![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What leukemia shows a positive DAT (autoimmunity) in 30% of cases?
|
CLL
Hemolytic anemia in half of these (15%). |
|
|
What leukemia shows hypogammaglobulinemia in 50% of cases?
|
CLL
|
|
|
CD38 and ZAP-70
Favorable or unfavorable? What disease is this used for? What gene? |
Expression = bad
CLL Expression implies unmutated IgVH status |
|
|
CD 5+, CD 19+ cell population on flow.
What is the differential dx? |
MCL
CLL RA, hep C, post-BM transplant |
|
|
What is the most common chromosomal anomaly seen in CLL?
|
del 13 > trisomy 12 > del 11q > del 14q > del 17p
|
|
|
What % of prolymphocytic cell must be present to deem CLL prolympocytic transformation?
|
11-55%
|
|
|
Which leukemia has the strongest genetic predisposition, with familial clustering demonstrated in 5-10% of cases?
|
CLL
|
|
|
Which cytogenetic abnormalities in CLL are considered prognostically bad? good?
|
Bad = del 11q, del 17p (p53) and 6q
Good= del 13q Others= Trisomy 12 |
|
|
Characteristic cytogenetic finding in MCL?
|
t(11;14) CCND1(cyclin D1); IgH
|
|
|
What is the single most important prognostic factor in MCL?
|
Mitotic rate (proliferation index)
>10 mitosis per HPF = bad |
|
|
5+, 10-
FMC7+, CD23- |
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
|
|
|
What is the gene found at chromosome 11 in the 11;14 translocation of MCL and what is its function?
|
CCND1 gene (cyclin D1)
stimulates entrance into G1-phase of cell cycle. |
|
|
Which lymphoma causes multiple lymphomatous polyposis?
|
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
|
|
|
In addition to several types of DLBCL, what other lymphomas express BCL-6?
|
Burkitt lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma |
|
|
What is the classic translocation seen in follicular lymphoma?
|
t(14;18) IgH; BCL2
|
|
|
What is the function of the BCL-2 molecule formed on chromosome 18?
|
Inhibits cell death by heterodimerization with BAX and caspase
|
|
|
What are the two types of lymphoma that commonly form paratrabecular aggregates in the bone marrow?
|
Follicular lymphoma
T-cell rich B-cell lymphoma |
|
|
What is the most common type of primary cutaneous lymphoma?
Where does it usually occur? |
Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma
scalp, forehead or trunk |
|
|
In comparison to follicular lymphoma, what is the staining pattern of primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma?
|
BCL 6 + (positive in both)
CD10 - BCL 2 - |
|
|
What is the associated stimuli?
Gastric MALT Ocular MALT Immunoproliferative small intestinal disease (IPSID) |
Helicobacter pylori
Chlamydia psittaci Campylobacter jejuni |
|
|
What is the associated stimuli?
Cutaneous MALT Salivary gland MALT Thyroid gland MALT |
Borrelia burgdoferi
Sjogren syndrome (44x risk) Hashimoto's thyroiditis (70x risk) |
|
|
What is the most common translocation seen in gastric MALT lymphoma?
|
t(11;18) API2-MALT1
|
|
|
What physical exam and peripheral blood findings are strongly associated with Hairy cell leukemia?
|
Pancytopenia, specifically monocytopenia (almost always affects the BM, fibrosis)
Splenomegaly |
|
|
Which mature b-cell leukemia/lymphoma primarily involves the red pulp of the spleen?
|
Red pulp- HCL
White pulp- FL, MCL, SMZL, CLL |
|
|
What is the most common genetic abnormality seen in 40% of cases of splenic marginal zone lymphoma
|
del 7p
|
|
|
What is the most specific non-IP stain for Hairy cell leukemia, especially when it stains brightly?
|
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)
PLL, Waldenstrom, mast cell disease and Gauchers also stain but weakly. |
|
|
What is the most specific IP stain for Hairly cell leukemia?
|
Annexin-1
-not expressed in any other b-cell lymphoma but is expressed in myeloid and some t-cells so must be compared with b-cell antigens |
|
|
Blood lakes are a characteristic finding of what disease?
|
Hairy cell leukemia
-usually spleen but can be anywhere (also peliosis) |
|
|
What is the "classic" cytogenetic finding seen in Hairy cell leukemia
|
none
|
|
|
What is the common characteristics on physical exam and peripheral blood in prolymphocytic leukemia?
|
Splenomegaly without lymphadenopathy
WBC > 100k |
|
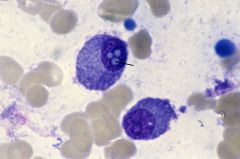
What is this?
|
Dutcher body - seen in plasma cells, PAS+ accumulations of immunoglobulin forming pseudo inclusions in the nucleus.
Cytoplamic= Russel bodies Numerous= Mott cell |
|
|
What is Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia?
|
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma with an IgM monoclonal gammopathy and marrow involvement
|
|
|
When DLBCL is CD5+, what IP stain should be done and why?
|
bcl-1
bcl-1 positivity would make it blastoid mantle cell lymphoma |
|
|
What chromosomal abnormalities (2) are seen in 60%(30% and 30%) of cases of DLBCL?
|
3q27 rearrangements (BCL6 gene)
t(14;18) IgH;BCL2 |
|
|
What is the most common lymphoma seen in the brain?
|
DLBCL
only rare example of other lymphomas have been reported |
|
|
What specific chromosomal abnormalities are specifically seen in Mediastinal DLBCL?
|
gains in 9p (JAK2)
MAL gene expression |
|
|
Name the 7 hematologic diseases associated with tyrosine kinase mutation or rearrangement?
|
CML, myeloid neoplasms with eosinophilia, PV, primary MF, ET and Mastocytosis and mediastinal DLBCL
|
|
|
Name the associated TK mutation for following.
CML, myeloid neoplasm with eosinophilia and mastocytosis |
CML- ABL1
MN with eos- PDGFR a&b, FGFR1 Mastocytosis- KIT (cd117) |
|
|
Name the associated TK mutation for the following.
PV, PMF, and ET |
All are JAK2 mutations (9p). PMF and ET are rearrangements with the MPL gene.
|
|
|
Gleevac (imatinib) inhibits what?
|
TK
(ABL1 in CML) (KIT in GIST) |
|
|
What are 2 unusual cells sometimes seen in CML?
|
pseudo-gaucher cells
sea blue histiocytes |
|
|
Which drug can cause a Hodkin-like lymphoid infiltrate?
|
Methotrexate
|
|
|
What is the only myeloproliferative neoplasm that does not cause splenomegaly?
|
Essential thrombocythemia
|
|
|
Name the 2 EBV+ DLBCL's?
|
Plasmablastic lymphoma
DLBCL of the elderly |
|
|
What is the status of each of the following markers in oral mucosal plasmablastic lymphoma?
CD38, CD138, CD56 |
CD38, CD138 +
CD 56 - "expression of CD56 should raise suspicion for underlying plasma cell myeloma" |
|
|
What virus is strongly associated with plasmablastic lymphoma? Where do they often occur in the body?
|
HIV and EBV
Mucosal sites (often oral) |
|
|
Name the 3 malignancies associated with HHV-8 infection.
|
Primary effusion lymphoma
Koposi's sarcoma Multicentric Casteman's disease |
|
|
What demographic does this tumor affect? cutaneous, bcl-2 and bcl-6 positive. CD10 neg.
|
Leg-type primary cutaneous DLBCL (cuteneous FL would be BCL-2 neg.) -- elderly women
|
|
|
What is thought to be the cause of most early (<5y) post-transplant LPDs?
|
EBV -increased risk if EBV negative before transplant
-most are clones from the recipient |
|
|
Where does endemic (African) Burkitt's often present and in what demographic?
|
Jaw
Children, strong EBV assosication |
|
|
Where does sporadic (Western) Burkitt's often present and in what demographic?
|
ileocecal valve
Children, not associated with EBV unlike endemic |
|
|
What is the classic IP of Burkitt's lymphoma?
|
CD10 +
c-myc + bcl-2 - bcl-6 + |
|
|
What is the most commonly seen molecular rearrangements in Burkitt's?
|
t(8;14) IgH (14), c-myc (8)
t(2;8) kappa (2) t(8;22) lambda (22) |
|
|
Patient with mediastinal mass and hypercalcemia?
|
T-LBL
B-LBL usually doesn't involve the mediastinum |
|
|
Which is the more common?
T-ALL vs. B-ALL T-LBL vs. B-LBL |
B-ALL (80%)
T-LBL |
|
|
Name the two translocations with good prognosis in B-ALL?
|
t(12;21) TEL-AML1
Hyperdiploid |
|
|
Name the four translocations with bad prognosis in B-ALL?
|
Hypodiploid
t(9;22) BCR-Abl 11q23 (usually 4;11) MLL t(1;19) |
|
|
Which IP marker is most sensitive for T-ALL?
|
CD 7
|
|
|
What is the expression of each of these marker in B-ALL and T-ALL?
CD7, CD19, CD20, surface Ig, Tdt, HLA-DR |
B-ALL- CD19+, CD20+/-, Tdt+, HLA-DR+, CD7-, surface Ig-
T-ALL- CD7+, Tdt+ HLA-DR-, surface Ig- |
|
|
What myeloid antigen is the most specific for determining lineage amoung hematopoetic cell lines?
|
CD117 (100%) 80% sensitive
CD33 and CD13 are also fairly specific but not 100% |
|
|
What is the order (most common to least) of Ig paraprotein deposits in plasma cell myeloma?
|
IgG - 55% IgA- 22%
light chain only (usually kappa)- 18% IgD, IgE, IgM- 2% |
|
|
What is the most common chromosomal abnormality seen in plasma cell myeloma?
|
14q32(IgH) translocations -70% esp. t(11;14)
Most have 4 or more abnormalities. del 13 -50% |
|
|
What are the good and bad prognostic groups in plasma cell myeloma regarding cytogenetics?
|
t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), del 17p, hyperdiploidy -bad
t(11;14), t(6;14), hyperdiploidy -good |
|
|
What is the major IP difference between plasma cell myeloma and plasma cell leukemia? Ig? cytogen?
|
Plasma cell leukemia is usually CD56 neg. Also usually IgE, IgD or light chain only. usually monos. 13
|
|
|
Where does extraosseous plasmacytoma usually arise and what is the prognosis?
|
nasal cavity/oropharynx area
Most do not develop to plasma cell myeloma |
|
|
What does the acronym POEMS stand for; what does it usually imply?
|
polyneuropathy,organomegaly,endocrinopathy, M-protein, skin changes. Implies plasmacytoma.
|
|
|
What disease is POEMS syndrome associated with?
|
plasma cell variant of Castleman's disease and HHV-8 infection
|
|
|
What is the most common T cell neoplasm?
|
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL)
|
|
|
What leukemia is caused by HTLV-1?
|
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
- classically flower cells |
|
|
What is a classic symptomatic manifestation of Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma?
|
Hypercalcemia and lytic bone lesions --> Osteoclast activating factor stimulation
|
|
|
Flower cells are classic for what leukemia?
|
Adult T-cell leukemia
|
|
|
Where is Adult T-cell leukemia endemic?
|
Southwest Japan
10% HTLV-1 infection |
|
|
Associated virus?
Angioimmunoblastic TCL Adult TCL Nasal type NK/TCL |
AILT -EBV (in associated b cells)
ATCL -HTLV-1 Nasal type NK - EBV (Aggresive NK-cell leukemia - EBV) |
|
|
What are some peculiar associated findings in angioimmunoblastic TCL?
|
autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Pleural effusion, anti-smooth muscle antibody, + rheumatoid factor |
|
|
What demographic group is most often affected by anaplastic large cell lymphoma?
|
Young adults and children
-represents about half of all high grade childhood lymphomas |
|
|
What is the classic cell, Immunophenotype, distribution and genetics of ALCL?
|
horse shoe cell, CD 4+/30+/45+ and ALK +, lymphadenopathy, t(2;5) ALK-NPM
|
|
|
EBV + lymphoma that characteristically shows angio-invasion and extensive necrosis.
|
Nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphomas
|
|
|
Patients with Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma have what classic history?
|
Celiac sprue
HLADQ2 and HLADQ8 |
|
|
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphomas is assocated with what demographic group?
|
If gamma-delta, young males
If alpha-beta, females(any age) |
|
|
What lymphomas can arise in children treated for Crohns
|
Hepatosplenic TCL
(azathioprine and infliximab) |
|
|
What cytogenetic abnormality is associated with gamma-delta hepatosplenic TCL?
|
isochrome 7q
|
|
|
What are the classic histologic findings in subcutaneous panniculitic t-cell lymphoma?
|
Tumor cell rim the subcutaneous fat, much apoptotic debris, histocytes (cleaning debris)
|
|
|
What disease is associated with subcutaneous panniculitic t-cell lymphoma?
|
SLE
|
|
|
What is a feared sequela of subcutaneous panniculitic T-cell lymphoma. In which subtype is it common?
|
Hemophagocytic syndrome
delta-gamma type |
|
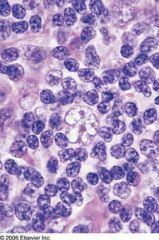
What disease is this?
|
This is a popcorn cell, classically seen in Nodular lymphocyte predominant hodkin lymphoma
|
|
|
What IP stain is useful for staining the cells surrounding the "popcorn" cell in HLPHL?
|
CD57 (and CD3)
|
|
|
What is the staining pattern of classic HL vs. NLPHL?
CD30, CD15, CD45? |
============CHL/////NLPHL
CD15(Leu-M1)/////(+/-)//////( -) CD30(Ki-1)//////////(+)///////(usually -) CD45//////////////////(-)////////(+) |
|
|
In differentiating NLPHL from t-cell rich DLBCL, what stain is most useful?
|
CD21 (dendritic meshwork)
If even slightly nodular with CD21, then is NLPHL |
|
|
What stain is usually negative in DLBC lymphomas that is usually positive in CHL?
|
CD15 (Leu-M1)
CD15 positivity rules out DLBCL and NLPHL. Not 100% of NLPHL are CD15 +. If neg. do PAX5 (similar staining). ALCL is not ruled out. |
|
|
In nodular sclerosing classical hodkin lymphoma, what is the main demographic group and presentation?
|
Young females, mediastinum
|
|
|
NLPHL vs. CHL
Single node involvement? Distall relapses? Double peak in age? EBV association? |
Single node- NLPHL
Distall relap.- NLPHL 2 age peaks- CHL EBV ass. - CHL (not used for diag or prognosis) |
|
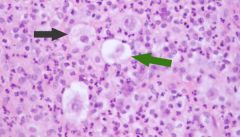
Name the disease
|
These are lacunar cells (caused by retraction artifact) and are seen in nodular sclerosing CHL
|
|
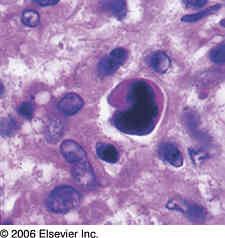
Name the disese?
|
This is a mummified cell (lacunar cell with shrunken, dark nuclei) and is seen in nodular sclerosing CHL
|
|
|
Nodular sclerosis CHL most often occurs where (body site)?
|
Mediastinum (80%)
|
|
|
Lymphocyte depleted CHL isaggressive, seen in dev. nations and generally occurs where (body site)?
|
Retroperitoneal lymph nodes
These are represented in the 2nd peak of age |
|
|
Which type of hodkin lymphoma least often show BM involvement?
|
LPHL (<1%)
50% for LD and HIV associated 10% overall |
|
|
Can a myeloproliferative neoplasm show dysplasia?
|
No, this would make it, by definition, MD/MPN
|
|
|
Which commonly show splenomegaly? MDS, MD/MPN, MPN, AML?
|
MD/MPN - Yes
MPN Yes MDS No AML No |
|
|
Most common chromosomal abnormality in MDS?
2nd? 3rd? |
Complex karyotype -bad
mono 7 or del 7q - bad del 5q - good |
|
|
MDS with favorable prognosis?
bad prognosis? |
good- normal karyotype, del Y, del 5q, del 20q
Complex karyotype(3 or more), mono or del 7 |
|
|
What is the usual presentation of MDS del 5q?
|
Old women
hypolobated megs (plts normal or increased) macrocytic anemia |
|
|
What is the classic morphology of MDS with del 17q?
|
small vacuolated neutrophils with pseudo-Pelger-Huet anomaly
|
|
|
What percent blast must be present to call something AML?
|
Tricky question. Usually it is 20% however the several of the AMLs with translocations have no lower limit defined.
|
|
|
Which small mature B-cell lymphoma is the most aggressive?
|
Mantle cell lymphoma
|
|
|
Cyclin D1 is present in what 3 lymphomas/leukemias?
|
Mantle cell lymphoma (diagnostic)
Hairy cell leukemia Plasma cell myeloma |
|
|
What is a normal cell in the LN that is a good internal control for cyclin D1?
|
Histiocytes
|
|
|
What is CMML?
|
A MD/MPN disorder with specific features:
Monocytosis <20% blasts myelodysplasia (or genetic or >3 mos) |
|
|
What specific findings must be investigated and ruled out in order to label something as CMML?
|
rule out a BCR-ABL1 fusion
No PDGFRa or b arrangement (esp. necessary if eosinophilia) |
|
|
What syndrome is associated with juvenile chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML)?
|
NF-1
|
|
|
What hematologic disorder is a result of mutations involving genes of the RAS/MAPK pathway?
|
JMML
|
|
|
What physical finding is almost always seen in patients with JMML?
|
hepatosplenomegaly
|
|
|
What protein is greatly increased in many cases of JMML?
|
hemoglobin F
|
|
|
What is the "hallmark" clinical diagnostic feature of JMML?
|
hypersensitivity of myeloid progenitor cells to GM-CSF
|
|
|
CML cytogenetics?
|
t(9;22) ABL-BCR
Most commonly M-BCR p210 protein |
|
|
p290 BCR fusion protein manifestations?
|
CML with marked thrombocytosis
|
|
|
p190 BCR fusion protein manifestations?
|
CML with marked monocytosis
ph+ ALL |
|
|
What are the 3 major distinct fusion protein seen with CML?
|
p210 - most common
p290- marked thrombocytosis p190- marked monocytosis + ALL |
|
|
What are 2 unique testing abnormalities seen in CML?
|
markedly elevated B12 (increased transcobalamin 1)
Impaired aggregation of plts in response to epinephrine |
|
|
Neutrophilia with basophilia is highly suggestive of what disease?
|
CML
|
|
|
What is the most effective drug we have for treating CML and what is its mechanism?
|
Imatinib
Stops the enhanced TK activity of BCR-ABL1 (competative inhibitor with ATP at the BCR-ABL1 domain) |
|
|
What is the most important prognostic indicator in CML?
|
Response to imatinib
|
|
|
What is the natural history of CML?
|
Progression to AML (70%) or ALL (30%) within 2-3 years.
Overall, 95% progress |
|
|
What is the most common "deadly" complication of polycythemia vera?
|
Thrombosis (31%)
-Most common cause of budd-chiari syndrome |
|
|
How can one test for polycythemia vera by culturing the bone marrow?
|
In PV new erythroid colonies will grow without addition of erythropoietin
|
|
|
T/F JAK2 mutation is required for the diagnosis of PV?
|
False, while 90% of cases have the mutation, it is not required.
|
|
|
Why is assessing stainable iron helpful for diagnosing essential thrombocythemia?
|
Helpful to ruleout reactive thrombocytosis due to iron deficiency
|
|
|
T/F Chronic Eosinophilic leukemia is a clonal population of eosinophils without PDGFR or FGRF rearrangement?
|
T, the blast count must be under 20%
|
|
|
Which two AMLs with cytogenetic abnormalities are usually HLA-DR negative?
|
t(15;17) - also usually negative for CD34
t(1;22) |
|
|
What two AMLs involve core binding factor?
|
t(8;21) AML1/ETO
-- AML1 encodes CBFalpha t(16;16)/inv 16 CBFbeta |
|
|
AML's with favorable prognosis?
|
t(8;21)
t(16;16) / inv 16 t(15;17) |
|
|
Which AML translocation is strongly suggested with a positive CD 19 and CD 56? What characteristic morphology is also present?
|
t(8;21)
Salmon-colored cytoplasmic granules. |
|
|
What is the translocation that manifests as AML with morphologically abnormal eosinophils?
|
t(16;16) inv 16
MYH11 (myosin)- CBF-beta |
|
|
What three therapies can lead to therapy-related AML or MDS?
|
Topoisomerase 2 inhibitors (1-5years)
alkylating agents (5+ years) radiation (5+ years) |
|
|
What mutation (non-germline) is often seen in down syndrome patients with AML or transient myeloprolifeative disorder?
|
mutations in the GATA-1 gene
|
|
|
What cell line does a Leder stain identify and what specific material does it stain in these cells?
|
Stains the chloracetate esterase found in myeloid cells
(Normally CAE is negative in eosinophils except curiously in the abnormal eos in inv. 16 AML/ t(16;16) where it is positive) |
|
|
Increased polyclonal Ig production is seen in which type of T-cell lymphoma?
|
Angioimmunoblastic TCL
-also +Coombs, pleural effusions, cold agglutinins, +anti-smooth muscle antibody, +rheumatoid factor |
|
|
What is another name for CD25 and what two leukemias classically express it?
|
IL-2 receptor
Hairy cell leukemia Adult TCL |
|
|
What leukemia/lymphoma shows elevated soluble IL-2 receptor in the serum?
|
Adult T-cell leukemia
AKA CD25 CD25 (IL-2 rec) stains adult TCL and hairy cell leukemia |
|
|
What is another name for MAC-1 IP stain and what leukemia is classically positive for it?
|
CD 11b
Hairy cell leukemia |
|
|
The IgE receptor IP stain is helpful for differentiating what two leukemias?
|
AKA CD23+
CLL+ MCL - |
|
|
What is another name for CD15?
CD30? |
CD 15 = Leu-M1
CD 30 = Ki-1 or Ber-H2 |
|
|
Marginal zone lymphoma with circulating villous lymphocytes and hairy cell leukemia both affect the spleen; which do they involve, the white pulp or red pulp?
|
MZL - white pulp
HCL - red pulp In fact, HCL is the only mature b-cell leukemia to affect the red pulp |
|
|
PTLD in heart transplant recipients most commonly occurs where?
|
Heart or lung
|
|
|
Which type of hodkin disease most commonly progresses to DLBCL?
|
LP HD
|

