![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
An expression involving a combination of real and imaginary numbers |
Complex number |
|
|
|
Rational and irrational numbers taken together |
Real numbers |
|
|
|
The square roots of negative numbers |
Imaginary numbers |
|
|
|
Equation of the logarithmic form |
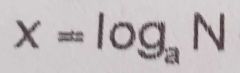
|
|
|
|
Equation of the exponential form of logarithm |
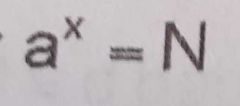
|
|
|
|
Equation that illustrates the additive inverse property of real numbers |
a + ( - a ) = 0 |
|
|
|
Identity element for addition |
0 |
|
|
|
Identity element for multiplication |
1 |
|
|
|
If a = b = a. This illustrates which axiom in algebra |
Symmetric axiom |
|
|
|
In algebra, the operation of root extraction is called |
Evolution |
|
|
|
If equals are added to equals, the result are equal. |
Axiom |
|
|
|
A mathematical argument that appears to prove something that we know is incorrect |
Fallacy |
|
|
|
"Googol" is one of the smallest large numbers. What does it stand for? |
1 followed by a hundred of 0s |
|
|
|
Irrational numbers are also known as? |
Transcendental numbers |
|
|
|
A number which is divisible by the sum of its own digit is called |
Harshad number |
|
|
|
Who introduced the multiplication symbol "X" in mathematics? |
William Oughtred |
|
|
|
Who introduced the symbol "=" for equality? |
Robert Recorde |
|
|
|
Who invented the symbol "n!" for factorial of n? |
Christian Kramp |
|
|
|
A recursive sequence where starting with the first two terms 1, 1, each new term is obtained by adding together the two previous terms |
Fibonacci Sequence |
|
|
|
A recursive sequence where starting with the first two terms 1, 3, each new term is obtained by adding together the two previous terms |
Lucas Sequence |
|
|
|
Formula for a_n of Fibonacci |
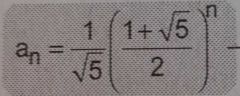
|
|
|
|
A sequence of numbers called terms in which the difference between any two consecutive term is constant |
Arithmetic Progression |
|
|
|
Sequence of numbers called terms in which the ratio of each term to its preceding term remains the same |
Geometric Progression |
|
|
|
Sequence of numbers called terms in which each term is the reciprocal of the corresponding term of a series in arithmetic progression |
Harmonic Progression |
|
|
|
An array of numbers in the shape of an Isosceles triangle, having a 1 at the top and also at the ends of each line. All the other numbers are made by adding the pair of numbers closest to them in the line above. |
Pascal's Triangle |
|
|
|
An arrangement of a set of objects or things in a specific or definite order |
Permutation |
|
|
|
An arrangement of a set of objects or things where order does not count |
Combination |
|
|
|
A branch of mathematics that deals with the theory and method of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpeeting data. |
Statistics |
|
|
|
Defined as the totality of objects, individuals, or reactions, which have common observable characteristics |
Population |
|
|
|
Variable that can be obtained through counting like the number of deaths, births, students, marriages at any given time |
Discrete variable |
|
|
|
The variable whose values can never be exact no matter what we do in getting the measurement |
Comtinuous variable |
|
|
|
A branch of mathematics dealing with the relations of the sides and angles of triangles and with the relevant functions of any angles |
Trigonometry |
|
|
|
A triangle having no equal sides |
Scalene Triangle |
|
|
|
A triangle having at least two equal sides |
Isosceles Triangle |
|
|
|
A triangle having three equal sides |
Equilateral Triangle |
|
|
|
A triangle having a right angle |
Right Triangle |
|
|
|
A triangle having an obtuse angle |
Obtuse Triangle |
|
|
|
A triangle having three acute angles |
Acute Triangle |
|
|
|
The point of intersection of all the medians of a triangle |
Centroid |
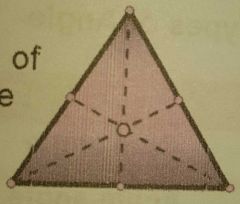
|
|
|
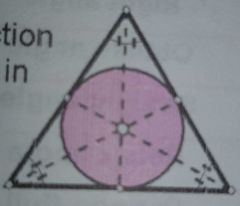
The point of intersection of all angle bisectors in a triangle. |
Incenter or Center of the inscribed circle in a triangle |
|
|
|
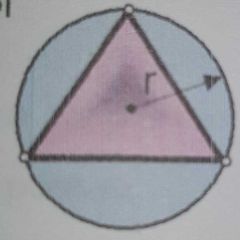
The point of intersection of all perpendicular bisectors of a triangle |
Circumcenter or Center of the circumscribed circle |
|
|
|
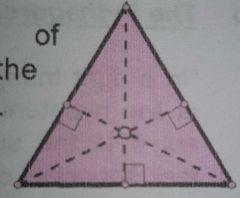
The point of intersection of all the altitudes of a triangle |
Orthocenter |
|
|
|
Center of the escribed center |
Excenter |
|
|
|
A circle that can be constructed for any given triangle by passing through nine significant points defined from the triangle |
Nine-point circle or Feuerbach's circle or Euler's Circle |
|
|
|
A line that passes through centroid, circumcenter, orthocenter, and the center of a nine-point circle of a triangle |
Euler's Line |
|
|
|
A theorem relating the lengthof a median of a triangle to the lengths of its sides |
Apollonius' Theorem |
|
|
|
Binomial Theorem's General term of the expansion |

|
|
|
|
nth term formula of an Arithmetic Progression |

|
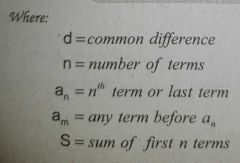
|
|
|
Sum formula of Arithmetic Progression |

|
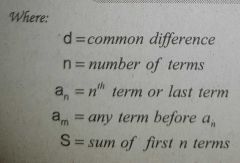
|
|
|
Arithmetic Progression Mean Formula |
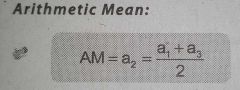
|
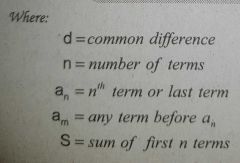
|
|
|
nth term formula of a Geometric Progression |
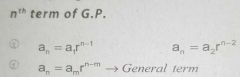
|

|
|
|
Formula for the Sum of Finite Geometric Progression |

|

|
|
|
Formula for the Sum of Infinite Geometric Progression |
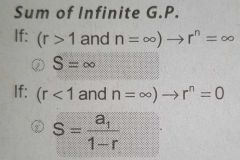
|

|
|
|
Formula for the Mean of a Geometric Progression |
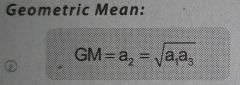
|

|
|
|
Formula for the Mean of an Harmonic Progression |
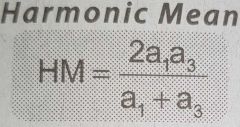
|
|
|
|
Formula for the Apollonius' Theorem |
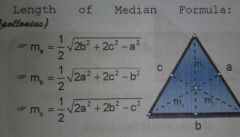
|
|
|
|
A repetition of an experiment |
Trial |
|
|
|
The result of each trial |
Outcome |
|
|
|
The set of all possible outcomes |
Sample Space |
|
|
|
An element of a sample space or the specific outcome of the experiment |
Sample Point |
|
|
|
A subset of a sample space - one or more sample points |
Event |
|
|
|
Formula for the Probability that the event will not happen |
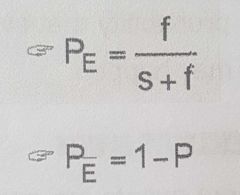
|

|
|
|
Formula for the Mathematical Expectation |
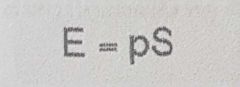
|

|
|
|
The ratio of the probability of an event's occuring to the probability of its not occurring |
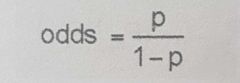
Odds |

|
|
|
Two or more events that cannot occur simultaneously |
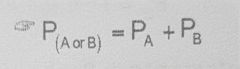
Mutually Exclusive Events |

|
|
|
Two or more events that one or the other or both can occur |
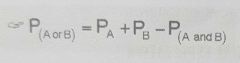
Mutually Inclusive Events |

|
|
|
Two events that its occurence or non-occurence of one has no effect on the probability of the occurence of the other |
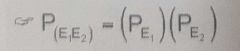
Independent Events |

|
|
|
Two events that its occurence or non-occurence of one affect the probability of the occurence of the other. |
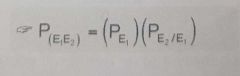
Dependent Events |

|
|
|
Given two events, A and B, if the probability of event B is affected of the occurence of event A, then the probability of event B is said to be conditional to that of A. In general, the condition that A occurs reduces the entire sample space to the sample space of A |

Conditional Probability |
|

