![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass and volume |
|
|
|
Mass |
A measure of the quantity of matter in an object (kg or g) |
A brick has more mass than an equal sized volume of styrofoam |
|
|
Volume |
A measure of how big an object is or how much space a fluid takes up (L or mL) |
A volleyball is larger than a baseball |
|
|
The particle theory of matter |
A way to describe the structure of matter and its behaviour |
Particles are arranged differently in a solid, a liquid, or a gas |
|
|
Different states of matter |
Have spaces between them Attract each other Are always moving Move faster at higher temperatures |
|
|
|
Classification of matter |
All matter is composed of particles Each pure substance has its own kind of particle (different form the particles of other pure substances) |
|
|
|
Pure substances are always homogeneous since.... |
Each pure substance contains its own unique kind of particle |
|
|
|
Types of pure substances |
Elements and compounds |
|
|
|
Element |
Cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means |
Gold |
|
|
Compound |
Made from 2 or more elements that are combined together chemically |
Water |
|
|
Mixtures |
Homogeneous and heterogeneous |
Contain at least 2 kinds if particles |
|
|
Heterogeneous mixtures |
Mechanical mixtures and suspensions |
|
|
|
Mechanical mixtures |
The different substances that make up the mixture are visible |

|
|
|
Suspension |
A cloudy mixture in which tiny particles of one substance are held within another |

|
|
|
Homogeneous mixtures |
Solutions |
|
|
|
Solutions |
The different substances that make it up are not individually visible |

|
|
|
A summary of matter classification |

|
|
|
|
Changes of state |
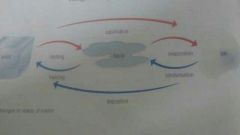
|
|
|
|
Physical properties can be measured/observed without changing the....of a substance. |
chemical identity |

|
|
|
A physical property is an.... characteristic of a substance. |
Observable |
Colour, lustre |
|
|
A physical property is a.... characteristic of a substance. |
Measurable |
Conductivity, density, ductility, hardness, malleability, viscosity |
|
|
Colour |
The light a substance reflects gives it colour |
Gold is golden |
|
|
Lustre |
The shine or dull of a substance |
Gold is lustrous, dirt is dull |
|
|
Conductivity |
Ability to conduct heat or electricity |
Copper wire is a conductor, plastic gloves are insulators |
|
|
Density |
Mass/volume |
Oil is less dense than water |
|
|
Ductility |
Any solid that can be stretched into a long wire |
Copper is ductile |
|
|
Hardness |
Ability to resist being scratched |
Diamonds |
|
|
Malleability |
How easily a substance can be pounded or rolled into sheets |
Aluminum foil |
|
|
Chemical properties describe the ability of a substance to....into.... |
Change, a new substance |
|
|
|
A chemical property is how a substance....with another |
Reacts |
|
|
|
Chemical properties can only be observed when a....occurs;that is when there is a....that results in the formation of a new substance(s) |
Chemical change, change in matter |
|
|
|
Heat absorption |
Ability to withstand temperature increase |
|
|
|
Combustible |
Ability to burst into flames with an ignition |
|
|
|
Forms gas |
Ability to release gas when reaction occurs |
|
|
|
Reacts with acid |
Will have a reaction with acid |
|
|
|
Reacts with water |
Will have a reaction with water |
|
|
|
Emits heat during reaction |
Temperature will increase during reaction |
|
|
|
Emits light during reaction |
Fluorescence during reaction |
|
|
|
Forms a precipitate in a solution |
Ability to form a solid when reaction occurs |
|

