![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Allocative efficiency |
occurs when resources are distributed in such a way that no consumers could be made better off without other consumers becoming worse off |
|
|
Dynamic efficiency |
occurs when resources are allocated efficiently over time |
|
|
Market failure |
where resources are inefficiently allocated due to imperfections in the working of the market mechanism |
|
|
Productive efficiency |
achieved when production is achieved at lowest cost |
|
|
Static efficiency |
occurs when resources are allocated efficiently at a point in time |
|
|
Technical efficiency |
achieved when a given quantity of output is produced with the minimum number of inputs |
|
|
Causes of market failure |
1. Negative externalities
2. Positive externalities 3. Imperfect information or information failure 4. Market dominance by monopolies 5. Factor immobility 7. Equity (fairness) issues |
|
|
1. Negative externalities |
(e.g. the effects of environmental pollution) causing the social cost of production to exceed the private cost
|
|
|
2. Positive externalities |
(e.g. the provision of education and health care) causing the social benefit of consumption to exceed the private benefit
|
|
|
3. Imperfect information or information failure |
means that merit goods are under-produced while demerit goods are over-produced or over-consumed
|
|
|
4. Market dominance my monopolies |
can lead to under-production and higher prices than would exist under conditions of competition, causing consumer welfare to be damaged
|
|
|
5. Factor immobility |
causes unemployment and a loss of productive efficiency
|
|
|
6. Equity issues |
Markets can generate an 'unacceptable' distribution of income and consequent social exclusion which the government may choose to change
|
|
|
MC |
- marginal cost - the extra cost of one extra unit |
|
|
MB |
- marginal benefit - the extra benefit of one extra unit |
|
|
MSC |
- marginal social cost - private marginal costs plus external costs of one extra unit |
|
|
MSB |
- marginal social benefit - private marginal benefit plus external benefits of one extra unit |
|
|
Positive externality definition |
when a consumption or production process gives a benefit to a third party that the third party does not pay for e.g. education |
|
|
Negative externality |
when a consumption or production process imposes a cost on a third party that is not paid for by the consumer/producer e.g. air pollution by factories, smoking |
|
|
Consumption externality |
an externality that affects the consumption side of a market, which may be either positive or negative |
|
|
Production externality |
an externality that affects the production side of a market, which may be either positive or negative
|
|
|
Negative externality diagram |
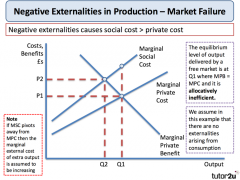
|
|
|
Positive externality diagram |
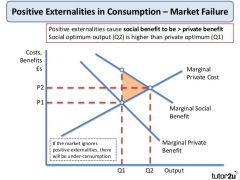
|

