![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
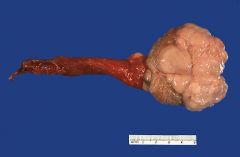
Positive stains: PLAP (almost all); ferritin, PAS with and without diastase, vimentin, angiotensin-1-converting enzyme
Negative stains: cytokeratin (may be weak/focal; syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells are positive), AFP, hCG (syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells are positive), CD30, EMA |
Seminoma
|
|
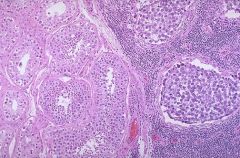
30-50% of testicular germ cell tumors
Mean age 40 years vs. 25 years for nonseminomatous germ cell tumors (NSGCT); rare in infants |
seminoma
|
|
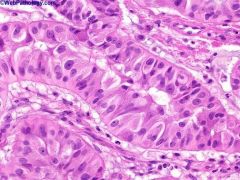
Patients usually under age 20
Part of Carney syndrome with testicular Leydig cell tumors, pituitary tumors, pigmented nodular hyperplasia of adrenal cortex, myxomas of skin, soft tissue, heart and breast; spotty skin pigmentation (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome) Gynecomastia is common clinical presentation Usually benign |
Large cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumor the tumor cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, round or oval nuclei and punctate nucleoli.
|
|
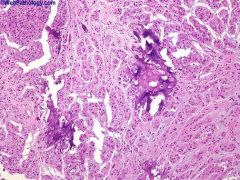
Micro: sheets, nests, cords and solid tubules of cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm separated by fibrous tissue with marked calcification; usually marked neutrophilic infiltration
|
Positive stains: S100 (strong and diffuse), vimentin
Negative stains: keratin (usually), EMA, AFP, hCG, SMA |
|
Originates from tunica vaginalis (image), which derives from evagination of peritoneum into scrotum
Epidemiology: rare, mean age 55 years, but varies from children to elderly (AJSP 1995;19:815) Clinical: usually associated with asbestos exposure |
Malignant mesothelioma of testisPositive stains: calretinin, EMA, thrombomodulin, CK7, CK5/6 (variable) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1)
Negative stains: CK20, CEA |
|
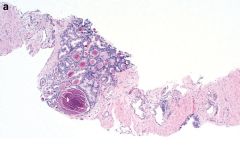
Originates from tunica vaginalis (image), which derives from evagination of peritoneum into scrotum
Epidemiology: rare, mean age 55 years, but varies from children to elderly (AJSP 1995;19:815) Clinical: usually associated with asbestos exposure |
Malignant mesothelioma of testisPositive stains: calretinin, EMA, thrombomodulin, CK7, CK5/6 (variable) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1)
Negative stains: CK20, CEA |
|
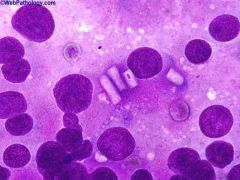
|
This touch-prep was obtained from freshly cut surface of a Leydig cell tumor and stained with Diff-Quik stain. Several plump rod-shaped intracytoplasmic crystals of Reinke can be seen in the center of the photomicrograph. Reinke’s crystalloids are seen in about 40% of cases
|
|
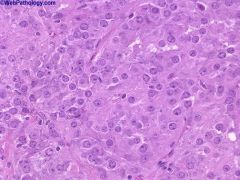
|
Leydig (interstitial) cell tumors
comprises about 3% of all testicular tumors. This photomicrograph shows sheets of large polygonal cells with round nuclei, single prominent nucleolus and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm Positive stains: steroid hormones, vimentin, inhibin, calretinin, MelanA, keratin (variable) Negative stains: anti-mullerian hormone, S100 (usually) |

