![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Epitympanic recess
2. Malleus 3. Incus 4. Stapes 5. Vestibular apparatus 6. Cochlea 7. External Auditory canal 8. Tympanic membrane |
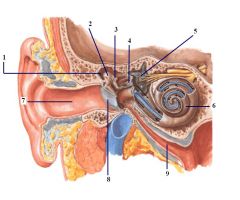
Posterior View
|
|
|
Which part of the ear contains the ossicles?
|
Middle ear
|
|
|
Which part of the ear contains the cochlea?
|
Inner
|
|
|
What structure separates the outer and middle ears?
|
Tympanic membrane.
|
|
|
Name all the ossicles.
|
Malleus
Incus Stapes |
|
|
What is the purpose of the ossicles?
|
Transfer sound from the tympanic membrane to the cochlea
|
|
|
Where is the epitympanic recess?
|
Space in the middle ear cavity above the ossicles.
|
|
|
What does the Eustachian tube connect?
|
Ear with nasopharynx
|
|
|
What allows for the mechanical advantage allowing for amplification of sound in the ear?
|
Large tympanic membrane area transfers sound waves via the small footplate of the stapes, causing 10:1 amplification
|
|
|
The inner ear contains what?
|
Cochlea
Vestibular apparatus |
|
|
What is the purpose of the vestibular apparatus?
|
Balance and equilibrium
|
|
|
Describe the double slanted orientation of the tympanic membrane.
|
Inferior portion is slanted medially
Posterior portion is slanted medially. Superior portion is slanted laterally Anterior portion is slanted laterally |
|
|
The manubrium of the malleus attaches to the tympanic membrane where?
|
Umbo
|
|
|
How does the chorda tympani travel in the middle ear?
- enters? - pathway? - exits? - goes to where? |
Enters from the posterior iter
Travels between the malleus and the incus Exits to the anterior iter Goes to the petrotympanic fissure |
|
|
The tensor tympani m. comes out of what structure into the middle ear?
|
Processus cochleariformis
|
|
|
The stapedius muscle comes out of a what structure in to the middle ear?
|
Pyramidal eminence
|
|
|
Describe the articulations of the malleus ossicle.
|
Head articulates with the Incus
Lateral process articulates with the manubrium |
|
|
Describe the articulations of the incus ossicle.
|
Articulates with head of malleus
The Lenticular process articulates with stapes. |
|
|
How is the tensor tympani positioned in respect to the Eustachian tube?
|
On top of it.
|
|
|
Where does the tensor tympani muscle insert into?
|
Malleus
|
|
|
What creates anterior and posterior malleolar folds of the tympanic membrane?
|
Chorda tympani.
|
|
|
Which CN does the chorda tympani branch off of?
|
CN VII
|
|
|
What is the smallest bone in the body?
|
Stapes
|
|
|
What are the two sacs of the vestibule?
|
Utricle
Saccule |
|
|
The bony labyrinth contains what type of fluid?
|
Perilymph
|
|
|
The membranous labyrinth contains what fluid?
|
Endolymph
|
|
|
What are cristae?
|
Special receptors in the ampulla.
|
|
|
What is a macula and where is it located?
|
Specialized sensory epithelium.
Located in the utricle and saccule. |
|
|
Hair cells in the macula are innervated by what nerve?
|
Vestibular branch of the vestibulotrochlear nerve
|
|
|
1. Helix
2. Antihelix 3. Lobule 4. Tragus 5. Antitragus |
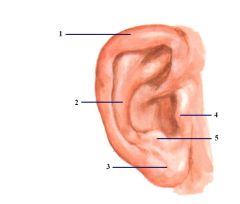
Name
|
|
|
1. Pars Flaccida
2. Posterior Malleolar fold 3. Anterior Malleolar fold 4. Manubrium of Malleus 5. Umbo 6. Cone of light |
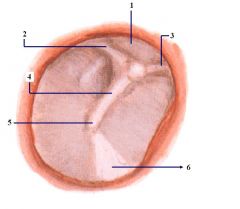
Name
|
|
|
1. Fossa Ovalis
2. Semicircular prominence 3. Facial Prominence 4. Greater Petrosal nerve 5. Pyramidal eminence 6. Tensor tympani 7. Eustachian tube 8. Cochlear Promontory 9. Internal carotid 10. Stylomastoid foramen with facial nerve coming out. |
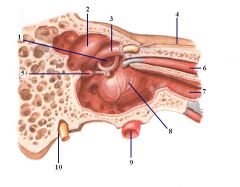
Name
|
|
|
1. Semicircular canal
2. Vestibule 3. Bony Cochlea |
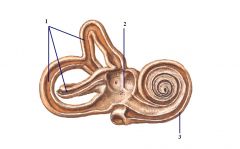
Question
|
|
|
1. Semicircular ducts
2. Ampulla 3. Utricle 4. Saccule 5. Cochlear duct |
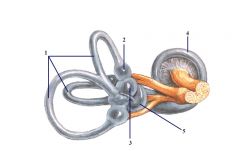
Question
|
|
|
1. Spinal ganglion
2. Scala Vestibuli 3. Scala Tympani 4. Vestibular Membrane 5. Tectorial Membrane 6. Scala Media (aka - cochlear duct) 7. Hair cells 8. Basilar membrane |
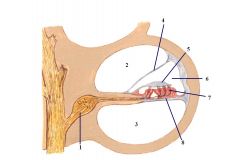
Question
|

