![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
GENERAL
- what is the most complex and dominant component of the Endocrine system? |
- Hypothalamus/Pituitary unit
|
|
|
GENERAL
- Hypothalamus/Pituitary unit controls what general physiologies? x6 |
(RG FLAT)
- Reproductive glands - Growth - Fluid hemostasis - Lactation - Adrenals - Thyroid |
|
|
GENERAL
- initial hormones from the hypothalamus will be sent to pituitary via what structure? |
- Pituitary stalk
|
|
|
PITUITARY
- Pituitary sits inside what bone structure? - Pituitary connected to hypothalamus via what? |
- Selica Turcica
- Pituitary stalk |
|
|
PITUITARY
- Anterior Pituitary originates from what type of tissue? - Posterior Pituitary originates from what type of tissue? |
- Epithelium of roof of oral cavity
- Neural tissue |
|
|
PITUITARY
- general size of pituitary? - diameter of pituitary? - how may hormones is secreted by the Anterior Pituitary? - how many hormones are secreted by Posterior Pituitary? |
- 1 cm
- 0.5 to 1.0 grams - 6 (or 7 including Beta-LPH)) - 2 |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- List the 5 cells of the Anterior Pituitary |
(SL GCT)
- Somatotropes - Lactotropes - Gonadotropes - Corticostropes - Thyroidotropes |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- FSH is secreted by what cell? - FSH target? - Hypothalamic stimulator? - Hypothalamic inhibitor? |
- Gonadotropes
- Gonads - GnRH - nothing |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- LH is secreted by what cell? - LH target? - Hypothalamic stimulator? - Hypothalamic inhibitor? |
- Gonadotropes
- Gonads - GnRH - nothing |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- ACTH is secreted by what cell? - ACTH target? - Hypothalamic stimulator? - Hypothalamic inhibitor? |
- Corticotropes
- Adrenal Gland - Melanocytes - CRH - nothing |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- TSH is secreted by what cell? - TSH target? - Hypothalamic stimulator? - Hypothalamic inhibitor? |
- Thyrotropes
- Thyroid - TRH - nothing |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- Prolactin is secreted by what cell? - Prolactin target? - Hypothalamic stimulator? - Hypothalamic inhibitor? |
- Lactotropes
- Breasts - PRH - PIF (dopamine) |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- Growth Hormone (GH) is secreted by what cell? - GH target? - Hypothalamic stimulator? - Hypothalamic inhibitor? |
- Somatotropes
- All tissues - GHRH - GHIH (somatostatin) |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- what cell type is the predominant population in anterior pituitary (30-40%)? - what cell type is the least abundant in the population in anterior pituitary? |
- Somatotropes
(followed by lactotropes, then corticotropes) - Thyrotropes |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- what cell is the only one to secrete more than 1 type of hormone? |
- Gonadotropes
(FSH & LH) |
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- the Anterior Pituitary is under the control of what? |
- Hypothalamic hormones
|
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- name of the System involved in transporting Hypothalamic hormones to Anterior Pituitary |
- Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Portal System
|
|
|
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- Describe the steps involved in getting the hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior pituitary. |
Hormones are:
- Secreted into Median Eminence - Absorbed in Portal System - Carried to Anterior Pituitary |
|
|
HYPOTHALAMIC HORMONES
- hypothalamic hormones controlling the Anterior pituitary get released in what area? - hypothalamic hormones controlling the Posterior pituitary get released in what area? |
- Median eminence / Neural stalk
(portal system) - Posterior Pituitary (portal system) |
|
|
HYPOTHALAMIC HORMONES
- Diffusion of molecules/horrmones is inhibited between the anterior and posterior pituitary except through what sole communication path? |
- Short Portal Vein
|
|
|
HYPOTHALAMIC HORMONES
- Hormones from the Anterior Pituitary that end up systemic are actually from? - Hormones from the Posterior Pituitary that end up systemic are actually from? |
- Tropic hormone-producing cells
(SL GCT) - Hypothalamus (via neurohypophysis & short portal vein) - Hypothalamus |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
What hypothalamic hormones stimulate ==> FSH ==> LH ==> ACTH ==> TSH ==> Beta-LPH ==> Prolactin ==> Growth Hormone |
- GnRH
- GnRH - CRH - TRH - CRH - PRH - GHRH |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- what 2 adenohypophysis hormones not only have stimulatory, but also Inhibitory hormones from hypothalamus? |
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Prolactin |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- what are the 2 inhibitory hormones? - what hormones do they inhibit? |
- GHIH inhibits GH
- PRH inhibits Prolactin |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- GHIH is also called what? - PIF is also called what? |
- Somatostatin
- Dopamine |
|
|
grå
|
grey
|
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- what hypothalamic hormones stimulate the release of 2 hormones of the adenohypophysis rather than 1? |
- GnRH
(FSH & LH) - CRH (ACTH & Beta-LPH) |
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- what type of feedback loop is UNSTABLE? - what type of feedback loop is STABLE? |
- Positive
(no baseline b/c too much or too little) - Negative |
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- for POS. Feedback loops, what happens to concentration of Y if there is more Y? - for POS. Feedback loops, what happens to concentration of Y if there is less Y (eliminated)? |
- increases too much
- decreases too little |
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- for NEG. Feedback loops, what happens to concentration of Y if there is more Y? - for NEG. Feedback loops, what happens to concentration of Y if there is less Y (eliminated)? |
- decreases to baseline
- increases to baseline |
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- whenever Positive Feedback loops are seen in the body, it is usually accompanied by what other mechanism? |
- Negative Feedback loop
|
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- what are the 3 types of Negative Feedback Loops seen in the HPA? |
- Long Loop
- Short Loop - Ultra Short Loop |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- describe the pathway for the Long Feedback Loop |
1.) Hypothalamus secretes XRH
2.) XRH stimulates Pituitary release of XTH 3.) XTH stimulates Peripheral gland hormone X 4.) Peripheral gland hormone X will either (a) inhibit Pituitary release of XTH or (b) stimulate Hypothalamic release of XIH, which will inhibit Pituitary release of XTH |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- describe the pathway for the Short Feedback Loop |
1.) Hypothalamic release of XRH
2.) XRH stimulates Pituitary secretion of XTH 3.) XTH inhibits Hypothalamus release of XRH |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- describe the pathway for the Ultra Short Feedback loop |
1.) Hypothalamus secretes XRH
2.) XRH comes back and inhibits Hypothalamus release of itself |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- which negative feedback loop ONLY involves Hypothalamic hormones? - which negative feedback loop involves Hypothalamic and Tropic hormones? - which negative feedback loop involves Hypothalamic, Tropic, and Gland hormones? - which negative feedback look involves an INHIBITORY Hormone? |
- Ultra Short Loop
- Short Loop - Long Loop - Long Loop |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- the Long Feedback Loop can have Inhibitory Negative Feedback on? |
- Hypothalamus
or - Pituitary (either directly or indirectly with XIH) |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- which Feedback loop involves Stimulus inhibition? |
- Long Feedback Loop
(stimulation of hypothalamic XIH release to inhibit pituitary XTH) |
|
|
FEEDBACK LOOPS
- what are the 3 ways the Hypothalamic secretion of XRH can be inhibited via Neg. Feedback Loop? |
(Ultra Short) - Hypothalamic XRH inhibits itself
(Short) - Pituitary (Tropic) XTH inhibits XRH (Long) - Gland hormone X inhibits XRH |
|
|
HORMONE RECEPTOR PATHWAY
- what are 3 ways that a hormone interacts with a Receptor? |
via:
- Membrane Receptor - Membrane Receptor + G Protein - Nuclear Receptor via diffusion (no membrane receptor involved) |
|
|
HORMONE RECEPTOR PATHWAY
- Hormone interaction with just a Membrane Receptor usually increases what levels? |
- cGMP
- Tyrosine Kinase |
|
|
HORMONE RECEPTOR PATHWAY
- Hormone interaction with a Membrane Receptor coupled with a G Protein usually increases what levels? |
- cAMP
- Ca2+ Calmodulin - Phospholipid Metabolism |
|
|
HORMONE RECEPTOR PATHWAY
- Hormone interaction with Nuclear Receptors usually increase what levels? |
- Protein synthesis
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what is the general effect of Growth Hormones? |
- promote growth by increasing size and numbers of cells
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH affects proteins how? |
- Protein deposition in tissues
(enhances AA tranport) (increases RNA & Protein synthesis) (decreases Protein breakdown) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH affects Fat utilization how?? |
- Fat utilization for Energy
(release of FA from adipose) (enhance conversion of FA to Acetyl-CoA or Ketoacids) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH affects Carbohydrates how? |
(PED PFC)
- Carb utilization (Increase Glucose uptake by liver) (increase Insulin secretion) (Decrease Glucose uptake by muscle/fat) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the Metabolic Effects of GH? x4 |
(CPA = D A SK)
- Diabetogenic effect - Anabolic effect - Sparing of Protein - Ketogenic effect |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- EXCESSIVE GH leads to what effect on fat untilization? |
- Ketogenic effect
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- how does GH cause a Diabetogenic effect? |
(due to excessive GH)
- GH-induced Insulin resistance |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH comes from where? |
- Pituitary Somatotropes
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- excessive GH leading to a GH-induced Insulin Resistance is often associated with which Dz? |
- Type 2 DM
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH effects on skeleton? |
- stimulates Cartilage growth
- stimulates Bone growth |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH requires what 2 things to have an effect? |
- Carbohydrates
- Insulin |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH exerts most of its effect through? |
- IGFs
(somatomedins) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- another name for IGF is? |
- SomatoMEDINS
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what is the most important Somatomedin? - what is the most important IGF? |
somatomedin C
(same as) IGF - I |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the mechanisms affected by GH in Adipose Tissue? x2 - thus the resulting effect is what? |
(LG)
- Increased Lipolysis - Decreased Glucose Uptake (thus) - Decreased Adiposity |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the mechanisms affected by GH in the Liver? x4 |
INCREASED: (RPG'S)
- RNA / Protein Synthesis - Glucose Synthesis / Storage - Somatomedins |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the mechanisms affected by GH in the Muscle? x3 - thus the resulting effect is what? |
(PGA)
- Increased Protein synthesis - Decreased Glucose Uptake - Increased Amino Acid Uptake - Increased Lean Body Mass |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what is the effect of Somatomedins on cellular mechanisms? x5 |
Increased Synthesis of
- DNA - RNA - Protein Increased Cellular - Size - Number |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the Gross effects of Somatomedins (induced by GH) on the body? x3 |
INCREASE
- Linear Growth - Organ Size - Organ Function (organs include Visceral organs, Heart, Lung, Bone, etc) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH effects on Adiposity? - GH effects on Lean Body Mass? |
- decreases Adiposity
- increases Lean Body Mass |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- Somatomedins are produced where? |
- Liver
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- from Birth, GH will steadily rise, then SPIKE to a PEAK when? - during one's life, the 1st TWO FOLD DECREASE occurs when? - during one's life, the 2nd TWO FOLD DECREASE occurs when? |
- Puberty
- Puberty to Adult - Adult to Senescence |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what is the only major mechanism that is decreased with GH? |
- decreased Glucose Uptake
(in Adipose and Muscles) (not in liver) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- which gender experiences the first Peak Spike of GH at puberty? |
- Girls (@ 12)
- Boys (@14) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- Enhanced GH secretion can be caused by what 2 daily activities? |
- Strenuous Exercise
- First few hours of Deep Sleep (phase II & IV) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH circulating half-life is? - Somatomedin C half life is? |
20 minutes
20 hours |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- why does Somatomedin C have a longer half life? |
- due to the fact it binds to the stable Plasma Protein Carrier
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH secretion is Enhanced during what phases of sleep? |
(first few hours of DEEP SLEEP)
- phase 2 - phase 4 |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what factors would stimulate GH secretion? x10 |
(EGG & FASTED states)
- Estrogen/Testosterone - GHRH - Glucose Decrease - FFA Decrease - Amino Acid Increase - Starvation (Fasting) - Trauma/Excitement/Stress - Exercise - Deep Sleep (stage 2 & 4) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what factors would inhibit GH secretion? x7 |
(FAG MESS inhibits Growth)
- FFA increase - Aging - Glucose increase - Morbid obesity - Exogenous GH - SomatoMedins (IGF) - SomatoStatins (GHIH) |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
PROTEIN effects on : - GH - SomatoMedins - Insulin |
- increase
- increase - increase |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
CARB intake effects on : - GH - SomatoMedins - Insulin |
- decrease
- BOTH - increase |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
FASTING effects on : - GH - SomatoMedins - Insulin |
- increase
- decrease (b/c insulin effects >> GH) - decrease |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
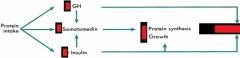
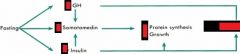
PROTEIN intake effects on: - Somatomedin? and Why? Thus, what effect on: - Protein synthesis? - Growth? |
- Increased
- Synergistic effects of increased GH and increased Insulin - Increase - Increase |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
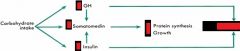
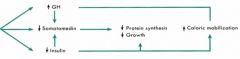
CARB intake effects on: - Somatomedin? and Why? Thus, what effect on: - Protein synthesis? - Growth? |
- BOTH (thus offset)
- Antagonistic effects of decreased GH and increased Insulin - BOTH (thus offset) - BOTH (thus offset) |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
FASTING/STARVATION effects on: - Somatomedin? and Why? Thus, what effect on: - Protein synthesis? - Growth? |
- Decreases it
- Antagonistic effects of Decreased Insulin is >> than Increased GH - Decreased - Decreased |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
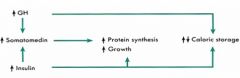
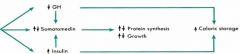
How does Caloric Storage get affected with: - Protein intake? - Carb intake? - Starvation/Fasting? |
- Both incr. and decr. (thus OFFSET)
- Increase Caloric Storage - Increase Caloric MOBILIZATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

