
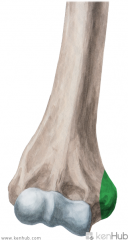
|
Medial Epicondyle of the Humerus:
Site of the common flexor origin. Ulnar collateral ligament of the elbow joint attaches to the medial epicondyle. A medial epicondyle fracture could damage the ulnar nerve, resulting in a deformity known as ulnar claw. There will be a loss of sensation over the medial one-and-a-half fingers of the hand, on both the dorsal and palmar surfaces. |
Medial Epicondyle of the Humerus
|
|
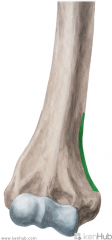
|
Medial Supracondylar Ridge:
Brachialis originates from the anterior lip of the medial supracondylar ridge. Pronator teres originates from the anterior lip of the medial supracondylar ridge. Triceps brachii's medial head inserts partially onto the medial supracondylar ridge. A supracondylar fracture occurs by falling on a flexed elbow. It is a transverse fracture, spanning between the two epicondyles. Direct damage, or swelling, can cause interference to the blood supply of the forearm from the brachial artery. The resulting ischaemia can cause Volkmann’s ischaemic contracture – uncontrolled flexion of the hand, as flexors muscles become fibrotic and short. There also can be damage to the medial, ulnar or radial nerves. |
Medial Supracondylar Ridge
|
|

|
Olecranon Fossa:
Receives the olecranon of the ulna during extension of the forearm. |
Olecranon Fossa
|
|
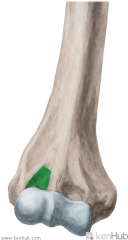
|
Radial Fossa:
Receives the head of the radius during flexion of the forearm. |
Radial Fossa
|
|
|
Radial Sulcus or Spiral Groove:
Radial nerve travels adjacent to the humerus in the radial sulcus. Deep brachial artery travels adjacent to the humeus in the radial sulcus. |
Radial Sulcus or Spiral Groove
|
|
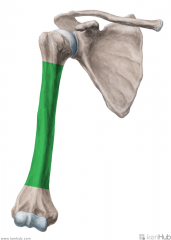
|
Shaft of the Humerus:
A mid-shaft fracture may damage the deep brachial artery and radial nerve where they are closely bound to the humerus in the radial sulcus, resulting in paralysis of the extensors. This results in unopposed flexion of the wrist, known as ‘wrist drop’. There is a some sensory loss over the dorsal surface of the hand, and the proximal ends of the lateral three-and-a-half fingers dorsally. |
Shaft of the Humerus
|
|
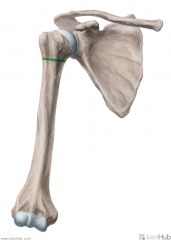
|
Surgical Neck of the Humerus:
A frequent site of fracture, occurring by a direct blow to the area, or by falling on an outstretched hand. This may damage the posterior circumflex humeral artery and the axillary nerve. Damage to the axillary nerve will result in paralysis to the deltoid and teres minor muscles; the patient will not being able to abduct their arm. The "regimental badge" area, innervated by the axillary nerve, may lose sensation also. |
Surgical Neck of the Humerus
|
|
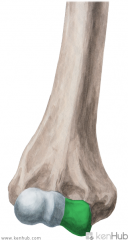
|
Trochlea of the Humerus:
Articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna. |
Trochlea of the Humerus
|
|
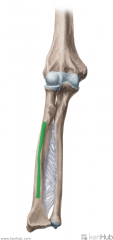
|
Anterior Border or Oblique Line of the Radius:
Limits the insertion of supinator. Supinator inserts on the lateral surface of the proximal third of the shaft of the radius, superior to the anterior oblique line. Flexor digitorum superficialis' radial head originates from the anterior oblique line. Flexor pollicis longus originates from the middle two quarters of the anterior surface of the radius. Pronator quadratus inserts onto the bottom quarter of the anterior surface of the radius. |
Anterior Border or Oblique Line of the Radius
|
|

|
Dorsal Radial Tubercle:
Serves as a pulley for extensor pollicis longus. |
Dorsal Radial Tubercle
|
|
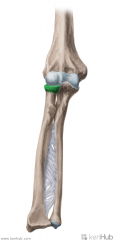
|
Head of the Radius:
Articulates with the capitulum of the humerus, forming the radiohumeral joint (synovial, ball-and-socket, shares a common synovial cavity with the proximal radioulnar joint and the humeroulnar joint). Articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, forming the proximal radioulnar joint (synovial, pivot joint, shares a common synovial cavity with the radiohumeral joint and humeroulnar joint). Annular ligament embraces the remaining surfaces of the head of the radius. |
Head of the Radius
|
|
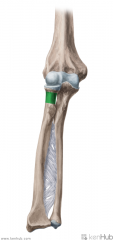
|
Neck of the Radius:
Supinator inserts partially onto the posterior surface of the neck of the radius. |
Neck of the Radius
|
|
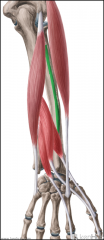
|
Posterior Surface of the Radius:
The posterior oblique line limits the insertion of supinator and pronator teres. Supinator inserts on the lateral surface of the proximal third of the shaft of the radius, superior to the posterior oblique line. Pronator teres inserts on the midpoint of thelateral surface of the shaft of the radius. Abductor pollicis longus' radial head originates from the middle of the posterior surface of the shaft of the radius, just inferior to the posterior oblique line. Extensor pollicis brevis originates from the medial border of the posterior surface of the shaft of the radius, just inferior to the abductor pollicis longus. |
Posterior Surface of the Radius
|
|
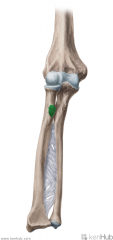
|
Radial Tuberosity:
Biceps brachii inserts onto the posterior (rough) surface of the radial tuberosity. On the anterior (smooth) surface of the radial tuberosity, a bursa is found between the tendon and the bone. |
Radial Tuberosity
|
|
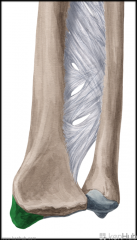
|
Styloid Process of the Radius:
(Styloid -> Pen -> Nib) Brachioradialis inserts onto the base of the styloid process of the radius. The radial collateral ligament of the wrist attaches to the apex of the styloid process of the radius. The lateral surface has a groove for the tendons of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis. "Chauffeur's fracture" of the radial styloid is caused by compression of the scaphoid bone against the styloid. |
Styloid Process of the Radius
|
|

|
Ulnar Notch:
Articulates with the head of the ulna, forming the distal radioulnar joint (pivot joint). The distal end of the radius articulates with the scaphoid and lunate bones. |
Ulnar Notch
|
|

|
Anterior Border of Ulna:
Pronator quadratus originates from the distal quarter of the shaft of the ulna. Supinator originates from the medial surface of the proximal quarter of the shaft of the ulna. |
Anterior Border of Ulna
|
|
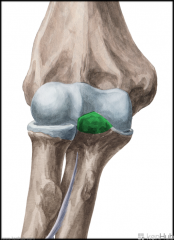
|
Coronoid Process:
Received into the coronoid fossa of the humerus during flexion of the forearm. Brachialis inserts partially onto the coronoid process. Pronator teres' ulnar head originates from the medial surface of the coronoid process. Flexor digitorum superficialis' ulnar head originates from the coronoid process. Flexor digitorum profundus' ulnar head originates from the coronoid process. |
Coronoid Process
|
|
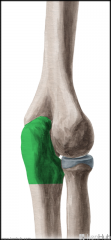
|
Olecranon:
Received by the olecranon fossa of the humerus during extension of the forearm. Prevents hyperextension. Triceps brachii inserts onto the superoposterior surface of the olecranon. Anconeus inserts onto the lateral surface of the olecranon. Flexor carpi ulnaris originates from the olecranon and posterior surface of the ulna. |
Olecranon
|
|

|
Radial Notch:
Articulates with the head of the radius, forming the proximal radioulnar joint (synovial, pivot joint, shares a common synovial cavity with the radiohumeral joint and the humeroulnar joint). |
Radial Notch
|
|
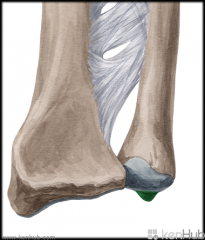
|
Styloid Process of Ulna:
(Styloid -> Pen -> Nib) The ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist attaches to the apex of the styloid process of the ulna. The lateral surface has a groove for the tendon of extensor carpi ulnaris. |
Styloid Process of Ulna
|
|

|
Trochlear Notch:
Articulates with the trochlea of the humerus. |
Trochlear Notch
|
|
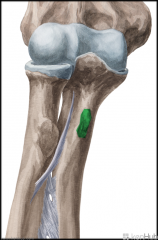
|
Ulnar Tuberosity:
Brachialis inserts partially onto the ulnar tuberosity. |
Ulnar Tuberosity
|
|
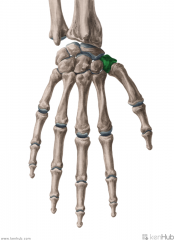
|
Trapezium:
Short bone. Radial border of the carpal tunnel. Articulates with the metacarpal of the thumb. |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
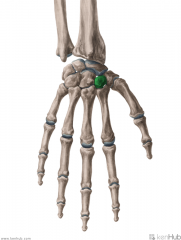
|
Trapezoid:
Short bone. |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
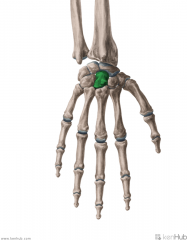
|
Capitate:
Short bone. |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
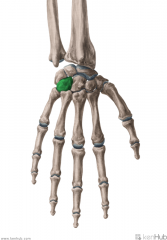
|
Hamate:
Short bone. Medial border of the carpal tunnel. Hook of hamate is a projection on its palmar surface. |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
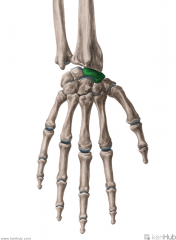
|
Scaphoid:
Short bone. Radial border of the carpal tunnel. Articulates with the radius to form the wrist joint (condyloid joint). |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
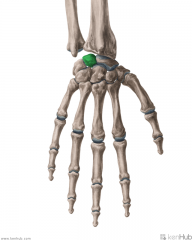
|
Lunate:
Short bone. Articulates with the radius to form the wrist joint (condyloid joint). |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
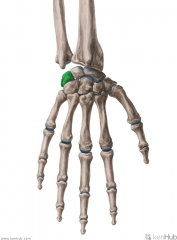
|
Triquetrum:
Short bone. |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
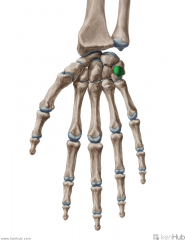
|
Pisiform:
Sesamoid bone, formed within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris. Medial border of the carpal tunnel. |
Touching Titties Can Help Students Learn To Palpate
|
|
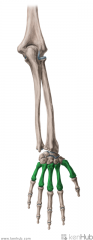
|
Metacarpals:
Long bones. |
Metacarpals
|
|
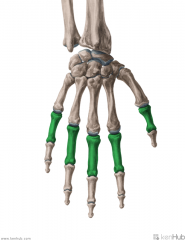
|
Proximal Phalanges of Hand:
Long bones. |
Proximal Phalanges of Hand
|
|
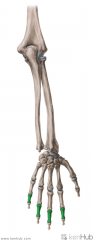
|
Middle Phalanges of the Hand:
Long bones. |
Middle Phalanges of the Hand
|
|
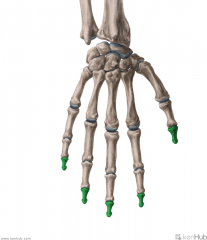
|
Distal Phalanges of the Hand:
Long bones. |
Distal Phalanges of the Hand
|
|
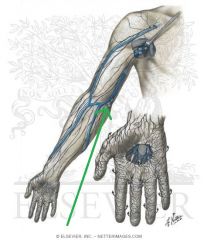
|
Cubital Lymph Nodes:
Position: Comprised of a deep and a superficial cubital lymph node. Afferent Vessels: Drain the forearm and hand on the ulnar side Efferent Vessels: Brachial and Axillary Lymph Nodes |
Cubital Lymph Nodes
|
|
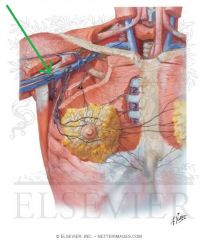
|
Brachial (Lateral Axillary) (Humeral) Lymph Nodes:
Position: Situated medial and posterior to the axillary vein. Afferent Vessels: Drain the arm except for the portion whose vessels accompany the Cephalic vein Efferent Vessels: Central Nodes Subclavicular Nodes Inferior Deep Cervical Nodes |
Brachial (Lateral Axillary) (Humeral) Lymph Nodes
|
|
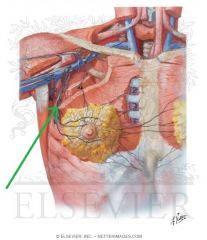
|
Pectoral (Anterior Axillary) Lymph Nodes:
Position: Along the border of pectoralis minor, tracing the Lateral thoracic artery Afferent Vessels: Skin and muscles of anterior and lateral thoracic walls Central and lateral parts of mamma Efferent Vessels: Central Lymph Nodes Subclavicular Nodes |
Pectoral (Anterior Axillary) Lymph Nodes
|
|
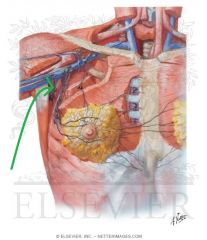
|
Subscapular (Posterior Axillary) Lymph Nodes:
Position: Lower margin of posterior wall of axilla, tracing Subscapular artery Afferent Vessels: Inferior part of dorsal neck Posterior thoracic wall Efferent Vessels: Central Axillary Lymph Nodes |
Subscapular (Posterior Axillary) Lymph Nodes
|
|
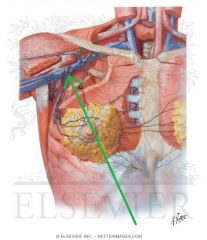
|
Central Axillary Lymph Nodes:
Position: Base of axilla, embedded in adipose tissue Afferent Vessels: Continuous with all preceding efferent vessels Efferent Vessels: Subclavicular Lymph Nodes |
Central Axillary Lymph Nodes
|
|
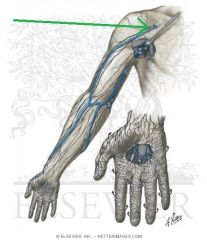
|
Deltopectoral (Infraclavicular) Lymph Nodes:
Position: Beside Cephalic vein, between pectoralis major and deltoid, immediately below the clavicle Afferent Vessels: Accompany Cephalic vein Efferent Vessels: Subclavicular Lymph Nodes |
Deltopectoral (Infraclavicular) Lymph Nodes
|
|
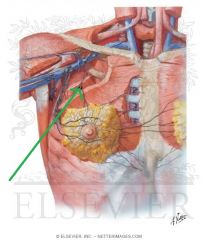
|
Interpectoral (Rotter's) Axillary Nodes:
Position: Between pectoralis major and pectoralis minor Afferent Vessels: Drain the muscles and mammary nodes Efferent Vessels: Subclavicular Axillary Lymph Nodes |
Interpectoral (Rotter's) Axillary Nodes
|
|
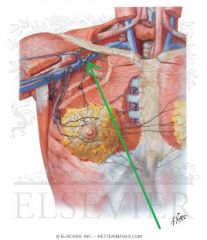
|
Subclavicular (Apical / Medial Axillary) Lymph Nodes:
Position: Posterior to the upper border of pectoralis minor Afferent Vessels: Accompany Cephalic vein Upper peripheral mamma Continuous with the efferent vessels of the Central Axillary and Deltopectoral Lymph Nodes Efferent Vessels: Unite to form the Subclavian Trunk On right: Opens into the junction of internal jugular and subclavian veins OR into the jugular lymphatic trunk On left: Ends in the thoracic duct |
Subclavicular (Apical / Medial Axillary) Lymph Nodes
|
|
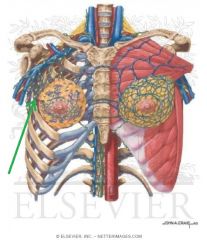
|
Paramammary (External Mammary) Axillary Lymph Nodes:
Position: Lateral to mammary gland Afferent Vessels: Mammary gland Efferent Vessels: Subclavicular Axillary Lymph Nodes |
Paramammary (External Mammary) Axillary Lymph Nodes
|
|
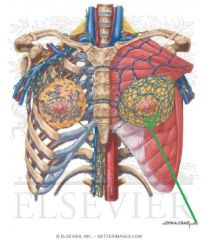
|
Sappey's (Subareolar Lymphatic) Plexus:
Position: Each lobule of breast has an extensive lymphatic plexus, which merge to form Sappey's subareolar plexus Afferent Vessels: Breast Efferent Vessels: Pectoral Axillary Lymph Nodes via the main collecting trunks |
Sappey's (Subareolar Lymphatic) Plexus
|
|
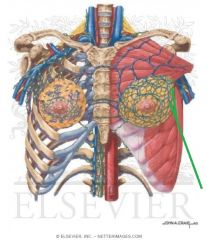
|
Main Lymphatic Collecting Trunks of the Breast:
Origin: Curve around the inferior surface of the breast, originating from either side of the areola Termination: Transmits lymphatic material from Sappey's plexus to the Pectoral Axillary Lymph Nodes |
Main Lymphatic Collecting Trunks of the Breast
|
|
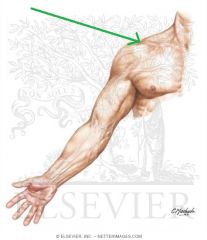
|
Acromion
|
|
|
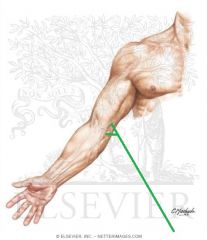
|
Basilic Vein
|
|
|
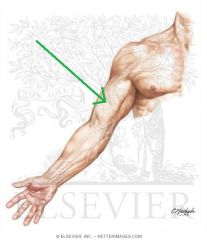
|
Biceps Brachii
|
|
|
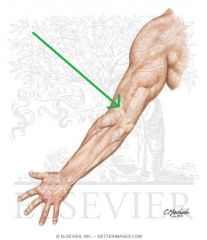
|
Brachioradialis
|
|
|
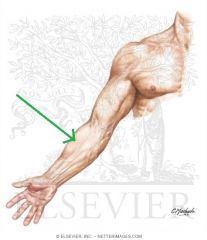
|
Brachioradialis
|
|
|
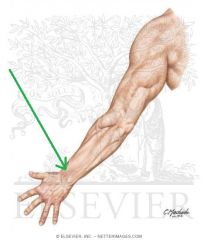
|
Cephalic Vein
|
|
|
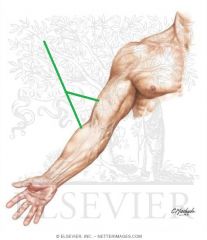
|
Cephalic Vein
|
|
|
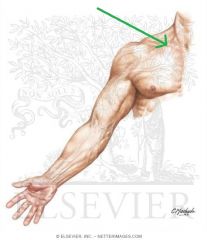
|
Clavicle
|
|
|
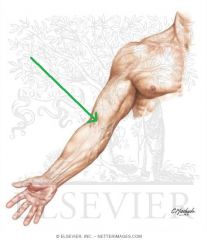
|
Cubital Fossa
|
|
|
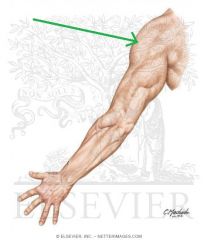
|
Deltoid
|
|
|
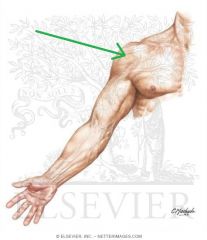
|
Deltoid
|
|
|

|
Distal Digital Crease
|
|
|
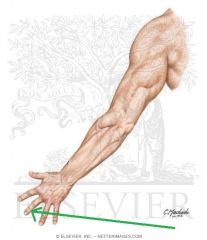
|
Distal Interphalangeal Joint
|
|
|
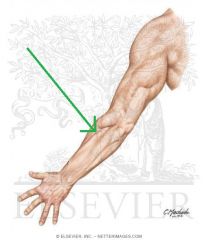
|
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
|
|
|
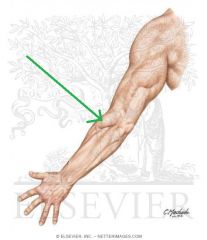
|
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
|
|
|
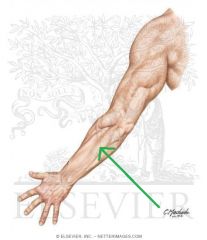
|
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
|
|
|
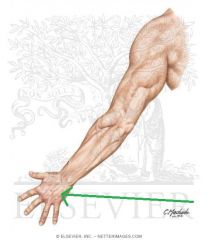
|
Extensor Digiti Minimi Tendon
|
|
|
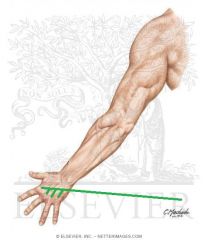
|
Extensor Digitorum Tendons
|
|
|
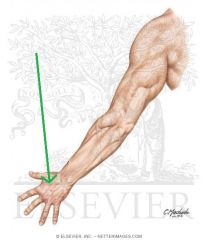
|
Extensor Indicis Tendon
|
|
|
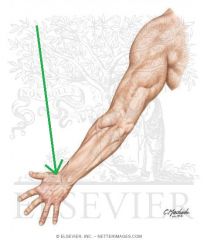
|
Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon
|
|
|
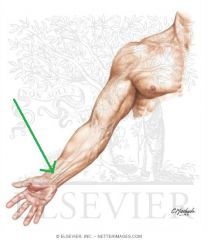
|
Flexor Carpi Radialis Tendon
|
|
|
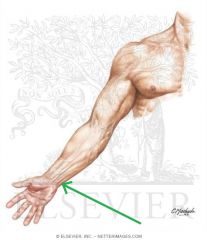
|
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Tendon
|
|
|
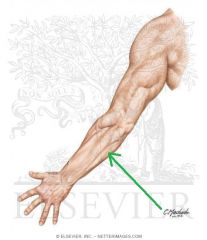
|
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
|
|
|
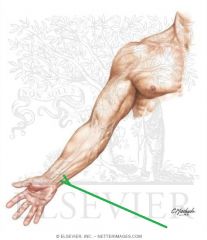
|
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Tendons
|
|
|
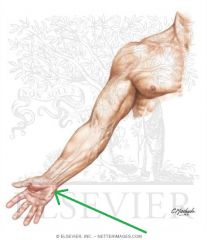
|
Hypothenar Eminence
|
|
|
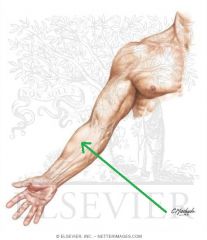
|
Median Antebrachial Vein
|
|
|
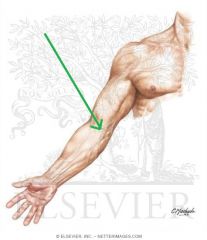
|
Median Cubital Vein
|
|
|
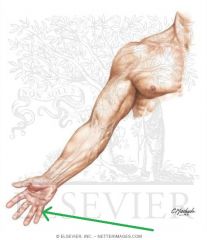
|
Middle Digital Crease
|
|
|
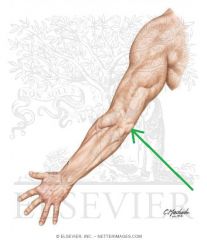
|
Olecranon
|
|
|
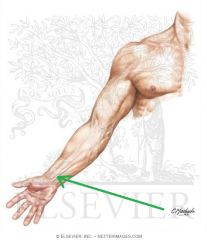
|
Palmaris Longus Tendon
|
|
|
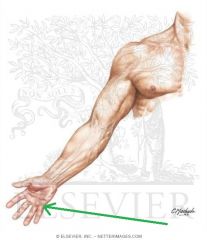
|
Proximal Digital Crease
|
|
|
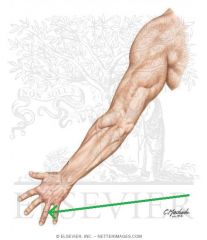
|
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
|
|
|
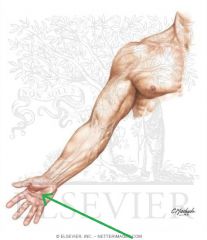
|
Proximal Palmar Crease
|
|
|
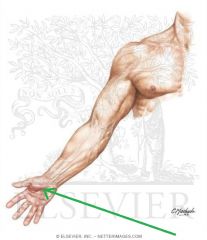
|
Radial Longitudinal Crease
|
|
|
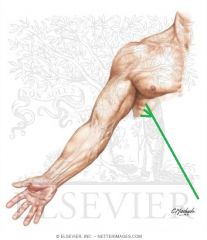
|
Serratus Anterior
|
|
|
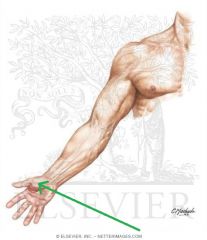
|
Thenar Eminence
|
|
|
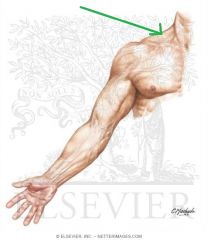
|
Trapezius
|
|
|
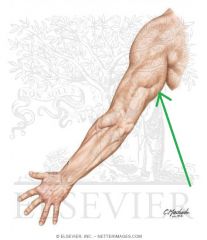
|
Triceps Brachii Long Head
|
|
|
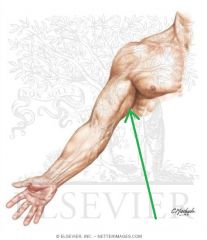
|
Triceps Brachii Long Head
|
|
|
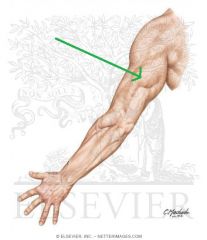
|
Triceps Brachii Medial Head
|
|
|
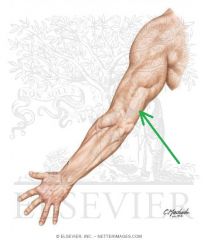
|
Triceps Brachii Tendon
|
|
|
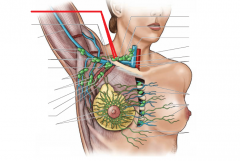
|
Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes:
Position: Superior to clavicle, palpable in the supraclavicular fossa Afferent Vessels: Right: From midsection of chest, oesophagus, lungs Left: Thoracic duct, abdominal region, thoracic region Efferent Vessels: Supraclavicular trunk |
Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes
|
|
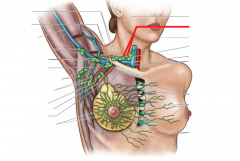
|
Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes:
Position: Near internal jugular vein Afferent Vessels: Neck Efferent Vessels: Jugular trunk |
Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes
|
|
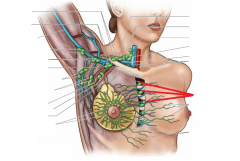
|
Parasternal Lymph Nodes:
Position: Lateral to the sternum Afferent Vessels: Mamma, liver, anterior abdominal wall, deeper parts of anterior thoracic wall Efferent Vessels: Bronchomediastinal trunk |
Parasternal Lymph Nodes
|
|
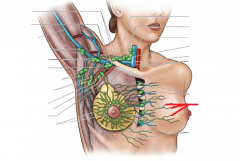
|
Lymphatics to Contralateral Breast
|
Lymphatics to Contralateral Breast
|
|
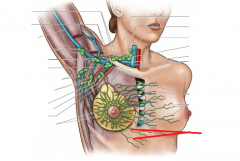
|
To Abdominal (Subdiaphragmatic) Lymphatics
|
To Abdominal (Subdiaphragmatic) Lymphatics
|

