![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Paraxial mesoderm forms a series of tissue blocks on either side of the neural tube. What are these called? x2.
|
1. Somatomeres in head
2. Somites from occipital region caudally |
|
|
Lateral plate mesoderm splits into what layers? x2
|
1. Somatic layers
2. Splanchnic layers |
|
|
Somites develop into what? x2
|
1. Sclerotome
2. Dermomyotome |
|
|
Sclerotome gives rise to what?
|
Mesenchyme which become fibroblasts, osteoblasts, and chondroblasts.
|
|
|
Dermomyotome develops into what?
|
Skin and muscles.
|
|
|
Neural crest cells form what?
|
1. Ganglia
2. Schwann cells 3. Contributes to development of musculoskeletal system. |
|
|
What cells contributes to the development of musculoskeletal system.
|
Neural Crest Cells.
|
|
|
The two parts of the skull.
|
1. Neurocranium - around the brain
2. Viscerocranium - forms face |
|
|
Membranous bones of the neurocranium are developed from what?
|
Neural crest cells and paraxial mesoderm.
|
|
|
What are the two parts of the neurocranium?
|
1. Membranous portion
2. Cartilaginous portion (chondrocranium) |
|
|
Describe what the membranous portion of the neurocranium is.
|
Flat bones of cranial vault
|
|
|
Condrocranium (or cartilaginous portion of neurocranium) formed from what?
|
SEPARATE cartilages derived from neural crest and paraxial mesoderm.
|
|
|
Describe what the cartilaginous portion of the neurocranium forms into.
|
Forms base of skull
|
|
|
Cartilaginous portion of the neurocranium is also known as what?
|
Chondrocranium
|
|
|
Viscerocranium forms what?
|
Face
|
|
|
Viscerocranium is formed from what embryonic cells? x3
|
1. Neural Crest
2. Somites/Somitomeres 3. Lateral Plate |
|
|
Anterior portion of skull is from what?
|
Neural crest cells
|
|
|
Posterior portion of skull is from what?
|
Paraxial mesoderm
|
|
|
What is a major target for teratogens?
|
Neural crest cells
|
|
|
Palpation of what gives info if ossification of skull is normal or whether intercranial pressure is normal.
|
Anterior Fontanelle during first few years.
|
|
|
What is a fontanelle?
|
Wide areas where more than two bones meet.
|
|
|
Where can you find the most prominent fontanelle?
|
Anterior fontanelle
|
|
|
What are sutures?
|
Where two bones meet narrow seems of connective tissue
|
|
|
How is the base of the skull formed?
|
When cartilages fuse and ossify.
|
|
|
The viscerocranium is formed mainly from what two things?
|
1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches.
|
|
|
Which pharyngeal arch and process is associated with the dorsal portion?
|
1st arch and maxillary process
|
|
|
Which pharyngeal arch and process is associated with the ventral portion?
|
1st arch and mandibular process
|
|
|
The first pharyngeal arch give rise to what in the dorsal portion? x3
|
1. Maxilla
2. Zygoma 3. Temporal |
|
|
The second pharyngeal arch (with contributions from 2st arch) give rise to what?
|
1. Incus
2. Malleus 3. Stapes |
|
|
The first pharyngeal arch contains what.......which will give rise to what in the ventral portion?
|
Contains
MECKEL's cartilage around with MESENCHYME which gives rise to MANDIBLE |
|
|
Why is the face small compared to the neurocranium?
|
Due to absence of sinus, teeth, and small bones.
|
|
|
Define cranioschisis.
|
Cranial vault fails to form
or there are small defects in the skull |
|
|
1. Cranioschisis
2. Anencephaly 3. Vault fails to form and brain tissue exposed to amniotic fluid. |
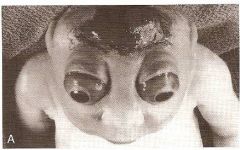
What type of condition is this?
What is this condition? How did this happen? |
|
|
Cranioschisis
Meningocele or Meningoencephalocele Small defects through which meninges or meninges with brain herniate. |
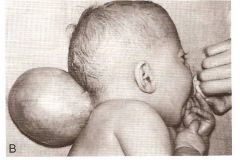
What type of condition is this?
What is this condition? How did this happen? |
|
|
Define craniosynostosis.
|
Caused by premature closure of one or more sutures.
|
|
|
What are some examples of craniosynostosis? x3
|
1. Scaphocephaly
2. Acrocephaly 3. Plagiocephaly |
|
|
Craniosynostosis
Scaphocephaly Premature closure of saggital sutures. |
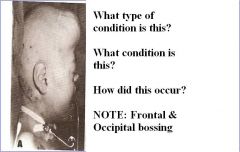
Question
|
|
|
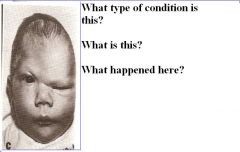
Craniosynostosis
Acrocephaly Premature closure of coronal sutures. |

Question
|
|
|
1. Craniosynostosis
2. Plagiocephaly 3. Premature closure of coronal and lamboid suture on one side. |
Question
|
|
|
Achondroplasia affects primarily what part of body?
|
Long bone.
|
|
|
At end of 4th week, limb buds consist of what? from where? covered by what?
|
1. Core of Mesenchyme
2. From somatic layer of lateral plate mesoderm 3. Cuboidal ectoderm |
|
|
In limb buds at the 5th week, ectoderm at distal end forms what?
|
Apical ectoderm ridge.
|
|
|
Describe the development of cartilage and muscle in limbs.
|
Development in a proximal to distal direction.
|
|
|
Upper limb rotates how?
|
Laterally 90 degrees
|
|
|
With upper limb rotation, describe the position of the extensor muscles and thumb.
|
Lateral & Posterior surface
with Thumb lateral |
|
|
Describe lower limb rotation.
|
Medial rotation of 90 degrees.
|
|
|
With lower limb rotation, describe the position of the extensors and big toe.
|
Anterior surface
with Big toe medial |
|
|
What is a joint interzone?
|
Where joints formed where cartilage development inhibited.
|
|
|
How are joint cavities created?
|
Cell death.
|
|
|
How does joint capsules form?
|
Surrounding tissue of joint cavity forms it.
|
|
|
Describe finger and toes formation.
|
Cell death separates the apical ectodermal ridges into five parts.
|
|
|
Embryo called a fetus when?
|
At beginning of 9th week.
|
|
|
How many epiphyseal plates in long bones? small bones (e.g. - phalanges)? or irregular bones (e.g. - vertebrate)?
|
1. At each end
2. Only at one end of extremity 3. One or more primary centers & several secondary centers. |
|
|
Define amelia.
|
Complete absence of one or more limbs.
|
|
|
Define Meromelia
|
Partial absence of limb
|
|
|
Phocomelia defined.
|
Hands and feet attached to trunk by irregular bones.
|
|
|
Micromelia defined.
|
All segments of limbs present but abnormally short.
|
|
|
Ectrodactyly defined
|
Absence of digit
|
|
|
Syndactyly defined
|
Fusion of digits or toes.
|
|
|
Describe lobster claw formation.
|
Abnormal cleft in 2nd and 4th MCP
Absent 3rd MCP & phalanges Thumb & index fused 4th and 5th digit fused |
|
|
Describe clubfoot.
|
Sole of foot turned inward.
Foot adducted. Plantar flexed. |
|
|
Clubfoot occurs primarily in which gender?
|
Males
|
|
|
Amniotic bands may cause what in limb defects?
|
Ring constriction & amputation of limbs or digits
|
|
|
Congenital hip dislocations occur primarily in which gender.
|
Females.
|
|
|
Describe the formation of the vertebrae.
|
Sclerotomes surround the notocord and spinal cord.
Caudal half of a sclerotome binds to the subjacent cephalic half of another sclerotome. This forms precartilaginous vertebral body. |
|
|
Describe the role of myotomes in vertebral formation.
|
Myotomes bridge the intervertebral discs, allowing the spine to have movement ability.
|
|
|
Describe Klippel-Feil anomaly.
|
Pts have fewer Cervical vertebrae. Other vertebrae are fused or abnormal in shape.
Usually associated with other abnormalities. |
|
|
Describe spina bifida.
|
Cleft vertebra usually in bony arch
|
|
|
Describe scoliosis
|
Lateral curving of spine
Resulting from two successive vertebrae fusing asymmetrically or half a vertebrae missing. |
|
|
Describe rib formation
|
Develop from costal processes of thoracic vertebrae,
from sclerotome portion of paraxial mesoderm |
|
|
Describe sternum formation
|
Develops from somatic mesoderm in ventral body wall as two sternal bands which fuse.
|
|
|
What is unique about clavicle formation.
|
Only postcranial bone that develops in mesenchyme instead of cartilage.
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle develop from what embryonic cells?
|
Paraxial mesoderm (somites & somatomere)
|
|
|
Myotomes form what two muscle forming regions?
|
Epimere and Hypomere
|
|
|
Describe epimere innervation.
|
Innervated by dorsal primary rami.
|
|
|
Describe hypomere innervation
|
Innvervated by ventral primary rami.
|
|
|
What is the association with nerves and muscle segments?
|
Nerves will remain with original muscle segment throughout its migration
|
|
|
Skeletal myoblast precursor cells fuse forming what?
|
Long multinucleated fibers.
|
|
|
Describe Prune-belly syndrome.
|
Absence of abdominal musculature, usually associated with malformation of bladder.
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles develop from what embryonic tissue?
|
Splanchnic mesoderm surrounding endothelial heart tube.
|
|
|
Cardiac myoblasts adhere to one another and develop into what?
|
Intercalated discs.
Some cells form Purkinje fibers. |
|
|
Common partial or complete absence of muscles occur in what muscles? x3
|
1. Pectoralis major
2. Palmaris longus 3. Abdominal (prune-belly) |

