![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
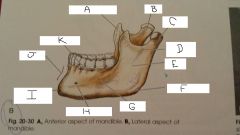
What is A?
|
Coronoid Process
|
|
|
OML perpendicular, PA, centered to exit the nasion, and a 0 degree tube angle is what projection?
|
PA projection to show the rami, body, and displacement
|
|
|
PA Axial Projection with a tube angle of 20-25 degrees and centered to exit the acanthion will show
|
rami, medial/lateral displacement, most of the body the center part is superimposed by the spine
|
|
|
The inner ear is located
|
in the bony labyrinth
|
|
|
tape a patients ear forward for what projection and why?
|
Mastoid projection and to prevent super imposition
|
|
|
Auricular point is
|
the EAM
|
|
|
For Caldwell projection the OML should form a
|
15 degree angle
|
|
|
To view mandibular rami on PA the CR will exit
|
the acanthion using a PA Axial
|
|
|
For AP axial TMJ the CR is
|
35 degree caudad
|
|
|
To see body of mandible in a PA position
|
AML perpendicular and 0 tube angle
|
|
|
To see the body and TMJ in a PA position
|
AML perpendicular and 30 degree cephalad angle
|
|
|
To see the Ramus in a lateral position
|
a 25 degree cephalad tube angle
|
|
|
To see the body in a lateral position
|
a 25 degree cephalic tube angle and a 30 degree head rotation
|
|
|
To see the Symphysis in a lateral projection
|
a 25 degree cephalic tube angle and a 45 degree head rotation
|
|
|
To see the coronoid and condyloid process of the rami
|
SMV projection
|
|
|
What sinuses develop at birth?
|
Maxillary
|
|
|
To see frontal sinuses what projection is needed?
|
Caldwell with the Petreous Ridges in the lower 1/3rd of the orbits, do not angle tube, bring OML to make a 15 degree angle with IR.
|
|
|
Describe the Axiolateral oblique projection for TMJS (Law)
|
CR centered to Exit the TMJ that is closest to the IR (tmj of interest), leave in false teeth, pt in a lateral position with 15 degree head tilt toward the IR and a 15 degree tube angle at about 1.5'' superior to the upside EAM and .5'' anterior - two projections open and closed mouth
|
|
|
Describe the Shuller
|
Pt in true lateral 25-30 degree caudal angle centered to exit the side closest to the IR should enter about 1/2'' anterior and 2'' superior to the EAM
|
|
|
AP Axial for Ramus
|
AML perpendicular 25 degree caudal tube angle that enters the acanthion
|
|
|
Centering and tube angle for Stenvers
|
CR enters 3-4'' posterior and 1/2'' inferior to the upside EAM, head angled 45 degrees set to exit 1'' anterior to the down side EAM with a 12 degree cephalic tube, IOML perpendicular
|
|
|
Centering and tube angle for Modified Law
|
CR enters 2'' posterior and 2'' superior to upside EAM, 15 degree caudal tube angle and 15 degree head rotation, IOML is parallel and IPP is perpendicular
|
|
|
Centering and tube angle for Arcelin
|
CR enters 1'' anterior and 3/4'' superior to the upside EAM, 10 degree caudal tube angle and a 45 degree head rotation. IOML is perpendicular
|
|
|
between the ages of 6-12 how many teeth do you have
|
20 teeth
|
|
|
After losing all your milk teeth you are left with
|
32 teeth
|
|
|
The crown of the tooth
|
goes beyond gum or gingiva and is 1/3rd the lengthof the tooth
|
|
|
Incisors are made to...
|
cut
|
|
|
Canines are made to...
|
Cut are bigger than incisors and longer
|
|
|
Premolars and molars are
|
square, broad, and have an irregular surface good for grinding
|
|
|
The horizontal/occlusial plane
|
passes through arches and parallel with occlusial processes
|
|
|
The carotid foramina is located
|
petrous portion of the temporal
|
|
|
infraorbital foramina is located
|
inferior to orbit in maxilla
|
|
|
Foramen magnum is located
|
occipital bone
|
|
|
Mandibular Foramina is located
|
medial surface of the ramus of mandible
|
|
|
Olfactory Formina is located
|
cribriform plate of ethmoid
|
|
|
Foramen Ovale is located
|
Greater Wing of spheniod
|
|
|
Foramen Rotundum is located
|
Junction of anterior and medial parts of sphenoid
|
|
|
Formen Spinosum is located
|
posterior angle of sphenoid
|
|
|
How many maxillary sinuses, where are they located, and shape
|
They are paired, located in the body of each maxilla, and are pyramidal in shape
|
|
|
How many Frontal sinuses, where are they located, and shape
|
They are paired, located between the tables of the vertical plated of the frontal bone, and they vary greatly in size and shape
|
|
|
How many Ethmoidal sinuses, where are they located, and shape
|
There are 2, they are located within the lateral masses of the labyrinths of the ethmoid bone, and they are divided into three main groups
|
|
|
How many Sphenoid sinuses, where are they located, and shape
|
they are paired, occupy the body of the sphenoid bone, and vary in size and shape, and lie immediately below the sella turcica and extend between the dorsum sellae and the posterior ethmoidal air cells.
|
|
|
The lateral projection of sinuses should show...
|
All four sinus groups but the Sphenoid sinus is of primary importance
|
|
|
Describe Lateral Sinus projection
|
IOML is perpendicular to the IR, NO TUBE ANGLE, Center .5-1'' posterior to the outer canthus
|
|
|
The Caldwell projection for Sinuses should show...
|
Frontal sinuses lying above the frontonasal suture and the anterior ethmoidal air cells lying above the petrous ridges
|
|
|
Describe Caldwell for Sinuses
|
Rest pt nose on IR with the OML making a 15 degree angle, center CR to exit the nasion
|
|
|
Parietoacanthial projection for sinuses should show..
|
Sphenoidal sinuses projected through the open mouth
|
|
|
Describe the Open mouth waters for sinuses
|
The OML will make a 37 degree angle with the IR and center the CR to exit the acanthion, then open the patients mouth
|
|
|
The SMV for sinuses what line is parallel with the IR and what sinuses are of interest?
|
The IOML is parallel with the IR and the Sphenoid and Ethmoid sinuses are of interest
|
|
|
PA Projection of Mandible with the OML perpendicular shows
|
Mandibular body, rami, and medial/lateral displacement in fractures of the rami
|
|
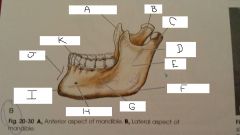
B?
|
Neck
|
|
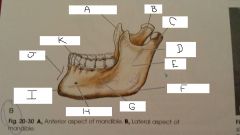
C?
|
Condylar Process
|
|
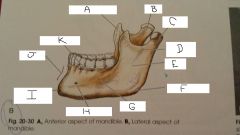
D?
|
Mandibular Notch
|
|
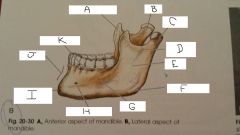
E?
|
Ramus
|
|
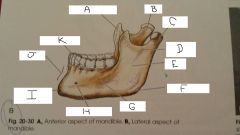
F?
|
Angle
|
|
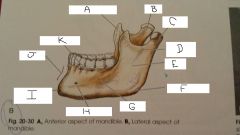
G?
|
Body
|
|
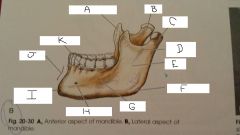
H?
|
Mental Foramen
|
|
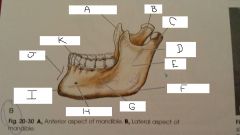
I?
|
mental protuberance
|
|
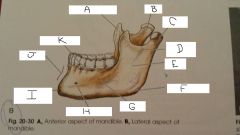
J?
|
Symphysis
|
|
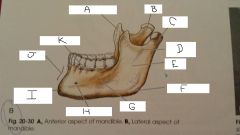
K?
|
Aveolar process
|

