![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Rewardsof Global Marketing
Having a global vision means… |
•Recognizingand reacting to international marketing opportunities
•Usingeffective global marketing strategies•Beingaware of threats from foreign competitors |
|
|
Importanceof Global Marketing to the U. S.
|
a. Derives13 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) from world trade.
b. 7percent of U.S. employment is supported by exports. c. U.S.businesses export over $1.7 trillion in goods and services annually. d. EverU.S. state has realized net employment gains directly attributed to foreigntrade. |
|
|
TheFear of Trade and Globalization
|
a. Millionsof Americans have lost jobs
b. Millionsfear losing jobs c. Threatof outsourcing if workers do not accept pay cuts d. Vulnerabilityto operations moving offshore |
|
|
TheFear of Trade and Globalization
|
Millionsof Americans have lost jobs
Millionsfear losing jobs Threatof outsourcing if workers do not accept pay cuts Vulnerabilityto operations moving offshore |
|
|
Benefitsof Globalization
|
Expands economic freedom
Spurs competition Raises productivity and living standards Offers access to foreign capital, globalexport markets, and advanced technology Promotes higher labor and environmentalstandards |
|
|
AreMultinationals Beneficial?
|
Pros
•Accountfor 19% of U.S. private Jobs •Provide25% of private wages •74%of R&D spending •48%of total exports Cons •Technologyis capital intensive and does not necessarily increase employment. •Supportgovernments that benefit the company, not necessarily the country and itspeople •Maytake away more wealth than they generate |
|
|
1. GlobalMarketing Standardization
2. Multidomesticstrategy |
1. Productionof uniform products that can be sold the same way all over the world.
2. Subsidiariesof multinational firms are allowed to compete independently in domesticmarkets. |
|
|
ExternalEnvironment Facing Global Marketers
5 |
1. Culture
2. Natural Resources 3. Economic & Technological Development 4. Political Structure 5. Demographic Makeup |
|
|
1. Culture
|
Thecommon set of values shared by its citizens that determine what is sociallyacceptable.
Factorsto keep in mind when dealing with different cultures: 1. Language and cultural idioms 2. Customs and traditions 3.Values and expectations of sales presentations |
|
|
The global economy
quote about america? |
“IfAmerica sneezes, the rest of the world catches a cold.”Understandingand forecasting growth and demand globally requires understanding countriesaround the world.
|
|
|
3. Economic & Technological Development
|
DevelopedCountry Fragment--> Complex, sophisticated industries
LessDevelopedCountryspan> Basicindustries |
|
|
EconomicDevelopment:Chinaand India
|
•Chinaand India have two of the highest growth rates in the world.
•Havethe world’s two largest populations.•Amonghighest levels of income disparity.•Greatlinguistic and cultural diversity. |
|
|
Tariff
|
Atax levied on goods Enteringa country
|
|
|
Quota
|
Limiton the amount of a product entering a country
|
|
|
Boycott
|
Exclusionof products from a country
|
|
|
Exchange Control
|
Foreignexchange must be sold to a control agency
|
|
|
Market Grouping
|
Commontrade alliance
|
|
|
Trade Agreement
|
Anagreement to stimulateinternational trade
|
|
|
TheUruguay Round made changes inworld trading practices in...
|
1. Entertainment,pharmaceuticals, integrated circuits, and software
2. Financial, legal, and accounting services 3. Agriculture 4. Textiles and apparel 5. And created a new trade organization: The World Trade Organization |
|
|
DohaRound
|
•Beganin 2001
•Highlycontentious from the beginning•Stalemateover lowering tariffs on industrial goods in exchange for cutting U.S. farmsubsidies. •Moreprotectionism has made talks increasingly difficult. |
|
|
Agreement and Organizations
3 types |
1. CAFTA
2. NAFTA 3. EU (European union) |
|
|
Memembers od G20
|
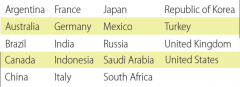
|
|
|
Demographic makeup
Marketing considerations |
1. Population density
2. Urban or rural 3. Age |
|
|
Natural Resources
Shortages in natural resources create: |
Internationaldependencies
Shiftsof wealth Inflationand recession Exportopportunities if resources are abundant Stimulusfor military intervention |
|
|
Why“Go Global”?
|
§Earnadditional profits
§Leveragea unique product or technological advantage §Possessexclusive market information§Saturateddomestic markets §Excesscapacity §Utilize“economies of scale” |
|
|
Entering Global Market
1. Export 2. Licensing and Franchising 3. Contract Manufactoring 4. Joint Venture 5. Direct Investment |
1. Sell domestically producedproducts to buyers in other countries
2. Legal process allowing use of manufacturing/patents/knowledge 3. Private-label manufacturing by a foreign country 4. Domestic firm buys/joins a foreign company to create new entity 5. Active ownership of a foreign company/ manufacturing facility |
|
|
ExportIntermediaries
1. Buyer for Export 2. Export Broker 3. Export Agent |
1. Assumes all ownership risksand sells globally for its own account.
2. Plays the traditional broker’srole by bringing buyer and seller together. 3. Acts like a manufacturer’sagent for the exporter in the foreign market. |
|
|
Risk levels for five methods of entering global market place....
Try to name them in order |
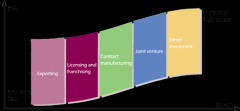
|
|
|
Place (Distribution) |
•Adequatedistribution is necessary for success in global markets
•Lack of distribution infrastructure andcultural differences create problems •Logisticsand shipping costs have been a growing challenge for U.S. companies looking tomove production overseas. •Globaltrade has added to strains and charges for all forms of transportation. |
|
|
Pricing
|
Must consider transportation andinsurance costs, taxes and tariffs
Determine what customers will spend Ensure that foreign buyers will pay price May need to simplify a product to lowerprice Don’t assume that low-income countriesare willing to accept lower quality |
|
|
Dumping may occur as a result of exporter business strategies that include: |
1.Trying to increase an overseas marketshare2.Temporarily distributing products tooverseas markets to offset slack demand at home 3.Lowering unit costs by exploitinglarge-scale production 4.Attempting to maintain stable pricesduring periods of exchange rate fluctuations |
|
|
Countertrade
|
Aform of trade in which all or part of the payment for goods or services is inthe form of other goods or services.
|
|
|
1. TheImpact of the Internet
2. Social Media |
1. •Opening an e-commerce site puts acompany in the international marketplace
•Internet Economy remains hinderedby brick and mortar rules, regulations, and habits 2. Globalmarketers use social media because: •Itis popular around the world •Tounderstand customers •Forglobal brand building |

