![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pythagoras' Theorum |
For any right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. side + side = hypotenuse. |
|
|
Finding Angles |
1. Label and identify which two sides are given. 2. Decide which rule to use (SOH-CAH-TOA) 3. Substitute values and solve using calculator: sin-1 / cos-1 / tan-1 |
|
|
Finding Angles (part 2) |

5 ÷ 10 angle = sin-1(5÷10) |
|
|
Finding a Side |
1. Label the sides H, O and A 2. Identify which two sides you are working with 3. Decide which rule to use 4. Substitute values and rearrange to solve. |
|
|
Finding a Side (part 2) |
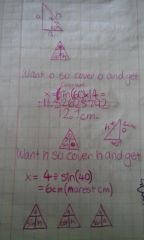
x = sin(60) x 14 |
|
|
Standard Form |
On average it is 3.84403x10^5 km to the moon. How far is it there and back again? 3.84403 x 10^5 x 2 = 768806 km or 7.68806x10^5 |
|
|
Calculating % of Amount |
Multiply the percentage as a fraction or a decimal by the amount. |
|
|
Calculate Original Quantity |
To calculate the original quantity we reverse the process of working out percentages of quantities. |
|
|
Increasing and decreasing % |
When you increase use (100 + %) ÷ 100 When you decrease use (100 - %) ÷ 100 |
|
|
GST |
To include or exclude GST use 1.15 GST increase = x 1.15 GST decrease = ÷ 1.15 |
|
|
Calculating Percentage Change |
Percentage = difference in values x 100 original amount The number of senior girls boarding at the hostel increases from 60 to 75. What % increase is that? 15 <-- 75 - 60 = 15 difference ---- = 0.25 x 100 = 25% 60 <-- original |
|
|
Rules |
A | M 1| 6 (+5) 2| 11 (+5) 3| 16 (+5) = M = 5A+1 |
|
|
Horizontal Line (Gradient) |
A horizontal line has a gradient of 0 (the rise = 0) |
|
|
Vertical Ling (Gradient) |
A vertical line has a gradient that is undefined (the run = 0) |
|
|
Uphill and Downhill lines |
A line that is going up hill is positive. / / / A line that is going down hill is negative. \ \ \ |
|
|
Zero Term |
The number (- x/ + x) at the end of the term M = 5A+1 +1 = zero term |
|
|
Draw Lines With a Certain Gradient |
1. Mark the start (Y intercept or zero term) 2. Count the number of squares up (go down if the gradient is negative) 3. Count the numbers of squares right 4. If there is no run (i.e. the gradient is a whole number) always go right 1. 5. Mark the end point 6. Join the points up |
|
|
Expanding |
(h+2)(h+7) F = h x h = h² O = h x 7 = 7h = h² + 9h + 14 I = 2 x h = 2h L = 2 x 7 = 14 |
|
|
Factorizing |
x² + 7x + 12 = (x + 3)(x + 4) The numbers in the brackets need to be factors of 12 that add to 7. Write a list of possible factors if needed and check which adds to the correct sum. |
|
|
Factorizing (HARD) |
6J - 5J = 3 x 2 x J x J - 3 x 5 x J = 3J (2J - 5) 3 = Outside 2 = Inside |

