![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Macro-environment
|
demographic
economic social-cultural competitive political / legal technological |
|
|
|
Micro-environment
|
the company itself
suppliers & distributors market intermediaries publics that influence effectiveness of strategic plans |
|
|
|
decision support systems
|
using databases and business models to gather, store, process, and present data in forms and formats pertinent to strategic planning decisions
|
|
|
|
balanced score card systems
|
planning and decision systems designed to furnish balanced measures and initiatives to activate and control strategic plans
|
|
|
|
relationship marketing (RM)
|
emphasis on long-term, mutually beneficial relationships
|
|
|
|
Integrated marketing communications (IMC)
|
mandate that all brand contacts received or divers online and offline communication channels be relevant to individual wants and needs
|
|
|
|
demographic environment
|
age
gender family size family life cycle income occupation education religion race nationality |
State of being variable
often the strongest variables in predicting consumer behavior |
|
|
population trends
|
growth rate (1.6%)
age mix |
|
|
|
key demographic variables
|
dispersion
ethnicity education |
|
|
|
spending patterns
|
1) disposable income - income after taxes
2) discretionary income - income after taxes and necessities 3) Engel's law |
|
|
|
Engel's law
|
as discretionary income goes up, the percentage spent on:
basic necessities decreases housing remains constant (except for utilities which decreases) other (i.e. luxury, recreation, education, self help) increases |
|
|
|
business cycles affect on buying patterns
|
prosperous - expanded product lines, increased promotion & distribution, increased prices
recessions - lower prices, eliminate marginal products, increase promotion, launch value-priced offers recoveries - consumers can buy but aren't willing to |
|
|
|
inflation's affects on purchasing patterns
|
1) buy now in anticipation of increasing prices
2) alter purchasing patterns to mitigate losses through inflation 3) postpone purchasing entirely |
|
|
|
per-capita income distribution possibilities
|
1) almost all low per-capita income
2) some high, lots of low per-capita income 3) roughly equal low, middle, and high per-capita income 4) roughly all middle per-capita income |
|
|
|
Social classes
|
relatively homogeneous and enduring divisions in a society
members have similar values, interests, and behaviors |
|
|
|
culture
|
a complex whole, learned, and shared by members of a society
encompasses beliefs, values, language, religion, art, morals, law, education, customs, habits, and capabilities |
|
|
|
values' characteristics
|
1) guides culturally appropriate behavior
2) difficult to change 3) widely accepted 4) Incline people to respond to stimuli in standard ways |
|
|
|
value categories
|
Core - highly persistent (getting married)
Secondary - more likely to change (age to get married, family size) Subculture - separate segments of a culture organized around race, nationality, religion, location, ect. instrumental values - focus on modes of conduct (means: ambition, self-discipline) terminal values - end States of existence (end: happiness, prosperity) material - things people buy non-material - ideas, customs, beliefs, |
|
|
|
marketer's first 2 tasks
|
1) identify variables that will predispose people to buy the product
2) incorporate predisposing values into their marketing plan/mix |
|
|
|
3 approaches for identifying cultural variables
|
observation fieldwork - trained researches observing a small sample
content analysis - inference by verbal and pictorial communication Value measurement surveys - scaled questionnaires call value instruments |
|
|
|
Rokeach Value Survey (RVS)
|
groups respondents by evaluation of
1) terminal values 2) instrumental values 3) related buying behaviors |
|
|
|
SRI International's Value and Lifestyle Survey (VALS)
|
1) need-driven consumers (11%)
2) outer-directed consumers (66%) 3) inner-directed consumer (21%) 4) integrated consumers (2%) |
|
|
|
political-legal environment's affects
|
1) monetary and fiscal policy
2) social legislation & regulatory agency policies 3) government relationships with individual industries 4) marketing legislation 5) information that helps marketers - census info |
|
|
|
Sherman Act 1890
|
prohibits restraint of trade and monopolization
States competitive marketing system is national goal |
|
|
|
Clanton Act 1914
|
strengthens Sherman Act
restricts price discrimination, exclusive dealing, tying contracts, and interlocking board of directors |
|
|
|
Federal Trade Commission Act 1914
|
Establishes FTC to investigate business practices
prohibits unfair competition |
|
|
|
Robinson-Patman Act 1936
|
prohibits price discrimination in sales to wholesalers, retailers, or other producers
prohibits selling at unreasonably low prices to cut competition |
|
|
|
Wheeler-Lea Act 1938
|
amends FTC Act to outlaw additional unfair practices
gives FTC jurisdiction over false & misleading advertising |
|
|
|
4 types of competition
|
Brand competition
Substitute products Generic competition from similar products Desire competition (other desires a customer might satisfy before buying the product) |
|
|
|
Monopoly
|
When a product is offered by the government, private regulated monopoly, or a private monopoly
Inelastic demand |
|
|
|
Oligopoly
|
Few, large sellers of similar products
Many smaller sellers following lead |
|
|
|
Kinked demand curve
|
When competitors quickly match any attempt to generate additional sales by lowering prices
|
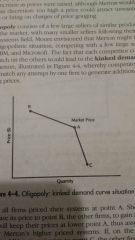
|
|
|
Pure competition
|
Many sellers offering similar products to many buyers
|
|
|
|
Monopolistic competition
|
Few or many sellers offer products that are at least perceived as different by customers.
|
|
|
|
Key questions in formulating competitive strategy
|
What markets should the company compete in?
How should the company compete in these markets? |
|
|
|
Micro-environmental threats and opportunities
|
The company
Customers Suppliers and marketing intermediaries Publics |
More control over these than over Macro-environmental threats and opportunities
|
|
|
Types of customers
|
The product market
The reseller market The government market The international market |
|
|
|
Company threats and opportunities
|
Conflicts from differing views on what publics and company resources are most important
|
Management must coordinate all functions towards customer satisfaction and get all functional areas to view their activities through customer eyes
|
|
|
Types of intermediaries
|
Financial intermediaries
Banks, insurance, credit card Selling intermediaries Agents, brokers, wholesalers, retailers, Physical distribution intermediaries Warehouse, rail, truck, airline Marketing service agents Marketing research firms, advertising agencies, media consultants |
|
|
|
Types of publics
|
Welcome
Stockholders Venture capitalists Unwelcome Negative product reviews Sought Favorable publicity |
|

