![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Marketing Mix |
Product- need satisfying market offering Price- how much it will charge Placement- how it will be made available to target customers Promotion- communicate with target customers about the offering and pursuade them of its merits |
4 Ps of Marketing |
|
|
Marketing |
1. Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships 2. The process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return |
|
|
|
Marketing myopia |
The mistake of paying more attention to the specific products a company offers than to the benefits and experiences produced by these products |
|
|
|
Needs, Wants, and Demands |
Needs- state of felt deprivation Wants- the form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality Demands- human wants that are backed by buying power |
|
|
|
Market offerings |
Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want |
|
|
|
Model of the marketing process 4 steps 1 result |
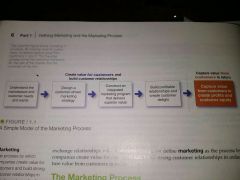
|
|
|
|
Exchange |
The act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return |
|
|
|
Market |
The set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service |
|
|
|
Marketing Management |
The art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them |
|
|
|
Costumer value and satisfaction |
Balance expectations and reality |
|
|
|
Market segmentation and target marketing |
Market segment- splitting the market up into categories Target Marketing- choosing which categories to go after |
|
|
|
Value proposition |
What you propose to the customer your product will do for them |
|
|
|
Marketing management orientations |
Production-consumers favor products that are affordable; focus on improving production and distribution Product- customer will favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and features; focus on product development Selling- customers will not buy enough of firm's products unless the firm undertakes large-scale selling and promotion efforts Marketing-a Philosophy in which achieving organizational goals depends on knowing the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfaction better than competitors do. Societal- a company's marketing decisions should consider consumers' wants, the company's requirements, consumers' long-run interests, and society's long-run interests |
|
|
|
Customer relationship management |
Overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction |
|
|
|
Customer-perceived value |
Customer's evaluation of difference between benefits and costs of a marketing offer relative to those of competing offers |
|
|
|
Customer Satisfaction |
The extent to which a product's perceived performance matches a buyer's expectations |
|
|
|
Customer managed relationships |
Marketing relationships in which customers, empowered by today's new digital technologies, interact with companies and with each other to shape their relationships with brands. |
|
|
|
Consumer-generated marketing |
Brand exchanges created by customers themselves- both invited and uninvited- by which consumers are playing am increasing role in shaping their own brand experiences and those of other consumers |
|
|
|
Partner relationship management |
Working closely with partners in other company departments and outside the company to jointly bring greater value to customers |
|
|
|
Customer lifetime value |
The value of the entire stream of purchases a customer makes over a lifetime or patronage |
|
|
|
Share of customer |
The portion of the customer's purchasing that a company gets in its product categories |
|
|
|
Customer equity |
The total combined customer lifetime values of all of the company's customers |
|
|
|
What is marketing chart |
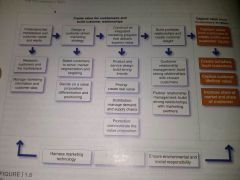
Bottom says managing global markets |
|
|
|
Steps in strategic planning |
Corporate level- 1. Defining the company mission 2. Setting company objectives and goals 3. Designing the business portfolio Business unit, product, and marketing level- 4. Planning marketing and other functional strategies |
|
|
|
Strategic planning |
The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization's goals and capabilities and it's changing marketing opportunities |
|
|
|
Mission statement |
A statement of the organization's purpose- what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment |
|
|
|
Business portfolio |
The collection of businesses and products that make up the company |
|
|
|
Portfolio analysis |
The process by which management evaluates the products and businesses that make up the company |
|
|
|
Boston Consulting Group's Growth-Share Matrix |
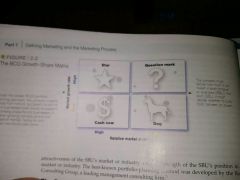
Grey dots represent SBUs (strategic business unit) |
|
|
|
SBU (Meaning) |
Strategic Business Unit |
|
|
|
Growth-Share Matrix |
A portfolio-planning method that evaluates a company's Strategic business units in terms of market growth and relative market share |
|
|
|
Product market expansion grid |
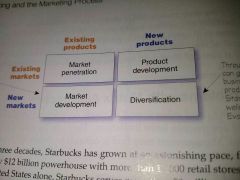
A portfolio-planning tool for identifying company growth opportunities through market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification |
|
|
|
Market penetration |
Company growth by increasing sales of current products to current market segments without changing the product. |
|
|
|
Market development |
Company growth by identifying and developing new market segments for current company products |
|
|
|
Product development |
Company growth by offering modified or new products to current market segments |
|
|
|
Diversification |
Company growth through starting up or acquiring businesses outside the company's current products and markets |
|
|
|
Value Chain |
The series of internal departments that carry out value-creating activities to design, produce, market, deliver, and support a firm's products |
|
|
|
Value delivery method |
The network made up of the company, its suppliers, it's distributers, and, ultimately, its customers who partner with each other to improve the performance of the entire system |
|
|
|
Managing marketing strategies and the marketing mix |

Flash covers "marketing control" |
|
|
|
Marketing strategy |
The marketing logic by which the company hopes to create customer value and achieve profitable customer relationships |
|
|
|
Positioning |
Arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target consumers |
|
|
|
Differentiation |
Actually differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value |
|
|
|
Marketing mix full definition |
The set of tactical marketing tools- product, price, place, and promotion- that the firm blends to produce the response it wants on the target market |
|
|
|
The four Ps of the marketing mix figure 2.5 |
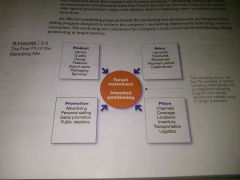
|
|
|
|
Managing Marketing: Analysis, Planning, Implementation, and Control fig 2.6 |
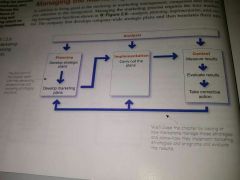
|
|
|
|
SWOT Analysis |

Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats |
|
|
|
Marketing implementation |
Turning marketing strategies and plans onto marketing actions to accomplish strategic marketing objectives |
|
|
|
Marketing Control |
Measuring and evaluating the results of marketing strategies and plans and taking corrective action to ensure that the objectives are achieved |
|
|
|
Return on marketing Investment (or marketing ROI) |
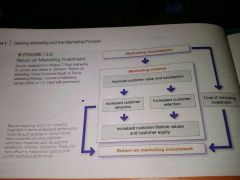
The net return from a marketing Investment divided by the costs of the marketing investment |
|

