![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what is a typical way that energy of interactions between two proteins or protein and small molecule can be written?
|
Etotal=(Ionic Pairs + H-bonding) + Van der Waals forces + removal of water from contact
|
|
|
|
a myelinated fiber can be translated to what?
|
a high frequency fiber
|
|
|
|
how big are the following
1)human body 2)organ, tissue 3)cell 4)subcellular organelle 5)macromolecule 6)small molecule |
1) 2m
2) 10^-1m 3)10^-4 - 10^-5 4) 10^-5 - 10^-7 5) 10^-8 - 10^-9 6) 2.8* 10^-10 |
|
|
|
describe humans as a biological species
|
Kingdom Animalia
Subkingdom Metazoa (many cells) Lineage Deuterostoma (first embryonic split becomes anus) Phylum Chordata (backbone originated from cartlidge) Subphilum Vertebrata Class Mammalia Family Hominidae Genus Homo Species H. sapiens |
king, louis, please, cof, good , stuff
|
|
|
Origins of humans
|
North eastern africa
|
|
|
|
how long ago did humans and neanderthalensis co-exist?
|
30,000 years ago
|
|
|
|
name the 3 major changes in human evolutionary change
|
200,000 YA: Phase 1: modern human origins
150,000 YA: population divergence in africa 100,000 YA: migration out of africa |
|
|
|
compare humans to chimps
|
humans: better at walking, larger brain
chimps: hands more adapt for their food |
|
|
|
Is a colony of protozoa an animal?
|
no
|
|
|
|
how was the first animal thought to be created?
|
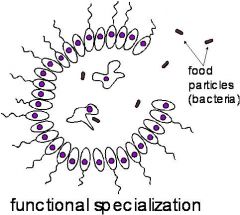
1)specialization of amoeba and protozoa
|
|
|
|
Trichoplax adhaerens is special why?
|
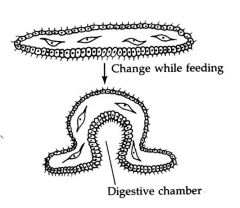
one of the most primitive living metazoans
|
|
|
|
What happened 550 M years ago when the Hox genes appeared?
|
a branching between protostome and deuterostome occured.
protostome has spiral clevage Deuterostome has radial cleavage: |
|
|
|
the C opening that early organisms ate out of was called what?
|
blastopore
|
|
|
|
nematodes
|
round worms
|
|
|
|
mollusca
|
squid, octapus....
|
|
|
|
annelida
|
segmented worms
|
|
|
|
arthropods
|
spiders, crabs, insects
|
|
|
|
echinodermata
|
coral, star fish
|
|
|
|
deuterostome
|
primary mouth becomes anus
|
|
|
|
describe the evolution of the coelom
|
1)acelomate:flatworm
-lack of body cavities -diffusion only -1mm or smaller 2)Pseudocelom -transvection across fluid -fluid can be mixed -no epithelia lining 3)true coelom -controls composition and volume of solute concentrations in coelom -has peritoneum lining that came from mesoderm -cavity is fluid filled and gives protection to organs -lining (peritoneum) allows organs to be by themselves in the coelom |
|
|
|
what is the gastrodermis?
|
the endoderm
|
|
|
|
mesentery
|
double layer of peritoneum
|
|
|
|
name the 3 main body cavities
|
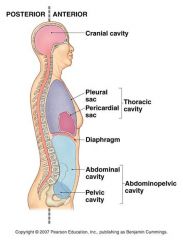
aa
|
|
|
|
draw the very first kidney
|
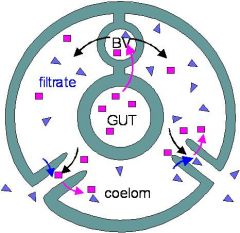
-tube could be selective to dump stuff out
|
|
|
|
what is the first body compartment?
|
the stomach
|
|
|
|
what are lungs a ramification of?
|
the intestine....the lungs also appeared later in evolution
|
|
|
|
epithelium vs. endothelium
|
epithelium: digestive and skin lining
endothelium: inner layers of cavities. line all blood vessels in the cardiac system |
|
|
|
exocrine gland examples
|
-stuff released in stomach
-sweat -saliva -milk |
|
|
|
endocrine glands
|
-stuff released in the blood
|
|
|
|
6 types of epithelia
|
1)exchange: lungs, lining of blood vessels
-pores between cells all passage 2)transporting: intestine, kidney, -tight junctions prevent movement between cells 3) ciliated: nose, trachea, female rep track, upper airways -one side covered with cilia to move fluid over surface 4)protective: skin, lining of cavities that open to environment -tightly connected by desmosomes(strongest cell-cell junction) 5)secretory: exocrine glands, including pancreas, sweat glands, and salivary glands; endocrine glands, such as thyroid and gonads 6)sensory: contain sensory cells that form synapses with nerve endings: taste buds, hair cells in the inner ear |
|
|
|
ectoderm
|
Epidermis of skin and its derivatives: hair, nails, skin glands, linings of oral, nasal, anal and vaginal cavities
Lens of the eye, enamel of teeth All nerve tissues: brain, spinal cord, sense organs Neuroendocrine glands: Adrenal medulla (part of the Sympathetic NS) and Pituitary |
|
|
|
endoderm
|
Lining of the gastrointestinal tract
Liver and pancreas Epithelium of pharynx, auditory canal, larynx, trachea, lungs, Epithelium of thyroid and parathyroid glands and thymus Urinary bladder and urethra |
|
|
|
mesoderm
|
Endothelium of blood and lymphatic vessels, smooth muscles (surrounding blood vessels and GI tract, urinary system)
Heart & Blood Skeletal muscles and bones (NOT skull) Kidneys, ureters. Gonads. Connective tissue: cartilage and ligaments Covering of internal organs and lining of body cavities, Adrenal cortex Dermis of skin, dentin of teeth |
|
|
|
4 connective tissues
|
Epithelial
Connective Muscle Nerve |
|
|
|
chondrocytes
|
cartlidge
|
|
|
|
types of connective tissue
|
Loose (gelous tissue in skin: fibroblasts cell)...skin,
Dense irregular (muscle and nerve sheaths: fibroblasts cell) Dense, regular (tendons and ligaments: fibroblasts cell) Adipose (white fat, brown fat cell) Blood: blood cell Cartilage (elastic, but fragile: chondrocytes cell) Bone (calcified tissue: osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts cell) |
|
|
|
blast vs. clast vs. cyte
|
blast: building
clast: breaking cyte: neither of the above |
|
|
|
fibroblast
|
cells that secrete a collagen rich matrix
|
|
|
|
collagen
|
main protein of connective tissue
|
|
|
|
3 muscle types
|
striated skeletal
cardiac smooth |
|
|
|
diffusion is said to be what?
|
a random walk because it doesn't happen in a straight path.
|
|
|
|
lumen
|
the inside of a path....vaginal cavity, artery, vein
|
|
|
|
apical side
|
the side near the lumen
|
|
|
|
basolateral side
|
the side oposite the apical side
|
|
|
|
interstitial fluid
|
fluid that bathes and surrounds cells
|
|
|
|
equation for a small molecule diffusing in the cytoplasm?
|
t=x^2/2D
x is distance t is time D is diffusion constant which is dependent on size of molecule and viscosity of the medium |
|
|
|
why does free energy change when hydrophilic molecules pass through a lipid bilayer?
|
the hydration shell must be broken
|
|
|
|
how many membrane spans may alpha helical membrane proteins have?
|
1-16
|
|
|
|
name 6 types of ion channels
|
Constitutively open “leakage” channels (K+ channels, epithelial Na+ and Cl- channels)
Voltage-gated (Na+, K+, Ca2+) channels Ligand-gated channels (AChR, GluR, GABAAR, GlyR, CNG, TRP ) Mechanosensitive and volume-regulated channels (K2P, TRP) Regulated anion channels (CFTR) Inracellular Ca2+- release channels (RyR, IP3R) |
|
|
|
5 solute transport systems
|
Water channels (aquaporins)
Intercellular gap junctions (connexins) Mitochondrial channels (ATP/ADP exchange) ABC transporters (MDR proteins, CFTR) Diffusion Facilitators: Glucose transporters (GLUT1-4) |
|
|
|
give an example of exchangers
|
sodium being exchanged for calcium
page 5 of chapter 3 |
|
|
|
4 examples of co-transport
|
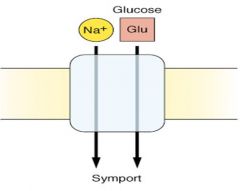
Na+-Glucose co-transporter
Na+-Amino Acid co-transporter Na+-monoamine co-transporter (neurotransmitter) K+-Cl- co-transporter (outward **process also called symporters page 5 of chapter 3 |
|
|
|
draw the lac permease functional cycle
|
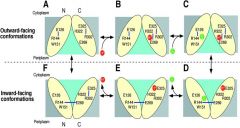
look
|
|
|
|
draw the sodium glucose co-transport system
|
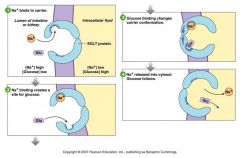
look
|
|
|
|
draw and describe the sodium potasium pump
|
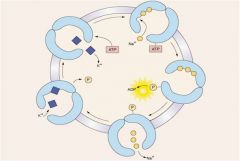
3Na+/2K+ per 1ATP
Phosphorylation of a specific site changes the topology of the pore (from open inside to open outside) and changes affinities of binding sites to permit the discharge of ions from the cavity. Release of phosphate is required to return the enzyme to the initial state |
|
|
|
equation for hydrostatic pressure difference at equilibrium
|
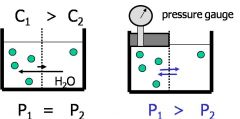
P2-P1=RT(M2-M1)
or the difference in osmotic pressure also hydrostatic pressure equals dgh+ absolute pressure |
|
|
|
osmotic pressure equation
|
osmotic= MRT
|
|
|
|
membrane transport obeys what?
|
michaelis-menten kinetics
V=(vmax*[s])/(km+[s]) V is the rate of substrate molecules converted to product per second vmax is the max rate with substrate saturating. |
|
|
|
Km =?
|
1/ (affinity of enzyme for substrate)
|
|

