![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Marketing |
Marketing is an organization function and a set of processes for creating, capturing, communicating, and delivering value to customers. |
|
|
Marketing Mix |
Product, Place, Promotion, Price |
|
|
Product |
Creating Value by developing a variety of offerings, including goods, services, and ideas, to satisfy customer needs. |
|
|
Place |
Delivering Value represents all the activities necessary to get the product to the right customer when that customer wants it. |
|
|
Promotion |
Communicating Value communication by a marketer that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers about a product or service to influence their opinions and elicit a response |
|
|
Price |
Capturing Value is everything the buyer gives up—money, time, energy—in exchange for the product. |
|
|
Where are we now with marketing? |
Value Based Marketing firms today are market oriented meaning they give the consumers what they need and want at a better value than their competitors |
|
|
Why is marketing important? |
Expands Firms' Global Presence expand firms' global presence and global career opportunities Pervasive across Marketing Channel Members supply chain relationship benefits all parties Enriches Society good corporate citizenry: greener products, healthier options, etc.. Can Be Entrepreneurial launch ventures that aim to satisfy unfilled needs
|
|
|
The Marketing Plan (flowchart) |
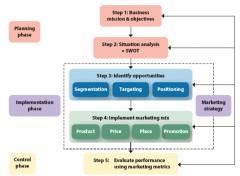
|
|
|
Sustainable Competitive Advantage |
Something a firm can persistently do better than its competitors and is not easily copied Consists of 4 Macro Strategies: 1. Customer Excellence 2. Operational Excellence 3. Product Excellence 4. Locational Excellence |
|
|
Customer Excellence |
focuses on retaining loyal customers and excellent customer service |
|
|
Operational Excellence |
Achieved through efficient operations and excellent supply chain and human resource management |
|
|
Product Excellence |
having products with high perceived value and effective branding and positioning |
|
|
Locational Excellence |
having a good physical location and internet presence |
|
|
Market Segmentation |
process of dividing the marketing into groups of customers with different needs, wants or characteristics |
|
|
Targeting |
aka: Target Marketing identifying and deciding with market segment to pursue |
|
|
Positioning |
process of defining the marketing mix variables so that target customers have clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does or represents compared to competing products |
|
|
Diversification |
introduces a new product or service to a market segment that currently is not served. |
|
|
product development strategy |
offers a new product or service to a firm's current target market |
|
|
market development strategy |
employs the existing marketing offering to reach new market segments, whether domestic or international. |
|
|
market penetration strategy |
employs the existing marketing mix and focuses the firm's efforts on existing customers. |
|
|
Growth Strategies |
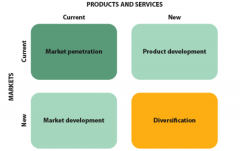
|
|
|
BCG Matrix |
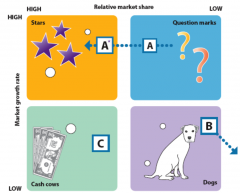
|
|
|
Macro-enviromental Factors |
Cultural Demographic Social Technology Economic Political |
|
|
Immediate Environment |
Company Competition Corporate Partners |
|
|
Marketing Environment |
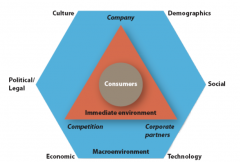
|
|
|
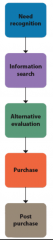
Consumer Decision Process |
|
|
|
Functional Needs |
Pertain to the performance of a product orservice. |
|
|
Psychological Needs |
Pertain to the personal gratification consumers associate with a product or service. |
|
|
internal locus of control |
believe they have some control over the outcomes of their actions, in which case they generally engage in more search activities |
|
|
external locus of control |
consumers believe that fate or other external factors control all outcomes |
|
|
Performance risk |
Involves the perceived danger inherent in a poorly performing product or service. |
|
|
Financial risk |
risk associated with a monetary outlay; includes the initial cost of the purchase, as well as the costs of using the item or service. |
|
|
Social risk |
The fears that consumers suffer when they worry others might not regard their purchases positively. |
|
|
Physiological risk |
AKA: Safety Riskthe fear of an actual harm should a product not perform properly. |
|
|
evoked set |
Comprises the alternative brands or stores that the consumer states he or she would consider when making a purchase decision. |
|
|
retrieval sets |
Includes those brands or stores that the consumer can readily bring forth from memory. |
|
|
Universal sets |
Includes all possible choices for a product-category. |
|
|
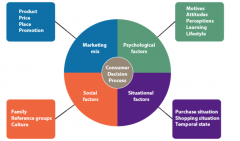
Factor influencing consumer decisions |
|
|
|
Cognitive Dissonance |
firms attempt to reduce dissonance by reinforcing the decisionthank you letter, congrats letter, quality ratings |
|
|
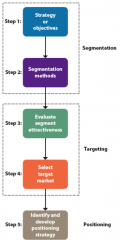
STP Process |
|
|
|
Step 1: Strategy or Objective |
the vision or objectives of the company’s marketing strategy consistent with & derived from mission and objectives and current situation (SWOT) |
|
|
Step 2: Segmentation |
Use a method or combination of methods to segment the marketGeographic, Demographic, Psychographic, Benefit, Behavioral |
|
|
Step 3: Evaluate Segment Attractiveness |
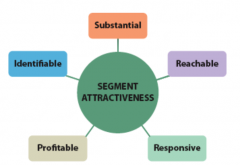
Identifiable - identify who is the target market Substantial- measure market sizeReachable - educate customer about product Responsive - customer must want to buy Profitable - make money |
|
|
Step 4: Selecting a Target Market |
Where do the firm’s competencies meet the attractiveness of a target market (SWOT & Profitability) |
|
|
Micro marketing/one-to-one marketing |
tailoring a product/service to suit an individual customer’s wants or needs Ex. My M&M’s |
|
|
Concentrated |
concentrate on a single, primary target market with all energies/resources Ex. Newton Shoes |
|
|
Differentiated |
target several markets with a different offering for reach Ex. Coca Cola |
|
|
Step 5: Develop Positioning Strategy |
Process of defining the marketing mix variables so that target customers have a clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does or represents incomparison to the competition |
|
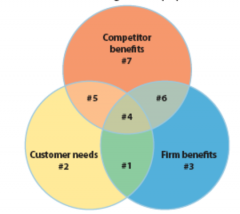
Value Proposition What is #1? |
The firm's value propositionReveals customer needs are effectively met by the firm provides but not by competitors |
|
|
The Research Plan |
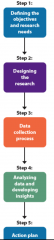
|
|
|
•Research is expensive and time-consuming •MUST know exactly what problem needs tone solved •Define objectives of the research •Assess value: Benefit of Answer vs. Cost of Research Question •Question(s) should be: relevant. able to be answered through research, currently unknown |
|
|
researchers identify the type of data needed and determine the research necessary to collect it. |
|
|
Data collection begins only after the research design process |
|
|
To generate meaningful information, researchers analyze and make use of the collected data |
|

|
•Summary of research findings •Prepare a detailed report and/or presentation for decision makers •Develop action plan •Implement action plan to solve the originally defined problems. |
|
|
Secondary Data |
Pieces of information that have already been collected from other sources and usually are readily available. Secondary data include both external and internal data sources National Purchase Diary Panel and ACNielsen |
|
|
Primary Data |
Data collected to address specific research needs.Some common primary data collection methods include focus groups, in-depth interviews, and surveys. |
|
|
qualitative research |
Informal research methods, including observation, following social media sites, in-depth interviews, focus groups, and projective techniques. Observations, Focus Groups, Social Media, In-depth interviews |
|
|
Quantitative research |
provides information needed to confirm insights and hypotheses generated via qualitative research or secondary data and helps managers pursue appropriate courses of action. experiments, scanner, survey, and panel data |
|
|
Chapter 11: Guest Speaker Columbus Crew |
wanted to keep somethings the same, make specific to Columbus. did "in-house", no one else knew the team, sport, Columbus like them 3 brand pillars - original, energetic, authentically Columbus measured success through social media, voted best logo, 90% approval rate, increase in sales, stadium sponsored for first time |
|
|
How Personal Selling Adds Value |
provides information and advise save time and simplify buying build relationships |
|
|
Selling Process |
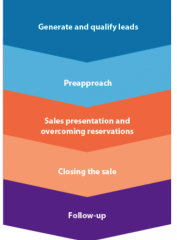
|
|
|
Integrated marketing communications (IMC) |
Represents the promotion dimension of the four Ps encompasses a variety of communication—general advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, and electronic media |
|
|
3 elements in any IMC strategy: |
the consumerthe channels through which the message is communicatedthe evaluation of the results of the communication. |
|
|
core customer value |
The basic problem solving benefits that consumers are seeking. |
|
|
actual product |
The physical attributes of a product including the brand name, features/design, quality level, and packaging. |
|
|
augmented product |
The non-physical attributes of the product including product warranties, financing, product support, and after-sale service. |
|
|
Specialty Products/Services |
Products or services toward which the customer shows a strong preference and for which he or she will expend considerable effort to search for the best suppliers. |
|
|
Shopping Products/Services |
Those for which consumers will spend time comparing alternatives, such as apparel, fragrances, and appliances. |
|
|
unsought product/services |
Products or services consumers either do not normally think of buying or do not know about. |
|
|
convenience goods/services |
those for which the consumer is not willing to spend any effort to evaluate prior to purchase. |
|
|
Depth vs. Breadth |

Bredth is the product mix Depth is the product lines |
|
|
Branding brings value
|
Facilitate Purchases Establish Loyalty Brands Are Assets Protect from Competition & Price Competition Impart market value |
|
|
How to measure brand equity
|
brand loyalty
brand awareness brand associations perceived value |

