![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the muscle responsible for squinting, like when being hit in the face with a hairy testicle?
|
Orbicularis oculi - the orbital part
|
|
|
What is the muscle responsible for blinking?
|
Orbicularis oculi - the palpebral part
|
|
|
What is the origin of facial expression muscles?
|
Skull
|
|
|
What are the insertions of facial expression muscles?
|
Skin
|
|
|
What innervates the facial expression muscles (name and number)
|
Facial nerve (CN VII)
|
|
|
What connects the frontalis and occipitalis?
|
The Frontal-Occipital aponeurosis (AKA - Galea Aponeurotica)
|
|
|
What muscle protrudes lower lip?
|
Mentalis
|
|
|
The platysma muscle does what?
|
Assists in jaw movement
|
|
|
What muscle is known for assisting in smiling?
|
Risorius
|
|
|
Describe the travels of the parotid duct from the parotid gland.
- runs over - pierces - opens into - finally located where |
Runs over the Masseter muscle. Pierces the Buccinator muscle and opens into the Oral Cavity opposite the 2nd upper molar tooth.
|
|
|
Sensory (cutaneous) innervations of the face and scalp come from what CN? and how does it get to the face?
|
Trigeminal (CN V)
Through the anterior foramina |
|
|
Motor innervation of facial muscles for expression come from what CN? and how does it get to the face?
|
Facial (CN VII)
Through the stylomastoid foramen in the back. |
|
|
What innervates the cutaneous posterior of the head/scalp?
|
C1-C4
|
|
|
What are the divisions of the trigeminal nerves (V)?
|
V1 - Opthalmic
V2 - Maxillary V3 - Mandibulary |
|
|
What are the cutaneous branches of the opthalmic division of Trigeminal nerve (CN V)?
|
Supraorbital
Supratrochlear Infratrochlear |
|
|
What are the cutaneous branches of the Maxillary division of the Trigeminal nerve (V)?
|
Zygomasticotemporal
Zygomasticofacial Infraorbital |
|
|
What are the cutaneous branches of the Mandibular division of the Trigeminal nerve (V)?
|
Auriculotemporal
Buccal Mental |
|
|
Parts of the External Ear are innervated by what CN's?
|
5, 7, 9, 10,
|
|
|
Ear ache can be caused how?
|
Pain related to disease along the distribution of CN V, VII, IX, and/or X.
|
|
|
What are the branches of the Facial nerve (VII)?
|
Temporal
Zygomatic Buccal Marginal Mandibular Cervical |
|
|
What is a similar branch that is both shared by Trigeminal (V) and Facial (VII) nerves?
|
Buccal
|
|
|
Describe the orientation of facial nerves (CN VII) in respect to the parotid gland.
|
Nerves go through the gland
|
|
|
What artery goes to the brain?
|
Internal carotid
|
|
|
The internal carotid can anastamose with the external carotid via what artery?
|
Opthalmic artery
|
|
|
The external and internal jugular vein is separated by what muscle?
|
Sternocleidomastoid
|
|
|
What are the three major veins entering the face/scalp?
|
1. Internal jugular vein
2. External jugular vein 3. Retromandibular vein |
|
|
What are the five layers of the scalp?
|
1. Skin
2. Connnective Tissue (Dense) 3. Aponeurosis 4. Loose connective tissue 5. Periosteum |
|
|
What is the clinical significance of the Dense layer of connective tissue in the scalp?
|
Highly vascularized area, with the dense CT holding open vessels. Thus, lacerations would lead to extensive bleeding.
|
|
|
What is the clinical significance of the Loose layer of the connective tissue in the scalp?
|
Easy for infections to spread quickly
|
|
|
What is the clinical significance of the bone in the scalp?
|
Infection from scalp can spread into the bone or inside the cranial vault via Emissary veins.
|
|
|
Most of the deep drainage of lymphs drain into what?
|
Deep cervical lymph nodes.
|
|
|
1. Frontalis
2. Palpebral portion of Orbicularis Occuli 3. Orbit portion of orbicularis Occuli 4. Orbicularis Oris 5. Risorius 6. Galea Aponeurotica 7. Occipitus 8. Superior portion of Auricularis 9. Posterior portion of Auricularis 10. Anterior portion of Auricularis 11. Zygomaticus major 12. Platysma |
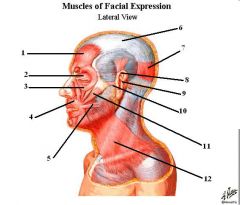
ID muscles
|
|
|
1. Procerus
2. Orbicularis occuli 3. Levator Labii Superioris 4. Depressor Anguli Oris 5. Depressor Labii Inferioris 6. Zygomasticus minor 7. Zygomasticus major 8. Rosarius 9. Mentalis |
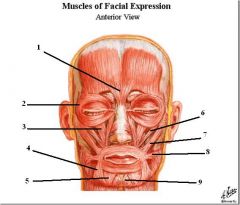
ID muscles
|

