![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List Porter's 5 forces |
- Threat of entry - Power of supplier - Threat of substitutes - Rivalry of competitors - Bargaining power of consumers |
|
|
Describe the levels of market competition |
- Product form: Convincing that brand is better that others in product form - Product category: Convincing that product is best in the category - Generic: Convincing that product category is best way to satisfy needs - Budget: Convincing that generic benefits most appropriate way of spending budget |
|
|
List the factors of a situation analysis |
- External --> Macro (Economic, technology, social, demographic & legal) --> Micro (Suppliers, substitutes, buyers, new entrants & competitors) - Internal --> Marketing --> Financial --> Human Resources --> Competitive advantages/disadvantages |
|
|
List the different aggregate market factors |
- Category size - Category growth - Stage in the product life cycle - Sales cyclicity - Seasonality - Profits |
|
|
List the different elements of the marketing plan |
- Executive summary - Situation analysis - Objectives - Product & brand strategies - Supporting marketing programs - Budget & financials - Monitor & controls - Implementation & contingency |
|
|
List conditions for a high threat of entry |
- Low barriers of entry - Low switching costs - Low capital requirements - Low supply side economies of scale - Low demand side economies of scale - Low incumbency advantages - Unequal access to distribution channels - Restrictive government policy |
|
|
List conditions for high power of suppliers |
- Few firms - Not dependent on customers for revenue - High customer switching costs - Supplier's products are highly differentiated - No substitutes for products - Easy supplier forward integration |
|
|
List conditions for high buyer bargaining power |
- Highly concentrated - Products of rivals are undifferentiated - Low switching costs for buyers - Easy backwards integration - Product is big part of costs and budget - Buyers have low income - Product quality doesn't affect offer quality |
|
|
List conditions for high threat of substitutes |
- When product performs the same, or a similar function as an industry's - Product provides an attractive price-performance trade-off - Low switching costs |
|
|
List conditions for high competitive rivalry |
- Numerous equal competitors - Slow growth - High exit barriers - Undifferentiated products - Low switching costs - High fixed costs, low marginal costs - Perishable products |
|
|
List the 5 steps of an industry analysis |
- Define the industry - Identify the participants and segment - Assess drivers of each competitive force - Analysis of future changes in the industry - Identify aspects of industry that can be influenced by us, competitors or new entrants |
|
|
List the purpose of Porter's 5 Forces model |
- Analysing market attractiveness - Identify where forces are driving the market - Whether businesses can influence these factors through marketing strategies |
|
|
List some common mistakes with utilising the 5 forces model |
- Defining the industry too broadly/narrowly - Making lists instead of analysing - Paying equal attention to all instead of one - Confusing effect with cause - Static analysis instead of trends - Declaring attractive or unattractive instead of guiding strategic choices |
|
|
List and describe the different stages of the PLC |
- Introduction: Small size, low growth & low attractiveness - Growth: Moderate size, high growth & high attractiveness - Maturity: Large size, low growth & low/high attractiveness - Decline: Moderate size, negative growth & low attractiveness |
|
|
List the indicative characteristics of the PLC |
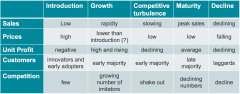
|
|
|
List the marketing strategies for each respective stage of the PLC |
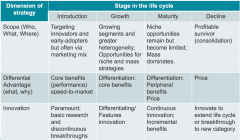
|
|
|
Describe the purpose of a consumer analysis |
- Aims to find new information to identify trends and gain consumer insight - Segmentation tool helps make results relevant |
|
|
List and describe the 6 W's and 1H of consumer behaviour |
- Who: Diffusion of innovation & buyer roles - What: Benefits, usage, purchase pattern - Where: Information search, customer decision making process, point of purchase - When: First decision, repurchase, marketing - How: Information use, multi-attribute model, means end chain, customer value - Why: Value, preference, importance, brand - Will: Repurchase, satisfaction, expectation, perceived & gap |
|
|
List the factors for evaluating segments |
- Financial value of segments - Size (no. or %) of segments - Growth trends of segments - Potential profits of segments |
|
|
List factors for measuring customer loyalty |
- Looking at repurchasing behaviour - Assessing retention rate, satisfaction or attitudes - Net promoter score |
|
|
Describe the Customer Lifetime Value |
- Net present value of future cash flows based on customer relationships - Factors involved --> Customer level operating profit --> Length of relationship --> Appropriate discount rate |
|
|
List the different profit potential scoring models |
- Core business potential - Cross selling potential - Networking potential - Learning potential |
|
|
Describe the different sources of information |
- Primary: Made specifically for the company, is expensive and can be used immediately - Secondary: Made independently of the company, is cheap and must be analysed and applied |
|
|
Describe the different theories of firm performance |
- Resource based: company is collection of resources which is the source of returns --> Valuable --> Rare --> Non-imitable: substitute needs --> Non-transferable: used as resource again - Market based: Success depends on positioning in the industry, adapt to structures & strategise |
|
|
List steps for identifying competitive advantages |
- What we do better than competitors --> Buying criteria --> Compare with strongest competitors --> Analyse using value chain - What resources and capabilities are the sources of these advantages - Which resources are valuable, unique and not imitable/transferable to other industries |
|
|
List factors of strategy development |
- Analyse strengths & weaknesses - Competitive advantages identified from them - Find industries, markets and segments targeted by the competitive advantages - Strategy/plan developed to implement advantages |
|
|
Describe the value chain |
- Looks at all activities performed to make value - Helps identify source of competitive advantage - Advantages lies where activities performed --> more cheaply than competitors --> better/effectively than competitors |
|
|
Describe McKinsey's Value Chain Model |
- 6 distinct activities to bring product into market --> Technology development --> Product design --> Manufacturing --> Marketing --> Distribution --> Service |
|
|
Describe Porter's Value Chain Model |
- Primary (directly product/distribution) - Secondary (needed for primary activities) - Internal or outsource? - Critical success factors: skills & resources necessary for superior performance |
|
|
List the primary and secondary activities under Porter's Value Chain Model |
- Primary --> Inbound logistics, Operations, Outbound logistics, Marketing & sales, Service - Secondary --> Firm infrastructure, HR development, Technology development, Procurement |
|
|
List the different types of resources |
- Tangible --> Financial --> Physical - Intangible --> Patents, brands, reputation etc --> Often harder to obtain |
|
|
List the non marketing capabilities for firms |
- Financial position - Management and leadership - HR management - R & D - Operations: production & supply - Coordination of activities - Competitive position/advantage |
|
|
List the marketing capabilities for firms |
- Marketing intelligence (creating/understanding) - Marketing planning - Value delivering strategies - Brand management - Ability to react to market requirements - Customer relationship management - Marketing performance |
|
|
List the contents of a Portfolio Analysis |
- Decisions for product to grow, hold or withdraw - Identifying how strong product is in market - Identifying how attractive the market is - BCG and GE matrices |
|
|
Describe the Boston Consulting Group matrix |
- Used to understand product fit in relation with other products - Primarily used for problem products - Looks at Relative Market Share (strength) and Market Growth Rate (attractiveness) - Size of circles represents sales volume |
|
|
Describe the four product types |
- Problem Child: Low RMS/High MG, early phase, investment, neg cash flow, has market share - Star: High RMS/High MG, market leader, investment, pos cash flow, low margins - Cash cow: High RMS/Low MG, mature, low investment, pos cash flow, future market - Dog: Low RMS/Low MG, end phase, withdrawal |
|
|
List the limitations of using a BCG matrix |
- Oversimplification of product and market - RMS proxy for cash generation - MG proxy for cash usage - Variables and values are arbitrary - Ignores product synergy - Doesn't consider trends |
|
|
List the limitations of using a GE matrix |
- Selection and weighting of criteria is subjective - Strategic implications not straightforward |
|
|
Describe the SWOT analysis |
- Used to identify key issues company can strategise with - Two components --> Analysis: Likely to happen/has happened --> Diagnosis: Seeing significance of data - Uses data from situation analysis |
|
|
List factors of Strength/Weakness for SWOT |
- Relate to brand for the plan - Identified by internal analysis - Must relate to capabilities - Can't be something everyone has - Relative to competition, context, consumer needs and critical success factors |
|
|
List factors of Opportunities/Threats for SWOT |
- In environment, not related to brand - Identified by external analysis - Predictions within certain time frame - Can apply to everyone in industry - Relative to competitor, context & consumer |
|
|
List factors determining most important SWOT |
- Strength (VRIO): Valuable, Rare, Inimitable & Organisationally aligned - Weakness (MUDU): Meaningful, Uncommon, Difficult & Uncompensated - Opportunity (CLAL): Complementary, Large, Accessible & Lasting - Threat (USUL): Unmitigated, Significant, Undefended & Lasting |
|
|
Describe how the internal and external lists are prioritised |
- Five point scale - External --> Degree of significance --> Likelihood of occurrence - Internal --> Degree of significance |
|
|
Describe how the situational analysis is applied to SWOT |
- Limited to 5 situational factors per category - Prioritised by importance of risk, gain & time - No new information introduced to SWOT - Consumer: external - Company: internal - Competition: external & internal |
|
|
List the different types of product/market objectives |
- Profitability - Market Share - Growth - Technological leadership - Social Contribution - International economic development |
|
|
Describe profitability objectives |
- Expressed in either % or $ - Allows performance evaluation - Has to have desired ROI - Can encompass firm or only product/market - Trade-off with cash flow |
|
|
Describe market share objectives |
- Expressed in %, based on volume OR $ - Long term vs. short term goals - Always limit for market share - Considers ability to finance and defend MS --> Optimal market share --> MS vs. Profit: Find balancing point |
|
|
Describe growth objectives
|
- For purpose of improving internal capabilities, to compete in market & adapt to opportunities - Balance with survival --> Market standing --> Productivity --> Innovation |
|
|
List the different factors for SMART objectives |
- Specific - Measurable - Actionable - Reasonable - Timely |
|
|
List the basic factors of targeting & positioning |
- Compare attractiveness & competitive position - Aim for core business: strong in both - Avoid falling into other categories --> Peripheral: low attract, good position --> Illusion: high attract, weak position --> Dead-end: Low & weak |
|
|
Describe the forces that shape market attractiveness |
- Market factors: Size, growth, PLC, predictability, elasticity, buyer power & cyclicity of demand - Eco. & tech. factors: Barriers, supplier power, tech utilisation, investments required & margins - Competitive factors: Intensity, quality, threat of substitution & degree of differentiation - Bus. environ. factors: Fluctuations, political & legal, regulation, social & physical environment |
|
|
Describe the different targeting strategies |
- Undifferentiated: One product to whole market - Differentiated: Diff. product to diff. market - Concentrated: Focus on one/few markets |
|
|
List the different types of strategic targeting choice |
- Size - Incremental costs - Extent & durability of differences - Stability & compatibility of targets - Whether company fits segment - Type & level of competition: Perfect, monopolistic, oligopoly or monopoly |
|
|
Describe the factors of positioning |
- Defining frame of reference: Target market & nature of competition - Points of parity: How you are similar - Points of difference: How you are better than --> Desirable, to consumer --> Deliverable, to company --> Differentiating, to competitor |
|
|
Describe the positioning triangle |
- Selection of values --> Target group: considers them important --> Brand: strong in that area --> Competitors: less strong in that area - Positioning: Mind position of target group |
|
|
Describe the different approaches to positioning |
- Transformational: Values - Informational: Tangible reasons - Two sided: Links product to values - Executional: Big idea of campaign execution |
|
|
Describe Porter's Generic Strategies |
- Overall cost leadership: low cost, not low price - Differentiation: superior quality, price premium - Focus (cost or differentiation) |
|
|
List the purpose of the 5W/1H strategy |
- Meant to enhance coordination - Defines resource allocation - Aims for superior market position |
|
|
List the different strategies of the Ansoff Matrix |
- Market penetration: Current market/current product - Product/service development: Current market/ new product - Market development: New market/current product - Diversification: New market/new product |
|
|
Describe different levels of product heirarchy |
- Product category: functional coherence - Product line: Closely related in product class - Product item: Individual product in line - Product mix: Set of all lines and items |
|
|
List the different levels of strategy decisions |
- Mix --> Breadth --> Consistency/diversity - Lines --> Depth --> Width - Items --> Components --> Branding |
|
|
List the different pricing methods |
- Markup pricing - Competition based pricing - Value based pricing |
|
|
Describe the four main consumer behaviours |
- Loyal customer: Value differences, inelastic - Price conscious: Doesn't value diff., elastic - Value seeking customers: value, elastic - Convenience seeking: doesn't value differences, price inelastic |
|
|
List the different factors of the promotional mix |
- Personal --> Face-to-face with potential buyers - Non personal --> Advertising: mass medium --> Sales promotion: direct inducement --> Public relations --> Direct marketing - Must take into account role in P's, nature of product & market |
|
|
Define "Integrated Marketing Approach" |
- Coordination of all elements of promotional mix to present a consistent message |
|
|
List the steps of distribution strategies |
- Review distribution environment - Establish distribution objectives - Design distribution structure |
|
|
List the parties involved with distribution |
- Not all necessary for distribution --> Manufacturer --> Agent --> Wholesaler --> Retailer |
|
|
List factors of implementation (tactics) |
- Activities to be done - Time & location - How it will be done - Who will be involved - Who will be accountable - How much it will cost - Coordination of objectives, strategies & tactics |
|
|
List factors of the control process |
- Setting standards of performance - Specifying necessary data feedback - Obtaining necessary control data - Evaluating feedback data |
|
|
List factors for setting standards of performance |
- Profitability: ROI, ROE, ROA - Market share - Sales - SBU level - Product market level - Costs: direct & indirect - Customer satisfaction |
|
|
Define benchmarking and list the different factors involved |
- Comparing business processes and performance with the best of the industry --> Competition: what, why, our reaction --> Customer: satisfaction, complaint, returns --> Company: Process, procedure, people --> Context: General current vs. future |
|
|
List the steps of contingency planning |
- Identify critical assumptions - Seeing profitability of assumptions being true - Rank order of critical assumptions - Tracking/monitoring of action plan - Setting triggers to activate contingency plan - Specify alternative options |

