![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Customer Value? |
Creation of superior PERCEIVED value, where Value = Relative Benefits / Relative Costs |
|
|
What are Relative Benefits? |
Defined as "results delivered", given by PRODUCT - SUPPORT SERVICES - RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT - IMAGE |
|
|
What are Relative Costs? |
Defined as "total tangible and intangible costs/savings", given by: SEARCH - ACQUISITION - SET-UP - MAINTENANCE - FINANCING - EXIT |
|
|
What is a Market-Oriented Firm? |
Involves creating value for customers, superior to simply being marketING-oriented (selling the product). Involves being value-driven and having market intelligence. |
|
|
The 3 Characteristics of a Value-Driven Organisation |
Encompassed by: 1. Value Driven Strategy, i.e understanding of context, competitors, customers, capabilities 2. Leadership, encouraging innovation, flexibility, responsiveness 3. Market-Oriented Culture |
|
|
The 3 Processes of Market Intelligence |
1. Generation of market intelligence 2. Dissemination of market intelligence 3. Responsiveness to market intelligence |
|
|
4 Reasons for shift from Transactional Marketing to Relationship Marketing |
1. Recognition of Market failure - customer switching costs, manufacturer idiosyncratic investments 2. Understanding of Consumer behaviour - irrational, incomplete information, people satisfice 3. Understanding of Value chain - can affect firm's ability to create value 4. Customer retention |
|
|
Why are LT relationships with few customers more profitable than multiple transactions with many customers? |
Cost of customer defections is high. Lower cost of operation if retain. If constantly go into market to find NEW customers to replace LOST customers, leads to "leaky bucket" approach. Eventually, will be diminishing returns to increasing retentions. |
|
|
How does Customer Value lead to firm value? |
1. Increased customer loyalty --> increased purchases/referrals --> premium prices 2. Increased volume sold --> increased cash flow --> reduced costs |
|
|
What is Marketing Myopia? |
Short sightedness by firms causing management to define their business (and hence, opportunities) too narrowly. Eg. "railroad company" is myopic, "transportation company" is broad. |
|
|
What are 4 drivers of customer defection? |
1. Difficult complaint procedures 2. Service delays 3. Slow, grudging response to service breakdown 4. Escape clauses An issue that perpetuates this is that there is rarely a reward for resolving customer issues (usually a commission/sales reward). |
|
|
What are the 6 rungs of the Customer Loyalty Ladder? |
1. Apostle 2. Advocate 3. Supporter 4. Client 5. Customer 6. Prospect |
|
|
Describe a model for loyalty |
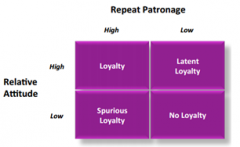
|
|
|
What is the relationship between satisfaction and loyalty? |
Customer satisfaction and repurchase probability (a facet of loyalty) are positively linearly related (although not perfectly). Can be explained in "Zones": - Zone of Outrage - poor or unanticipated scenario - Zone of Dissatisfaction - expectations not met - Zone of Satisfaction - expectations met or exceed - Zone of Delight - unexpected, valuable, memorable, positive |
|
|
What are the 3 consumer roles? |
1. User 2. Buyer 3. Payer May not be held by the same person. Eg. child = user, mother = buyer |
|
|
Describe consumer behaviour using a 5-step hierarchical model |
1. Need Recognition - Negatively originated (problem removal, problem avoidance, normal depletion) - Positivelyoriginated (sensory gratification, social approval, intellectual stimulation) 2. Information Search - effort directed to obtaining info related to purchase consideration. DEPENDS ON: - Product attributes - Involvement - Memory - Expertise & experience - Purchase situation 3. Alternative Evaluation - Evoked set (mental list of acceptable brands) - Heuristics 4. Purchase Decision - Product Trial 5. Post-Purchase Behaviour - Cognitive dissonance - Repeat purchase |
|
|
What are contextual factors that influence the way consumers behave? |
1. Reference group influence, social networks - reference group effects greater when credible, attractive, powerful 2. Situational factors 3. Personal traits 4. Cultural & socioeconomic factors 5. Marketing mix influences (4 P's) |
|
|
What is Customer Needs analysis? |
Customer needs analysis reveals options for creating value. Identifies: * Existing needs - limited opportunity for new products * Latent needs - unmet needs that consumers can articulate. Opportunity for innovation. * Incipient needs - unmet needs that consumers CANNOT articulate. Opportunity for breakthroughs. |
|
|
Define market segmentation |
Market segmentation involves dividing a larger segment into smaller segments, into groups that have similar needs, desires, or will respond in similar ways. |
|
|
What are the key benefits of segmentation? |
- Resource allocation is optimised - Repositioning opportunities - New product opportunities |
|
|
What are 4 features of effective segments? |
1. Homongeous within segments 2. Hetereogenous between segments 3. Profitable 4. Operational (i.e they are measurable and can be acted on) |
|
|
What are 3 segmentation criteria? |
1. Benefits sought 2. Price sensitivity 3. Loyalty After applying this criteria, can describe segments in proxy variables (eg. demographic, socio-economic) |
|
|
What is targeting? |
Targeting is a market segment that a firm has decided to aim its business towards. |
|
|
What are the types of targeting? |
- Differentiated - Undifferentiated (mass) - Concentrated (niche) - Micro (segment of 'one') |
|
|
What are some strategic considerations in target market selection? |
Strategic considerations involve evaluating segments for: 1. Size & growth 2. Segment interrelationships - some segments can provide platforms for entering other segments 3. Competitive response 4. Degree of fit with company |
|
|
Define brand equity |
Brand equity is the marketing and financial value associated with a brand's strength in a market. |
|
|
What are the 3 key benefits of brand equity? |
1. Incremental attraction (sales growth) - Easier to attract new customers - Resist competitors - Introduce line extensions - Global expansion 2. Cost advantages - Channel leverage - Lower advertising/sales ratios 3. Sustainable price premium - Greater loyalty - Premium pricing |
|
|
What is the role of brands? |
1. Functional (identification) 2. Risk reduction (guarantee, optimisation, characterisation) 3. Pleasurable / alturistic (continuity, hedonistic, ethical)
|
|
|
Define positioning |
Positioning involves a firms efforts to develop a set of characteristics that result in favourable and meaningful comparisons relative to competitors' offerings. |
|
|
What are the 4 determinants of brand image? |
1. Brand awareness 2. Strength of brand associations 3. Uniqueness of brand associations 4. Favourability of brand associations |
|
|
What are the origins of brand equity? |
Brand equity evolves from: 1. Strong brand identity - meaning, position and gola sprojected by the organisation. 2. Strong brand image - determined by brand awareness, strength/uniqueness/favourability of brand associations |
|
|
What are brand associations? |
Brand associations are anything that is deep-seated in a customers' mind about a brand. It may be PRODUCT-related (functional, experiential, symbolic) or NON-PRODUCT-related (imagery, personality, feelings). Can be described in terms of STRENGTH, FAVOURABILITY and UNIQUENESS. |
|
|
Define the augmented product. |
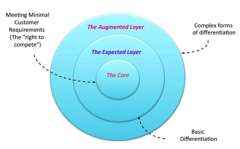
A product is a means by which value is delivered to customers. A product may be described by the following model. |
|
|
Depict the product life cycle. |
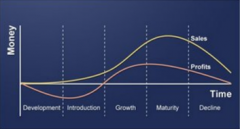
|
|
|
Describe the 4 P's in terms of product lifecycle |
P - INTRO - GROWTH - MATURITY - DECLINE Product: New - Improved quality - modify - maintain Pricing: Premium - stable - low - maintain, possibly raise Place: Specialist - Increase - Increase - Limit Promotion : Inform - Comparative advertising - Product positioning - Cut back |
|
|
Use a model to describe product adoption / diffusion |
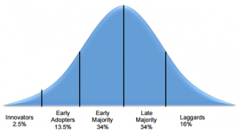
|
|
|
Use a model to describe the diffusion of innovation |
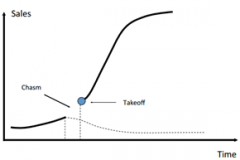
|
|
|
What are 5 factors influence the rate of diffusion? |
1. Relative advantage (benefits much greater than losses) 2. Compatibility 3. Complexity 4. Divisibility (ease of trial) 5. Communicability (value is observable) |
|
|
What are product development objectives and disadvantages? |
Product development is extremely important as innovation is the "lifeblood" of every firm. A key aim: Minimise time to market. This enables: - First mover advantage - Amortise - Increased chance product becoming dominant design |
|
|
What is co-creation? |
Co-creation involves creating products with customers. It may be necessary for long term survival. Leads to INCREASES in: - perceived switching costs - tolerance of service failure - perceived control - firm productivity - service innovations |
|
|
How does co-creation change a firm? |
Firm becomes more: - Porous (let others in) - Gives employees greater behavioural lattitude - Creates need for operational flexibility (i.e can make small quantities w/o additional cost) |
|
|
What is Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)? |
IMC involves developing and implementing various forms of persuasive communications with customers, to change attitudes and behaviour. |
|
|
What are the 4 key elements of IMC? |
1. Affect purchase behaviour - elicit favourable brand attitude. 2. Use all forms of contacts 3. Begin with the customer/prospect - then work backwards to determine most effective communication. Consistent with value-based strategy. 4. Achieve synergy - IMC implies a co-ordinated delivery with a consistent message across medias. |
|
|
What are the key marketing communication decision areas? |
1. Media and vehicle selection - Advertising - Publicity - Sales promotions - Personal communications 2. Message content 3. Promotional budget |
|
|
What is encoding variability? |
Memory is enhanced when multiple pathways are created between the product/brand, which is an advantage of mixing advertising medias. |
|
|
What is repositioning? |
Repositioning involves delivering a modified set of characteristics that result in favourable, meaningful comparisons relative to competitor's offerings. |
|
|
What are the possible objectives of a firm that may affect message content? |
1. Arouse interest 2. Repositioning 3. Inform & educate customers - Elaboration Likelihood model (ELM) - high involvement = central route - low involvement decision = peripheral route 4. Generate immediate buying action - Negative purchase motivation: message should be informational (similar to central route of persuasion) - Positive purchase motivation: msg should be transformational (similar to peripheral route of persuasion) 5. Confirm purchase decisions/remind buyers |
|
|
What are some factors that determine advertising budgets and campaign effectiveness? |
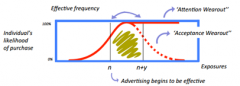
Effective frequency - optimum range of exposures The optimum range determines the advertisign budget. Dependant on: - brand loyalty - message creativity - newness |
|
|
What are the advantages/disadvantages of price? |
ADVANTAGES - Immediate, direct - Short lead times - No initial negative cash flow DISADVANTAGES - Competitors can react quicker |
|
|
Why is price so important? |
A small change in price can lead to a large change in profit. |
|
|
In what 4 ways to customers perceive price? |
1. Money 2. Time 3. Behavioural effort 4. Cognitive effort - heuristics - brand loyalty (if extremely brand loyal, will disregard price) - evoked sets - reference groups, family |
|
|
In what 3 ways can price be used to convey meaning? |
1. Quality Assurance Pricing - a greater price reflects a superior product 2. Prestige pricing 3. Pricing framing - Prospect theory (consumers make decisions relative to a reference point) - Reference pricing |
|
|
What considerations are given to low involvement products? |
Provided a product falls between an implicit price range, it will not be evaluated as a purchase criterion |
|
|
What is the optimal basis for setting pricing? |
Should consider Value / Margin and Anchors, with a focus on: - Customer-Based (Value) Pricing, where customers pay for what they value. Depends on WTP and Elasticity. This is as opposed to strictly. - Cost-Based Pricing - Competition-Based Pricing |
|
|
Describe 3 Pricing Tactics |
1. Penetration - Set below value pricing. Gain marketing share, discourage new entrants. However, may be difficult to rise prices subsequently. 2. Skimming - Setting price aboev price level. New unique products, maximise short-run profits, prestige pricing. However, be careful of price discrimination 3. Stability - maintaining between competitors to maintain market stability. |
|
|
What is a distribution channel? |
A network of organisations that create time, place, and possession value for customers. |
|
|
What are the basic channel characteristics and intensity of distribution? |
Channel characteristics 1. Length of channel 2. Intensity of Distribution - Intensive - Exclusive - Selective |
|
|
What factors determine the structure of distribution channels? |
1. Distribution functions 2. Economics of distribution functions 3. Management's desire for distribution control |
|
|
What is meant by "multi-channel world"? |
Customers are increasingly shopping across and expecting multiple channels. Benefits: - Low-cost access to new markets - Increased customer satisfaction/loyalty - Creation of strategic (knowledge) advantage |
|
|
What are the 2 types of channel design? |
- Long design - small amounts, purchased frequently - Shorter design - high involvement, speciality goods, high service component. - Multiple routes to market Need to consider product characteristics. Bulky? High unit value? Perishable? Non-Standardised? |
|
|
What are the 2 key ways a channel may be organsed? |
1. Conventional Marketing Channel - channel members act independently and seek to maximise their own profits. 2. Vertical Marketing System - Members integrate and act as a unified system. - Corporate VMS (single ownership) - Contractual VMS (independent, contract) - Adminsitered VMS (one large, creates co-ordination) |
|
|
What characteristics of intermediaries, competitors and the company are improtant to consider in channel design? |
1. Intermediary characteristics - need to consider SELECTION and MONITORING 2. Competitive characteristics - distribution location. Tension between distributing NEAR vs AVOIDING competition. 3. Company characteristics - resources, product mix, value propositon. |
|
|
What are some of the drivers for growth in Service Marketing? |
- Growth in service industries - Deregulation - Intensification of competition - Changing demographic and socioeconomic profile in Australian society. Services more affordable. |
|
|
What are the 4 major problems faced by service firms? |
1. Intangibility 2. Inseperability: Services are SOLD THEN PRODUCED THEN CONUSUMED, so there is an inseperability of production and consumption. 3. Variability 4. Persishability - can't inventory services |
|
|
What additional marketing tools (the three extra P's) can address the major problems faced by service firms? |
1. Physical evidence - Create an environment where service is assembled, and offer tangible elements of the service offering. 2. Participants - Be aware of all who play a role in service delivery. 3. Process - Create support processes for the delivery of services. |
|
|
Describe a framework for how service quality is perceived. |
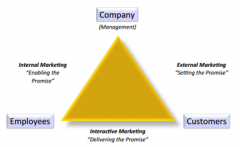
|
|
|
How is service quality perceived? |
Service quality is perceived in terms of: 1. Technical outcome - Reliability - Responsiveness 2. Functional outcome - Assurance - Empathy - Tangibles |
|
|
How is service failure damaging? |
Service failure can: - Drive up costs, profitable customers leave - Tarnish brand image, spread negative word of mouth - Demoralise employees However, if resolved, vast majority will return. |
|
|
What is meant by the "service recovery paradox"? |
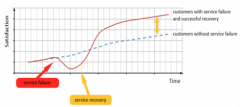
|
|
|
Outline a framework for detecting and correcting failure (4 steps). |
1. Identify 2. Resolve 3. Communicate and classify failure 4. Integrate data to improve overall service |
|
|
How can employees be utilised to resolve service failure? |
Train employees to: - gather customer information - measure their own performance - identify unhappy customers and find root causes - provide increased latitude - pay employees for performance |
|
|
What is meant by the "ethical tension that exists for all business"? |
There is a tug between: 1. Business reasons - opportunities, rewards, risks, penalties 2. Moral reasons |
|
|
What is Corporate Social Responsibility? (CSR) |
CSR involves a consideration of a broader set of stakeholders. |
|
|
What is Instrumental Stakeholder Theory? |
This involves employing Corporate Social Responsibility to: - make customers more satisfied - make employees more attracted/committed - risk management - reputation/brand enhancement or differentiation Studies have shown a positive relationship between socially responsible CSR and financial performance. |
|
|
What is meant by "stakeholders"? |
Stakeholders encompass many different groups. This includes: shareholders, customers, employees, business partners, governments, community, environment |

