![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Faunal regions were originally proposed by who? |
Alfred Russel Wallace, co-discoverer of the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection. |
|
|
Paleartic includes which regions? |
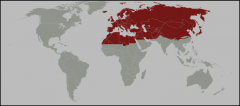
Europe, North Africa (to Sahara), Asia (except India, Pakistan and SE Asia) and Middle East.
Number of families = 42; endemics = 0 |
|
|
Neartic includes which regions? |
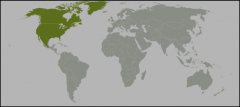
Canada, USA, Mexico to tropics
Number of families = 37, endemics = 2 (maybe 4) |
|
|
What is Holartic? |
Holartic is Paleartic plus Neartic. |
|
|
What does Endemic mean? |
An endemic organism is one that is exclusively native to a place or biota. |
|
|
Neotropical includes which regions? |
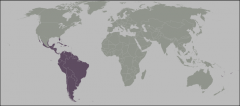
Tropical Mexico south to South America, plus Antilles and south Florida
Number of families=50; endemics = 19 |
|
|
Afrotropic (Ethiopian) includes which regions? |
Madagascar, Africa south of the Sahara, southern Arabian Peninsula
Number of families=52; endemics= 18 |
|
|
Indomalaya includes which regions? |
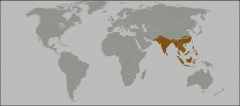
Pakistan, India, Southeast Asia, Phillipines, Indonesia west of Wallace line (Sumatra, Java, Borneo)
Number of Families=50; endemics=4 |
|
|
What is the Wallace Line? |
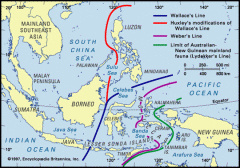
The Wallace Line is a boundary that seperates the zoogeographical regions of Indomalaya and Wallacea (a transitional zone between Asia and Australia).
Overall, this is a region of on-going plate techtonics at the line of collision between the Australian and Asian plates. As a consequence this is a very volcanic region.
Some islands are less than 20 miles apart. On the Australian side, principal mammals are marsupials, on the Asian side, they are placental. |
|
|
Australasia includes which regions? |
Australia, New Guinea, Tasmania, Indonesian Islands east of the Wallace line (Celebes, timor, etc.)
Number of families = 28; endemics =17 |
|
|
Oceanic includes which regions? |
Oceans of the world and truly oceanic, isolated, small islands.
Number of families=14; endemics = 14 |
|
|
Antarctica includes which regions? |
Antarctic continent and several island groups in the southern Atlantic and Indian Oceans.
The continent of Antarctica is so cold and dry that it has supported virtually no vascular plants for millions of years, and its flora presently consists of lichens, mosses, liverworts, and terrestrial and aquatic algal species, which live on the areas of exposed rock and soil around the shore of the continent.
Several species of mammals use it for breeding purposes. |
|
|
What is biogeography? |
-Biogeography is the study of how the spatial patterns of living things developed. -Continents have split apart, moved around, then rejoined, all very slowly. -Identical rock layers with particular fossils in them are found in different continents--they were laid down as one bed, then the continents broke up and now they are widely seperated. -Distribution of current species can also be explained by continental movements. |
|
|
In 1912, who proposed the idea of continental drift? |
Alfred Wegener |
|
|
Why did Alfred Wegener propose the idea of continental drift? |
-The shapes of the continents seemed to fit together like a puzzle -The alignment of mountain chains, rock strata, and glacial deposits suggest movement over time. -The distribution of organisms on Earth is hard to explain if one assumes the continents never moved. |
|
|
About 280 MYA in the Permian period, continents were united in a single land mass called ___? |
Pangaea |
|
|
By 100 MYA, during the Cretaceous period, Pangaea had seperated into ___ and ___ land masses. |
northern (Laurasia) and southern (Gondwana) land masses. |
|
|
What strongly influence Earth's climates? |
Global air circulation patterns, which result from global variation in solar input. |
|
|
What is the intertropical convergence zone? |
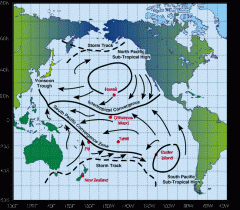
+Air rises when heated and releases moisture. Warm air rises in the Tropics and is replaced by air flowing towards the equator from north and south. The intertropical convergence zone is where these air masses come together. +Heavy rains usually fall in regions close to the intertropical convergence zone. |
|
|
What latitudes are many deserts located at? |
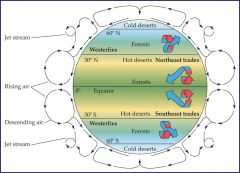
30 degrees North and South |
|
|
What is a rain shadow? |
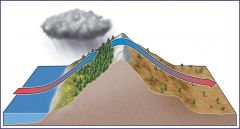
When air encounters mountain ranges, it rises, cools and drops moisture on the windward slopes resulting in a precipitation distribution called a rain shadow where the leeward slopes are dry. |
|
|
What do global window circulation patterns do to ocean water? |
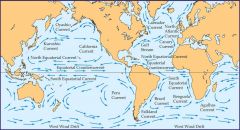
They drive the circulation of ocean water. Ocean water generally moves in the direction of the prevailing winds.
-Winds blowing toward the equator cause warm water to converge at the equator and move west until it encounters a landmass. When warm equatorial water encounters a landmass, it splits and moves north and south; this is a major mechanism of heat transfer to high latitudes. |
|
|
What is a biome? |
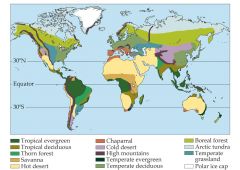
+Biomes are major ecosystem types based on the structure of the dominant vegetation. +The vegetation of a biome has a similar appearance wherever that biome is found on Earth. +The distribution of biomes on Earth is influenced by annual patterns of temperature and rainfall. +Each biome has a characteristic climate, seasonality, and vegetation, and typical patterns of species richness.
|
|
|
What is tundra? |
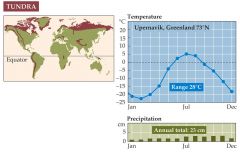
+The tundra biome is found in the Arctic and high on mountains. +In the arctic, permafrost underlies tundra vegetation. +Plants grow only during short summers when the first few centimeters of permafrost melt. +Lowland Arctic tundra is very wet because water cannot drain through permafrost. +Arctic tundra animals either migrate into the area for the summer only or are dormant for most of the year.
|
|
|
What is tropical alpine tundra? |

It is not underlain by permafrost, so photosynthesis and other biological activities continue throughout the year and more plant forms are present. |
|
|
What is the boreal forest biome? |
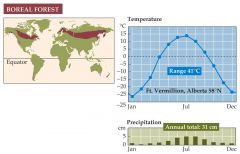
-Is found south of the tundra biome and at lower elevations on temperate-zone mountains. -winters are long and cold, while summers are short and warm. -the short summer favors trees with evergreen leaves. -boreal forests have only a few tree species.
|
|
|
Where is a Temperate Deciduous Forest found? |
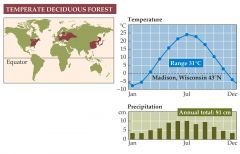
-Is found in eastern North America, eastern Asia, and Western Europe. -temperatures fluctuate dramatically from season to season. -precipitation is evenly distributed throughout the year. -deciduous trees lose their leaves during the winter. -many more tree species are present relative to boreal forests.
|
|
|
What is a temperate grassland? |
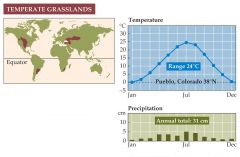
-Is found in many parts of the world, all of which are relatively dry much of the year. -most grasslands have hot summers and cold winters -grasslands are structurally simple, bu they are rich in species of perennial grasses, sedges, and forbs. -grassland plants are adapted to grazing and fire -most of the grassland biome has been converted to agriculture.
|
|
|
What is a cold desert? |
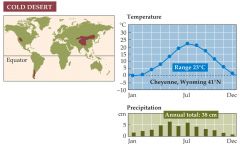
-Is found in dry regions at middle to high latitudes. -cold deserts are also found at high altitudes in the rain shadows of mountain ranges. -seasonal temperatures vary greatly -cold deserts are dominated by a few species of low-growing shrubs. -the most common taxa in the biome are seed-producing plants, birds, ants and rodents. |
|
|
What is a hot desert? |
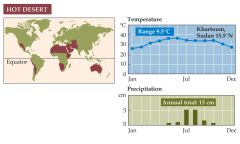
-Is found in two belts, centered around 30 degrees north and 30 degrees south latitudes. -Central Australia and the middle of the Sahara Desert are the driest regions within the biome -Except in the driest regions, hot deserts have richer and more diverse vegetation than cold deserts do. -Succulent plants that store large quantities of water in their stems are common. Annual plants germinate and grow when rain falls.
|
|
|
What is the chaparral biome? |
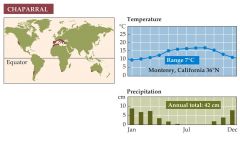
-Is found on the west sides of continents at moderate latitudes, where cool ocean waters flow offshore. -The Mediterranean region of Europe, coastal California, and central Chile are examples of chaparral. -Low-growing shrubs and trees with evergreen leaves are the most common plants in chaparral. The vegetation is adapted to periodic fires. -Large populations of small seed-eating rodents are present in the biome.
|
|
|
What is a thorn forest? |
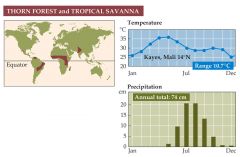
-Are found on the equatorial sides of hot deserts. The climate is semi-arid with little or no rain in the winter, but sometimes heavy rain in the summer. -The dominant plants are spiny shrubs and small trees. Acacia is common.
|
|
|
What are Savannas? |
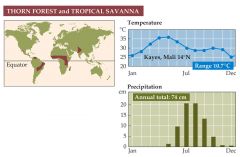
-Savannas are found in dry tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, South America, and Australia. -The savanna biome is characterized by its vast expanses of grassland and scattered trees, and by huge numbers of grazing and browsing mammals. |
|
|
What is a tropical deciduous forest? |
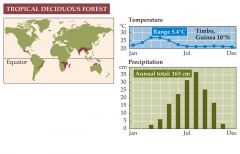
-Is found closer to the equator relative to thorn forests and has a long summer rain season. -Species richness is moderate for plants and high across all other categories, including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. -The tropical deciduous forest biome has some of the best soils in the tropics for agriculture. Most of it has been cleared. |
|
|
What is a tropical Evergreen Forest? |
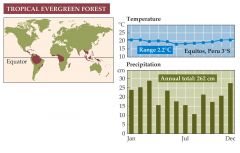
-Is found in equatorial regions where total rainfall exceeds 250 cm annually. -The biome is the richest on Earth in both plant and animal species. -Overall productivity of tropical evergreen forests is the highest among the terrestrial ecological communities. -There many epiphytes, plants that grow on other plants and derive nutrients and moisture from air and water. |
|
|
What are epiphytes? |
a plant that grows on another plant but is not parasitic, such as the numerous ferns, bromeliads, air plants, and orchids growing on tree trunks in tropical rain forests. |

