![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
263 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is branding
|
Brand is a valuable asset and a actually a product in which the company tries to differentiate from competitors, persuade and inform customers as well as reinforce. Even going so far, through intensive and long years of marketing communications, as the brand represnting the product in the case of Tempo for example that for the customer, Tempo represents tissue paper or in the case of google where the word google is a synonyme for search engines.
|
|
|
What is the aim of branding
|
Aim is to provide is to give the brand a positive personality and thus reduce the decision process of buyers, reduce the percieved risk there by turning high invovement decisions into low involvement decisions and promoting repeated buying process. Brand also helps differentiate from competitors therby given the product a competitive advantage, allowinfg for premium pricing and loyalty which other products can profit from through brand extension or cross product promotion
|
|
|
Characteristics of brand
|
Brand has two main attributes - intrinsic (functional attributes - shape, performance, physical characteristics and extrinsic (emotional attributes - refering to lifestyle and is intangible, the feeling the brand evokes or should evoke
|
|
|
Brand elements
|
Skills - Particular functional attribute that distinctive to the brand, personality - lifestyle, perceived value, relationship - how the buyer thinks that the brand sees it.
|
|
|
Brand development work
|
This involves creating a brand experience
|
|
|
Brand identity prism
|
Consists of 6 facets - external: physique, relationship, reflection, Internal: personality, culture, self-image
|
|
|
Types of brands
|
passionate and pseudo brands
|
|
|
What a the benefits of branding for supplier
|
Premium price, differentiation, cross-product, loyalty, retention, repeat-purchase, assist in developing int. Marcom, contributes to CI programmes, legal prtection, greater thematic consistency and uniform messages and communication
|
|
|
Benefits of brand for buyers
|
assists in identification of preferred products, can reduse keveks if perceived risk, improve quality of shopping experience, easier to gauge lwvel of product quality, provide psychological reassurance, vues about nature of source of product and associated values
|
|
|
Structure of Brand portfolio
|
Brand house achitecture (IBM), House of brands achitecture(Procter and Gamble)
|
|
|
Organisation or product brand relationship
|
solo style (coca cola), isolated style( nivea isolated from beiersdorf), balanced style (ford - ford fiesta, ford transit), mixed style - a mixture of iso. and balanced eg bosch with products und bosch name and products under blaupunkt or TFS with TS and FS products), corporate style - aims to reinforce corporate image - e.g IBM, HP
|
|
|
Portforlio of brands
|
bastion brand, flanker brands, fighter brands,
|
|
|
Brand forms
|
manufacturer brand e.g. ford, coca cola, distributor brand e.g. tesco, price brand e.g. Aldi, lidl, generic brand
|
|
|
Strategic role of branding
|
differentiation, integration - consisitent, uniform, reinforcing, added value through percieved performance, psychlogical meaning and brand-name awareness
|
|
|
Individual brand - brand finger printing
|
This is developing a single document that can be used by everyone involved with the brand development process. This is based on a brand audit and comes from understanding the consumer.
|
|
|
Benfits of finger printing
|
allows for continuity, focuses an consumer and helps maintain relationship, fosters good team practice
|
|
|
Contents of a brand fingerprint
|
target - despcription of person for whom the brand is always first choice, insight - elements of the consumer, his or needs upon which the brand is founded, competition - relative values and alternative choices as seen by the consumer, benefit - functional and emotional benefits, proposition - single most compelling competitive statement a consumer would make for buying the brand, Values - what the brand stands for, reasons to believe - proof to substantiate positioning, essence - distillattion of brand's genetic into one clear thought, properties - tangible things of which the merest sound taste, smell or touch would evoke the brand
|
|
|
Role of marketing comunications in branding
|
. It is a means by which products become brands. It is vital in the dev. Of brands and is the means by which a product becomes a brand i.e. how customers see a product, how it is different, what it stands for and what the values are.
|
|
|
Types of marcom roles in branding
|
show buyers how benefits of a brand can be transfered or extended to a new brand when it comes to brand extension, clarify each individuals role within the organisation - reinforce and remind comsumers of their brand perception in order to maintain and defend market share.
|
|
|
Determinant of marcom
|
Available financial resources - high budget for advertising used to create and maintain brand associations and not necessarily the use and functions of the brand and low budget for below-the-line approach where the brand name is closely associated with functions and use experience of product and packaging also plays a big role in building brand associations
|
|
|
Brand building through advertising
|
Rational or informative approach - functional aspects, benefits for the customer, product performance, a key attribute (USP) is identified and used to position the brand, emotional approach - create positive associations with the brand based on psychological and socially acceptable meanings, little or no emphasis is laid on product performance characteristics and marcom has to develope an ESP instead of USP. Create positive attitudes - likeability plays a role, ad should be relevant, meaningful, credible and of significant value. Customer has to enjoy the ad and complements expressive positioning
|
|
|
Brand building through advertising
|
Through advertising consumers can develop associations about content and positioning through the advertising message, through direct marketing and public relations - note that by low budget branding, packaging, labeling, brand name, mercahndising and POP (signs and display at point of purchase) are crucial. Note one can not rely anymore on low budget marcom one has to add a value based and positive attribute to brand such as loyalty schemes ore carelines.
|
|
|
Devices for brand association
|
co-branding - two or more brand that customer clearly identifies e.g.microsoft and nspcc, geographical identifiers - scource creidiblity e.g. origin labels, picture or map of country, ingredient branding - brand available only within other brands e.g. lycra, support services - relationship strength and continuity e.g. miles and more, tech. help, award symbols - qualifying marks e.g ISO certificate
|
|
|
Goals of B2B branding
|
develope an identity that customers percieve as valuable, establish stronger relationship with manufacturer, incorporate and perpetuate brand personality in marcom - CI,
|
|
|
Marcon for B2B
|
event sponsorship, joint promotional activities between manufacturers and resellers, personla selling and publicity also plays a role
|
|
|
Online branding is stronger and should be used when
|
overall comm. Strategy exists, not expected to establish relationship through on site visit, developement of personlised pathway for continued dialog, record is kept of changing nedds and interests, attempt to be seen as trustmark not trademark, integrate relationship building activities - face-to-face relationship or brick and mortar solution.
|
|
|
role of website
|
differentiation to competitor, depending on the rate of stickiness one wishes to achieve - customer spend some time on the site and thereby be influenced by cross selling opportunities, or get to the information need as soon as possible or easily buy a product and experience quality internet shopping. This satisfies both goal-driven behaviour and experiential motivation.
|
|
|
Brand equity perspective
|
The value of a brand is measured on the financial - brands value as a definable asset based on net present value of discounted future cash flows and the marketing perspective - beliefs, images and core associations which vary between groups that have to be segmented and targeted
|
|
|
Contents of brand equity
|
(Feldwick)brand value - financial and accounting base, brand strength - consumers attachment to brand and brand description - specific attitudes towards brand, (cooper and simons) brand future - refelection of brand ability to grow and remain unhindered by environmental challenges such as changing retail patterns, buying behaviour, new technologies and regulations
|
|
|
Five ways of measuring brand
|
David aaker - awareness, associations, percieved quality, market leadership, loyalty, market performance measures; Brand dynamics (millward brown) - presence, relevance to consumer needs, product performance, competitive advantage, bonding; Equitrend (total research) - salience, percieved quality, user satisfaction ; 3-D3 (Tbwa simmons and pamer) - brand quality, quantitiy and future measured against variety of stakeholders; Brand asset valuator (young & rubicam) - strength (differentiation and relevance), stature (esteem and knowledge)
|
|
|
Principle dimensions through which brand equity can be measured
|
brand dominance - market strength and financial performance, brand associations - beliefs held by buyers about what brand represents and stands for, brand prospects - capacity to grow and extend in new areas
|
|
|
Linkages within MCPF
|

|
|
|
Marcom strategy options
|
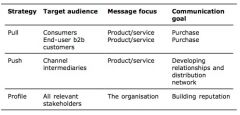
|
|
|
Issues to be considered when developing marcom
|
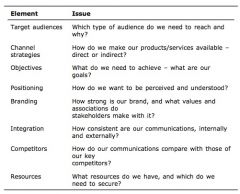
|
|
|
How to reduced percieved risk of org purchase decision
|
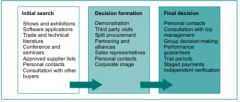
|
|
|
Promoional strategies for different levels of involvement
|
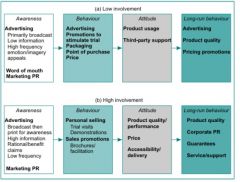
|
|
|
The Marketing Communications plan framework
|
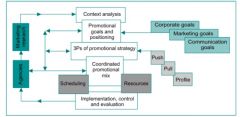
|
|
|
Why is buying decision important in marcom plan
|
Buying decision is the first stage of the marcom plan and the knowledge of the decision making process is vital if the correct type of information is to be transmitted at the right time and in the right or appropriate manner.
|
|
|
Buying decision process
|
problem recognition, information search - internal and external, alternative evaluation, purchase decision, post-purchase evaluation
|
|
|
Types of decision making and appropriate marcom
|
Extended problem-solving (EPS) - great deal of external search and and time taken before decison can be made e.g. cars, house. Marcom - provide information to assist decision making e.g sales literature, websites for products that do not need to be experienced and personal selling for products that have to be tried out, also ads can provide information; Limited Problem-Solved (LPS) - more internal search and limited external search actually only for updates. Marcom - convey messages that highlight key attributes important to the customers, routinised response behaviour (RBB) - distress purchase e.g food at petrol stations or petrol stations just at the highway, frequent purchase of low value items that only required internal search i.e purchase based on memory e.g. toothpaste. Marcom - aim to keep product within this set or get it into this set. Learning can be enhanced through repetition of messages.
|
|
|
Percieved risk
|
Uncertainty of proposed purchase and the outcomes that will result from the purchase. Level risk varies across product, through time and a reflection of an idividuals propensity to manage risk. Risk is related to involvement, trust and other buyer-behaviour concepts
|
|
|
Types of percieved risk
|
performance, financial, physical, social, ego, time
|
|
|
How to reduce risk for cons. decision
|
provision of information through mass media, word-of-mouth, personal selling; brand loyalty; guarantee; third-party endorsements; money-back offers; trial samples
|
|
|
Involvement characteristics
|
phase 1 - contextual elements: individual context - experience, values, expecations; reason for purchase (self or gift), nature of product (direct or indirect experience), nature of stimulus (friends, media); phase 2 Influences -level of personal relevance (high or low), focus (product or communication), duration (temp. or longlasting); Phase 3 - outcome: low involvement (behavioiur then attitude formation) Marcom= emotional or expresive messages, high involvement (attitude formation then behaviour) Marcom= message should stress attributes and benefits (functional)
|
|
|
Perspectives of involvement
|
cognitive view, pre-disposition to act, response view
|
|
|
Hedonic consumption
|
Purchase decision based on historical or fantasy imagery
|
|
|
High involvement decision making process
|
awareness, extensive information search, attitude/intention, trial/experimentation, long-run behaviour
|
|
|
Low involvement decision making process
|
awareness, short internal information search, attitude/intention, trial/experimentation, long-run behaviour
|
|
|
Impact of involvement on communication
|
|
|
|
Organisational buying decision process
|
recognistion of need or problem, product specification, suppliers and product search, evaluation of proposals, selection of suppliers, evaluation
|
|
|
Types of buying situation or classes
|
New buy, modified rebuy, straight rebuy
|
|
|
People involved in the buying decision
|
Users, gatekeepers, deciders, Influencers, buyers
|
|
|
Influences on buying center
|
stakeholder influences - regulations, economic conditions, competitor strategy, sociocultural values; Org. influences - corp. Strategy, org. values and culture, resources and costs, purchasing policy and procedure, interpersonal relationship; individual influences: personality, age, status, reward structure and systems
|
|
|
Marcom strategies
|
1. (Andrews) Planning - based on strategy development and implementation, explicit, rational and planned as a sequence of logical steps. Incrementalist - strategy developes step by step as organisation learn, trial and error. 2. (Mintzberg) Plan - course of action, implementation and evaluation, position - attempt to locate an organisation within the market, perspective - collective view of the world, one that is ingrained within the org. and its position within, ploy - manouvre to outwit competitors and pattern - stream of actions in which there are consistent patterns of behaviour 3. (whittington) classical, evolutionary, processual and sytematic.
|
|
|
Market segmentation
|
A division of a mass market into definable and distinct groups, each with a common characteristics and needs and display similar responses to marcom
|
|
|
Market segments
|
Demographic - income, sex, education, etc, geographic - region, geodemographic - both, psychographic - activites, interest, opinion, core values, behaviouristic - usage purchase pattern and situation and life stage - priorities in terms of money allocation, different need at different stages
|
|
|
3 Ps of marcom strategy
|
Pull/remind or Pull/position - influence end user (consumer and b2b), Push/inform, push/position, Push/key accounts/discounts - influence marketing (trade) channel buyers, Profile - influence a range of stakeholders
|
|
|
Issues to consider when developing marcom
|
Target audience, channel strategies, objectives, positioning, branding, integration, competitors, resources
|
|
|
Internet strategy
|
Extranet, intranet
|
|
|
Marcom plan framework(MCPF)
|
context analysis, promotional objectives, marcom strategy, coordinated promo mix (methods, tools and media), scheduling and implementation, resources (human and financial), evaluation and control, feedback
|
|
|
Context analysis
|
customer context: characteristics, level of awareness, perception of brand, level of involvement, percieved risk, decision-making unit characteristics and issues; business context: corp. And marketing strategy, brand/org analysis, competitor analysis; internal context: finanacial constraints, org. identity, culture and values, marketing expertise, agency availability and suitability; external context: key stakeholders? why important? communication needs? social, political, economical and tech restraints and opportunities
|
|
|
Importance of Promotional objectives
|
provide balance, indicate positioning issues, highlight required balance, provide time parameter, provide means by which marcom is evaluated
|
|
|
Elements of promotional objectives
|
corporate objective: from business or marketing plan showing mission and business area org should be in; marketing objectives: from marketing plan, output oriented and are usually sales-related e.g. market share, sales revenue, volume, ROIa nd profitability; marcom objectives: from current context in which brand exists and where it wants to be in future, presented as awareness level, perception, knowledge, attitude and overall degree of brand preference. Goal depends on task to be accomplished - reposition, position
|
|
|
Draw an FCB grid
|
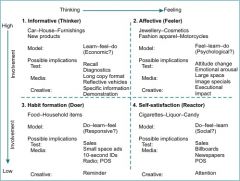
|
|
|
Draw a rossiter-percy grid
|
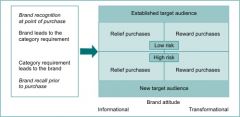
|
|
|
Draw the models of Publich relations
|
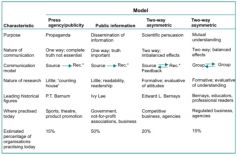
|
|
|
Draw an organisations crisis matrix
|
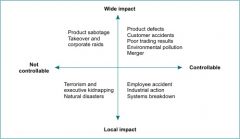
|
|
|
What are the crisis phases and models
|
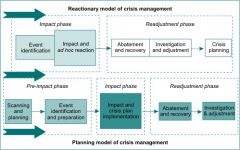
|
|
|
What are the causes of desaster and need for crisis management
|

|
|
|
Draw an awareness grid
|
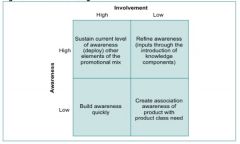
|
|
|
Explain the diffrent postioning approaches
|
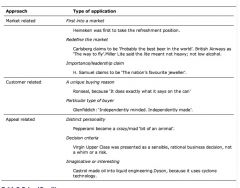
|
|
|
Advert tactic for high involvement and informational target
|

|
|
|
Advert tactic for low involvement and informational target
|

|
|
|
Advert tactic for high involvement and transformational target
|

|
|
|
Advert tactic for low involvement and transormational target
|

|
|
|
Describe the corporate management process
|
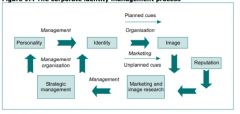
|
|
|
Describe the 3 dimensional attribute process
|
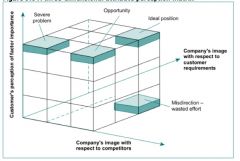
|
|
|
Compare the different selling channels
|
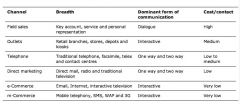
|
|
|
Draw the account investment matrix
|

|
|
|
Draw the multichannel mix allocation matrix
|
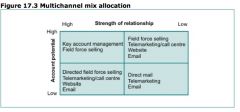
|
|
|
Show images of sales promotion typology
|

|
|
|
Show a sales promotion grid
|
|
|
|
Show a sales promotion grid
|

|
|
|
What are the difficulties of marginal analysis
|
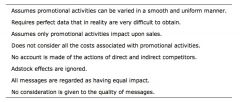
|
|
|
Summarize media richness grid
|
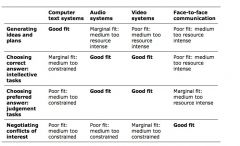
|
|
|
What are the factors influencing choice of technology
|
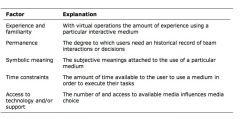
|
|
|
What are differences between effectiv frequency and recency frequency
|
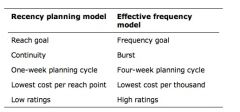
|
|
|
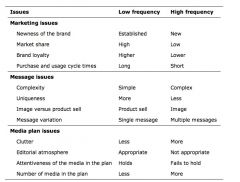
What are the Issues to be considered when setting frequency plans
|
|
|
|
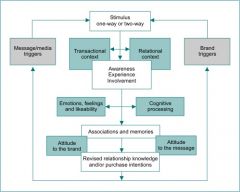
Describe a model of how marcom might work
|
|
|
|
What are the Five features of dialogical orientation
|

|
|
|
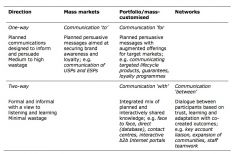
Draw the communication or matrix
|
|
|
|
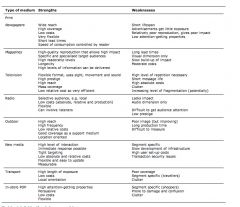
Write a summary of media characteristics
|
|
|
|
Transformational motives in ad
|
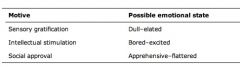
|
|
|
Informational motives in ad
|
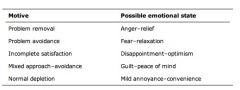
|
|
|
What is public relations
|
Management of relationship between organisations and their stakeholders
|
|
|
What Opportunities can be derived from Sponsorship
|
Provides exposure to particualr audience, suggests association between sponsor and sponsored, percieve indirectly through third party, opportunity to blend a variety of tools
|
|
|
What are the Characteristics aof PR
|
No purchase of air time or space, decision to tranmit depends on media resource manager not on message sponsor, carry greater percieved credibilty as it is not paid for, , provokes trust and confidence reducing percieved risk, cost is minimal, used to reach a particular audience, org control is limited
|
|
|
Who are Public relation stakeholders
|
Employees (internal PR), financial group (investors), customers (media - most crucial within is press), organisation and communities (corp. PR) - public affairs, community relations, industry relations, issues management
|
|
|
What are the models of PR
|
(Gruning) Press agency or publicity model (one-way propaganda e.g media events and press releases), public information (truthful information, one-way), two-way assymetric (feedback from recievers but organisation has control and purpose is still to persuade and influence attitude), two-way symmetric model (true dialog)
|
|
|
What are the Types of PR
|
Corporate and Marketing public relations
|
|
|
What are the Objectives of PR
|
provide series of coordinated programmes that compliment the overall marcom strategy
|
|
|
What is cause-related marketing
|
, take into considertion credibility, ethic and reputation, non profit and profit oriented firms join together to exploit association for mutal benefit e.g. microsoft and NSPCC
|
|
|
Name and explain PR methods and techniques
|
Media relations e.g press release, press conference, interviews, publicity and events e.g. product event e.g. seminars, trade shows, corporate event e.g. open doors, factory day, product donation, community event - fun runs, contribution to centers , lobbying e.g. relationship to government management, corporate advertising, crisis management,
|
|
|
Outline the History of Corporate advertising
|
Institutional, Issue, Umbrella, Focus, relationship
|
|
|
What are the Goals of corporate ad
|
enhance reputation, improve credibility, provide point of differentiation, support products and services, attract higher-quality employees, underpin sharholder value, gain easier access to supplier and new market, advocate position, communicate ist social and environmental actions to public
|
|
|
What are the Reasons for use of corp. Ad
|
Change and transition, poor image, product support, recruitment, repostioning, advocacy or issues
|
|
|
What are th causes of disaster (crisis management9
|
Economic, managerial, political, climate, technology
|
|
|
What are the variables of crisis
|
Control - controllable and non-controllable, Potential impact - wide and local impact
|
|
|
What are the crisis phases
|
Reactionary model - Impaact phase: event identification, impact - ad hoc reaction, Readjustment phase: abatement and recovery, investigation and adjustment, crisis planning: Planning model - pre-impact phase: scanning and planning, event identification and preparation, Impact phase: impact and crisis plan implementation, Readjustment phase: abatement and recovery, investigation and adjustment
|
|
|
Image restoration approaches
|
simple denial, evasion of reposnsibility, reducing offensiveness, corrective action, mortification
|
|
|
Forms of online crisis
|
Cyber squatting - similar domain names, anti-corporate sites, distributed denial of service - computer hijack, firewall attack, ip and web spoofing - sites look and feel like master site, direct and indirect attacks, email, password capture
|
|
|
Crisis roles for stakeholders
|
Image
|
|
|
What are the roles of PR in a promotional mix
|
creating goodwill and stimulatin interest, support marketing of org's products and services, means by which relationship can be developed
|
|
|
Factors that have led to growth in sponsorship
|
increase in media coverage of events, relaxation of gov. And ind. Regulations, increased incidents of sponsorship event supply and demand, relationship orientation and association between sponsorship participants, positive attitude towards sponsorship by senior management, awareness of drive towards integrated marcom, increasing rate of media costs, need to develop softer brand associations and reach niche audiences
|
|
|
What are the objectives of sponsorship
|
build awareness, develop customer loyalty, improve perception of brand or org, attract new users, support dealers, act as form of staff motivation - moral building
|
|
|
What are the types of sponsorship
|
Sports sonsorship, programme sponsorship, arts sponsorship, community sponsorship
|
|
|
What are the Elements of an advertising plan
|
Message, medium, timing or manner
|
|
|
What are Advertising costs
|
Absolute costs - cost of space, etc; relative costs - cost incurred to reach each member of the target group
|
|
|
What are the main roles of ad
|
build awareness, induce engagement, to position and reposition brand, create competitive advantage, anchor for many integrated campaigns
|
|
|
What are the types of emotional ad strategy
|
shock strategy - unexpected, audiences are surprised by messages because they do not conform to social norms and expectations
|
|
|
Advertising models and concepts
|
(from Hall and O'Malley) - four main frame works: sales, persuasion, involvement, salience, (from Prue) - alphabetical model
|
|
|
Theories of advertising
|
Strong theory: adverts can change knowledge, attitudes, beliefs or behaviour of target audience; Weak theory: adverts are capable of improving peoples knowledge as in strong theory but consumers are regarded as selective in determining which adverts they observe
|
|
|
Explain the alphabetical model
|
ABCD: Appreciation, branding, communication, desired effect
|
|
|
Strategical use of advertising
|
FCB Matrix is based on involvement and brain specialisation with elelments of thinking and feeling and run under four strategies: informative, affective, habitual and self-satisfaction; Rossiter-Percy grid is informational and transformational
|
|
|
What are components of promotional objectives
|
Issues relating to buyers of the product or customers, issues concerned with sales volume, market share, profitability, revenue, issues concerned with image, reputation, preferences of stakeholders have towards org.
|
|
|
Importance of promotional objectives in marcom
|
Provides means of communication an coordination between groups, improves performance because common goal is known, constraints number of options available, provides benchmark so promotion can be evaluated
|
|
|
Contents of promotional objective
|
Sales-related - objectives: sales turnover, market share movement, ROI, - dificulty: other programmes play a role, adstock or carry over or customer related - objectives: create awareness and positive attitude towoards brand
|
|
|
Communication-related promomotion model
|
Dagmar: Communication based on hierachy - awareness, comprehension, conviction, action
|
|
|
Difficulties of Dagmar model
|
sales orientation, restrictions on creativity, short-term accountability (not long enough as one currently have 12 weeks reports)
|
|
|
Where are promotional objectives derived form or the elements
|
corporate goal, marketing goals, communication goal
|
|
|
SMART
|
Objectives have to specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, timed and targeted
|
|
|
What is positioning
|
Positioning is a process whereby information about the org. or product is communicated in a way that the object is percieved to be differentiated from competition to occupy a particular space in the market.
|
|
|
Steps to developing and managing position
|
Which position is held by competitors (Perceptual mapping), which position is already held by focus brand, what could be the desired postion for the brand, is strategy feasable, implement programme to establish desired position, monitor perception held by consumer on a regular basis
|
|
|
Positioning strategies
|
Strategies have be long term. Product features, Price/Quality, Use, Product class dissociation e.g Dove - not a soap or magarine - like butter but softer, User - target user can be identified - for men, for women, etc, Competitor - position against competitor e.g Qualcast against market leader hover - lot less bovver than hover, Benefit, heritage or cultural symbol
|
|
|
Elements of a creative brief used to create a creative strategy (the message)
|
Message source, balance, structure, presentation of message
|
|
|
Characteristics of message source
|
Message source - percieved expertise, Personal motives of the source, Degree of trust placed on source.
|
|
|
Ways of establishing source credibility
|
Display key attibutes and signal trustworthiness through third-party endorsement or satisfied users (case study, testimonials, referrals)
|
|
|
Establishers of credibility
|
By initiator, by spokesperson - expert, celebritiy, ceo, consumer, Sleeper effects - message has to be repeated on a regular basis
|
|
|
Message balance
|
Emotional content and informational content
|
|
|
Message structural features
|
conclusion drawing - depends on complexity of issue, level of education of reciever, whether immidiate action is required or not, on level of involvement; one- only one argument in favour of the product - and two-sided - good and bad points of an issue are presented - messages; order of presentation - primary effect or recency effect (more important in personal selling than in television)
|
|
|
How can message be presented
|
Factual (hard sell) - information provision, mainly for high involvement decisions; slice of life - identification with scenario, Demonstration, Comparative advertising
|
|
|
How to apeal on emotions and feelings
|
Through fear, humor, animation, sex, music, fantasy and surrealism
|
|
|
Advertising tactics
|
Informational motves, transformational motives
|
|
|
Dimensions of corporate image
|
relational dimesions, management dimensions, product and services
|
|
|
Corporate brand criteria
|
rarity, durability, inappropriability, imperfect imitabilty, imperfect substitutabilty
|
|
|
corporate communication
|
transfering corporate identity to coporate image
|
|
|
Elements of CI
|
corporate personality, identity - differentiation and image/reputation - cues should be based on reality and reflect the values and beliefs of org.
|
|
|
Types of CI
|
Symbolism - color, name - strongest cue, typefaces, logos, symbols, behaviour, communication
|
|
|
Corporate personality is composed of
|
Culture and overall strategy and all characteristics that identitfy an organisation abd what the org. actually is
|
|
|
what is direct marketing
|
all media activities that generate series of communication and responses with an existing or potential customer, concerned with managing customer behaviour and offers collection and utilisation of pertinent and measurable data
|
|
|
Tools of direct marketing or direct response media
|
Direct mail, telemarketing, carelines, inserts, print, door to door, radio and television, internet and new media0
|
|
|
Two important issues associated with direct marketing are
|
Measurability and rewards each party percieves through participation in relationship e.g. Customer: tangible and intangible satisfaction - shopping convinience, time utiity, Provider: when customer realises and starts appreciating attention paid to him or her
|
|
|
Models or types of direct marketing
|
Complementary model, primary differentiator model, sales channel model, brand model
|
|
|
Complementary model
|
Used to compliment other promo activities, main purpose is t generate leads and to som extent awareness, reinforce and inform e.g banks
|
|
|
Primary differentiator
|
As the primary tool for communication, apart from complimentary purpose also to cut costs, avoid intermediaries and reach finely targeted audience e.g book, music and wine clubs
|
|
|
Growth drivers of direct marketing
|
Technology, changing market context
|
|
|
Advances in direct marketing technology
|
Generally, the ability to collect, store and analyse data is now easier, cost-effective and straight forward, stimulate dialog and interaction to collect more data. Data capture and collection, information processing, communication and interaction
|
|
|
Changes in direct marketing due to market context
|
Lifestyles and expectation - inner directedness, pluralism, idividualism, fragmentation - audience media, management requirements - costs, accountability, competition, speed of response
|
|
|
The role of database
|
A storage, sorting and administrative device to assist direct and personalised communications. One can use recency/frequency/monetary model, response analysis collected from data base and information from market research to build relationship, track and analys and develope this relationship.
|
|
|
Different types of IT systems in telemarketing
|
automatic call distribution, interactive voice response, call recording systems, computer interaction management, computer telephony integration, predictive diallers, computer assisted telephone interviewing, semi-structures interview, personal slaes presentation
|
|
|
Use of carelines
|
collect complaints about product performance and related experience, seek product related advice, collect suggestions regarding product developement and packaging, comment about action and devlopment concerning brand as a whole
|
|
|
Telemarketing supports sales force
|
search for an qualify new customers, service existing customer and prpare field force, seet repeat orders, provide a link between network members
|
|
|
How to categorise customers
|
Account investment matrix, multichannel mix allocation matrix
|
|
|
Why sales promotion
|
Offers added value and accelarates sales
|
|
|
Value orientation of sales promotion
|
Value increasing - by changes in quantity or quality or lower price, Value adding - by offering something to augment product or price eg. Gifts, information, delayed (postal premium), accumulated (loyalty premium) or instant (scratch and win competitions)
|
|
|
Role of sales promotion
|
Short termism, managerial accountability, brand performance, brand expansion - make decision making easier, competition for shelf space - help win valuable shelf space
|
|
|
Brand emotional loyalty
|
no presence, presence, relevance and performance, advantage, bonding
|
|
|
5 Loyalty trends are
|
Ubiquity, coalition, imagination, wow, analysis,
|
|
|
Sales promotion techniques (manufacturers to resellers
|
Objectives for new products: trial, establish distribution, task to marcom is to encourage retailers to distribute new product and establish trial behaviour; objectives for established products: usage - main objective is to develop greater exposure, motivating distributors to allocate shell space, task of marcom is to encourage resellers to buy and display increased amount of product to increase usage
|
|
|
Sales promotion methods manufacturer to reseller
|
Buying allowances, count and recount allowances, Buy-back allowance, mercahndise allowance - provide extra goods at no cost, advertising allowances - dealers listing, vertical advertising (manufacturer takes a portion of the cost and ad space), horizontal advertising - competitors join together to promote product class e.g milk industry, hostaging, dealers contests, dealers meetings and conventions, training and support, personal selling
|
|
|
Sales promotion objectives and methods for reseller to consumer
|
Objective: promote brand or store and increase usage - get the shelves empty and into the homes of users, methods usually come from manufacturers
|
|
|
Sales promotion objective for manufacturer to consumer
|
Objective: stimulate trial and increase usage
|
|
|
Sales promotion method for manufacturer to consumer for trial
|
Sampling, coupons, consumer deals, price-offs, bonus packs, refunds and rebates,
|
|
|
Five types of consumers and their attitudes towards sales promotion
|
Branded ELDP seekers - restricted income but brand loyal, looking for everyday bargain rather than promotions; Low price fixture ferrets - restricted income store not brand loyal, easily switch and like promotions; Promotion junkies - seek out bargains and promotions have zero loyalty, a hazard to marcom; Stockpilers - brand and store loyal and no income restrictions and buy in large quantities, react well to promotions; Promotionally oblivious
|
|
|
How to distribute coupons
|
Consumer direct distribution, media direct distribution, package direct distribution, instant coupons, bounce-back coupons, cross-ruff coupons
|
|
|
How to distribute samples
|
door to door, direct mail, central location, cross product sampling in or on pack, cooperative package distribtion, newspaper or magazine distribution, any of the above with coupon
|
|
|
Sales promotion method for manufacturer to consumer for usage
|
premiums, contests and sweepstakes,
|
|
|
Variables affecting premium
|
Attractiveness, immediacy, mention of premiums value, fit between premium and category
|
|
|
Types of premium
|
premiums - direct premium, inpack premium, delayed premium, self-liquidating
|
|
|
Sales promotion by promoting sales force
|
contests, sales meeting,
|
|
|
Other ways of sales promotion
|
brochures, sales literature, character licensing
|
|
|
Benfits of marcom budgeting
|
focus peoples attention on the costs and benefits of undertaking planned marcom, instills management discipline necessary to ensure that the objectives of the plan are capableof bieng achieved, cross function coordination and forces managers to ensure that the planned marcom are integrated and mutually supportive, means by which campaigns can be monitored and controlled, finacial review at the end of campaign enables management to learn and become more efficient
|
|
|
Dificulties with budgeting
|
difficult to quantify amount needed, does not fit into standard accounting practices, success can not be measured as the tools are so diverse, process is not clear cut
|
|
|
Budget decision stakeholders
|
Focus organisation, agencies, media, target audience
|
|
|
Models of appropriation or allocation
|
Abritrary: chairperson rules, Inertia: As usual as has always been done, media multiplierr: increase by rate at which media costs have increased, percentage of sales, affordable, quantitative approaches: object and task: payout plan, sensitivity analysis
|
|
|
Theoretical budget allocation method
|
marginal analysis
|
|
|
Other budgeting models
|
competitive parity, advertising to sales ratio
|
|
|
Objective of media planning
|
Devise an optimum route for the delivery of the promotional message
|
|
|
Difficulty in planning
|
media and audience fragmentation, money
|
|
|
Choices to be made in media planning
|
Media, vehicle, schedule
|
|
|
Criteria tha determine richness of content
|
availability of instant feedback, capacity to transmit multiple cues, use of natural calguage, degree of personal focus
|
|
|
What is media richness theory
|
It holds that there is a hierachy or spectrum of mediy, ranging from prsonal or face to face encounters as the richest medium through to single sheets or text based information as lean media at the other end
|
|
|
Rich media
|
encourages feedback and gives the posiblity of feedback, contains a dialog interaction, has an expresion of personal cues e.g. voice, body language which help to establish personal connection
|
|
|
Types media choice models
|
MRT, SIT, TAM
|
|
|
Types of switching behaviour
|
Involuntary, simple, complex
|
|
|
Considerartions for media planning concepts
|
Reach and coverage, frequency, gross rating point
|
|
|
Effective frequency
|
This is the number of times a person needs to be exposed before commnication is effective, Ideal is 3 times.
|
|
|
Types of reach
|
Duplicated and unduplicated
|
|
|
Opportunities to see(OTS)
|
|
|
|
Effective reach
|
Those aware of the advert not just exposed to
|
|
|
Recency planning
|
Reach more important that frequency
|
|
|
Advertising attitide for media determination
|
Cynics, Enthusiasts, ambivalents, aqcuiescents
|
|
|
Types of TV audiences
|
heavy, medium, light users
|
|
|
Efficiency and types of cost
|
Absolute cost - space and time required to transport message, Relative cost - costs incurred in making contact with each member of the target audience
|
|
|
CPT
|
space cost times 1000 divided by circulation
|
|
|
Miline rate
|
cost per line pace per million circulation
|
|
|
Programming/television ratings
|
TVR= number of target tv households tuned into a programme divided by total number of target tv households times 100
|
|
|
Cost per TVR
|
Times cost (absolute costs divided by TVR
|
|
|
Media source effects or Source factors that influence power of impact
|
Vehicle atmosphere, technical and reproduction characteristics, audience and product characteristics
|
|
|
Vehicle atmaosphere
|
editorial tone, vehicle expertise, vehicle prestige
|
|
|
Technical reproduction characteristics of vehicle
|
technical factors, expososure opportunities, perception opportunities
|
|
|
Audience/product characterisitcs
|
audience/vehicle fit, nature product, vehicle mood effects
|
|
|
Considerations when scheduling
|
Objective, purchasing pattern, level of involvement, characteristics of audience
|
|
|
Timing of ad placements
|
Continuity patterns - rising, fading pattern, flighting patterns, pulsing patterns
|
|
|
What are below the line communications
|
sales promotions, event marketing, roadshows, direct marketing
|
|
|
Drip role of marketing
|
differentiate, reinforce, inform, persuade
|
|
|
Sequencial models of how marcom works
|
AIDA, hierachy effects of models, information processing model
|
|
|
Difficulties in sequential processing
|
Attitude towards product does not necessarily lead to purchase
|
|
|
Types of cognitive processing
|
product/message thoughts - types of response: counter argument and surport argument thoughts; source-oriented thoughts - types: source derogation and source bolster, message execution thoughts; attitude towards message
|
|
|
Elaboration likelyhood model
|
extent to which an idividual needs to develop and refine information necessary for decision-making
|
|
|
What should marcom strategy be based on
|
it should be based on the level of cognitive processing the consumer is willing to engage in
|
|
|
Developing significant value
|
to be successful, marcom has to present an object that is new to the receiver, be interesting and stimulating, be personally significant
|
|
|
Three main psychological orientations
|
pschoanalytical, reinforcement, cognitive
|
|
|
Elements of internal information processing
|
personality, perception, learning, attitudes, environmental factors
|
|
|
Personality
|
pscychoanalytical (freud) theory - life and death instincts, ID, super-ego and ego, approach used in insurance and volvo(safety) and trait theory - idividual differences based on specific traits, types - mainstreamers, succeeders, reformers
|
|
|
Perception
|
perceptual selection; selective attention; perceptual organisation - figure-ground (article against a general background), grouping (associatons e.g food with images that show fitness and healthy), closure - information is incomplete e.g. gesalt psychology - part of a whole; perceptual interpretation - use of distortion
|
|
|
Distortion factors
|
halo effect, stereiotyping
|
|
|
Learning
|
behavioural - stimulus response orientation - classical conditioning; operant conditioning, cognitive learning - memory (sensory, short-term, long-term), functions - rehearsal, encoding categorisation, retrieval
|
|
|
Processes in cognitive learning
|
iconic rate learning, modelling, reasoning
|
|
|
Consideration in marcom
|
interference theory, decay (through selective perception or conter argument), cognitive response
|
|
|
Components of attitude
|
cognitive (learn), affective (feel), conative (do); multiple-attribute attitude model
|
|
|
Intentions
|
intention to buy - subjective norm and reasoned norm
|
|
|
(Compensatory models)Strengths and beliefs held about key attributes
|
compensatory, non-compensatory attributes
|
|
|
Changing attitudes with marcom
|
change physical product or service element, change misunderstanding, build credibility, vhange performance belief, change attribute priorities, introdice a new attribute, change perception of competitor product, change or introduce brand associations, use coporate branding, change number of attributes used
|
|
|
Environmental influences on information processing
|
culture, subculture, social class, groups - ascribed groups, primary and secondary groups, formal and informal groups, aspirational and membership groups; situational influences - usage situation, purchase situation, communication situation - physical aspects, time, task
|
|
|
four main stages of ad effectiveness measurement
|
direct response, executions (recognition and recall techniques are used), campaign evaluation (use of econometrics and modelling techniques to examine influence), research nirvana
|
|
|
Pretesting unfinished ads
|
concept test using photomatics or livematics, focus group, consumer juries
|
|
|
Pretesting finished ads
|
dummy vehicles, readability tests, theatre tests,
|
|
|
Psychological measures
|
pupil dilation, eye tracking, galvanic response - skin reaction tachiscopes - attention, electroencephalographs - brain frequencies
|
|
|
Post-testing methods
|
enquiry, recall - day ater recall, unaided recall, aided recall, verbatim response i.e. answers are recorded word for word, reliability is high but validity is low; recognition test - recency, specific issue, frequency
|
|
|
Principle readership scores
|
noted, seen-associated, read most, signature; sales test (direct response and enquiries)
|
|
|
Other testing methods
|
single-source data, simulated market tests, tracking tests -intervieing on a regular basis
|
|
|
Other analysis to be made
|
likeability, financial anlysis
|
|
|
Evaluating sales promotion
|
Generally depends on objective. M2R: retail audit; R2C: measures of image and/or stock turnover, M2C: consumer audit, redeption level; M2S: systematic trackin of sales and market share
|
|
|
Use of technologies in sales promotion evaluation
|
homescan, coupons
|
|
|
Evaluation of PR
|
What is measure are the obectives in the different PRS such as Corporate publich relations, coporate image, recruitment, crisis management, Marketint public relations (measured via leads generated) One can also use the pre and post test measures used for ads and tracking methods
|
|
|
Other PR measuring techniques
|
set objectives, evaluate press cuttings, evaluate media, employ tracking studies
|
|
|
Evaluation of sponsorships
|
Can only be measured through objectives set
|
|
|
Evaluation of personal selling
|
input, output, expense ratio, servicing ratios, activity ratios
|
|
|
Evaluating online communications
|
banner ads - click through rate, website effectiveness (develop profiles - all surfers, those aware, those interested, determined vistors, those who transacted
|
|
|
Linear model of communication
|
source, encoding, signal, decoding, receiver, feedback, nose
|
|
|
Influences media on the communication process
|
new technology, speed, roles revised between provider and reciever of message
|
|
|
Realms of understanding
|
a message is better understood if source and receiver understand each other
|
|
|
Influences of people on the communication process
|
one-step, two-step, multiflow word of mouth communication
|
|
|
Categories of output WOM
|
product involvement, self involovement, other involvement, message involvement. WOM is usually done by brand advocates
|
|
|
Types of WOM volunteer
|
opinion leaders, opinion formers, opinion followers
|
|
|
Process of adoption
|
knowledge, persuation, decision, implementation, confirmation
|
|
|
Process of diffusion
|
innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, laggards
|
|
|
Types of approaches to communication
|
interactional, relational or contectual, network approach
|
|
|
Marketing communication mix
|
advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations, direct marketing
|
|
|
The 4Cs framework - characteristics of marcom tools
|
communications - ability to deliver personal message, ability to reach a large audience, level of interaction, credibility - given by target audience, costs - absolute costs, cost per contact, wastage, size of investment, control - ability to target particular audiences, managements ability to adjust the tool as circumstances change
|
|
|
Selection criteria
|
degree of control required, financial resources, level of credibilty, size and geographic disperison
|
|
|
Communication differences between b2b and b2c
|
message reception, number of decision makers, balance of communication mix, comstituents of marcom mix, message content, length of purchase decision time, negative communication, target marketing and research, budget allocation, measurement and evaluation
|

