![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which spinal nerves are involved in plexus formation?
|
All except T2-T11
|
|
|
What is the relationship of muscles with their nerve supply?
|
Muscles retain their original SEGMENTAL nerve supply.
|
|
|
Myotome segmentation pattern is seen where?
|
All areas except in areas of plexus formation.
|
|
|
Dermatomes are arranged how?
|
In stripes.
|
|
|
Cutaneous nerves are arranged how?
|
In patches
|
|
|
A root lesion would in the UE, would manifest what type of sensory loss?
|
Loss of dermatome (stripe)
|
|
|
A cutaneous nerve lesion in the UE would manifest what type of sensory loss?
|
Parts of two or more dermatomes are lost.
|
|
|
What is the benefit of veins running superficially?
|
Temperature regulation
|
|
|
All lymphatic nodes of UE drain where?
|
Axillary nodes
|
|
|
Which ARM muscles flex the ARM?
|
Deltoid
Biceps Coracobrachialis |
|
|
1. Cephalic
2. Basilic 3. Median Cubital |
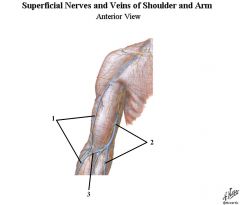
Name
|
|
|
1. Deltoid
2. Short head of bicep 3. Long head of bicep 4. Brachialis 5. Brachioradialis 6. Coracobrachialis 7. Musculocutaneous nerve 8. Brachial artery 9. Median nerve 10. Medial Brachial Cutaneous nerve 11. Triceps 12. Ulnar nerve 13. Medial Antebrachial cutaneous nerve 14. Bicipital aponeurosis 15. Pronator teres |
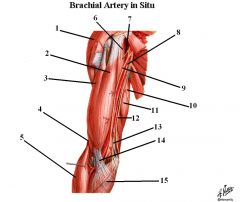
Name
|
|
|
Which muscles in the arm flex the forearm?
|
Biceps
Brachialis |
|
|
Which muscle(s) in the arm also acts as a supinator?
|
Biceps brachii
|
|
|
Describe the innervation of the ARM flexor muscles.
|
Axillary nerve -> deltoid
Musculocutaneous nerve -> all except deltoids |
|
|
What are the ARM Extensor muscles?
|
Triceps brachii
Anconeus |
|
|
What innervates the ARM extensor muscles?
|
Radial nerve
|
|
|
Which head of the tricep attaches to the scapula?
|
Long head.
|
|
|
1. Long head of triceps brachii
2. Medial head of triceps brachii 3. Lateral head of triceps brachii 4. Radial nerve 5. Anconeus |
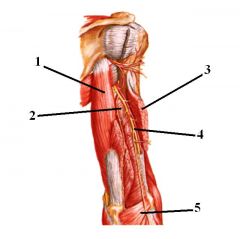
Answer
|
|
|
What are the components of the quadrangular space?
|
Posterior Circumflex Humeral artery
Axillary nerve |
|
|
What are the components of the triangular space?
|
Circumflex scapular artery
|
|
|
What are the components of the triangular interval?
|
Deep Brachial artery
Radial nerve |
|
|
What are the medial and lateral boundaries of the cubital fossa?
|
Medial boundary - Pronator Teres
Lateral boundary - Brachioradialis |
|
|
What is the roof of the cubital fossa?
|
Deep fascia of arm
Bicipital Aponeurosis |
|
|
What comprises the floor of the cubital fossa?
|
Biceps tendon
Brachialis Supinator |
|
|
What are the neurovascular contents of the cubital fossa?
|
Median nerve
Radial nerve Brachial artery and vein with their branches |
|
|
Deep brachial artery:
- follows what nerve - anastomosis with what aa. |
Radial nerve
Radial recurrent aa |
|
|
Superior Ulnar collateral:
- follows what nerve - anastomosis with what aa. |
Ulnar nerve
Posterior Ulnar Recurrent |
|
|
Inferior Ulnar collateral:
- anastomosis with what aa. |
Anterior Ulnar Recurrent
|
|
|
1. Brachial artery
2. Radial recurrent 3. Radial artery 4. Deep brachial artery 5. Superior ulnar collateral 6. Inferior ulnar collateral 7. Anterior ulnar recurrent 8. Posterior ulnar recurrent 9. Ulnar artery |
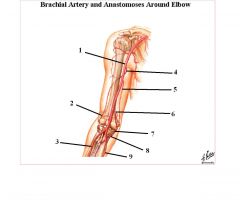
name
|
|
|
Deep brachial veins:
- form what? - attach to what? |
Venae communicates
Brachial artery |
|
|
What are the ligaments of the sternoclavicular joint?
|
1. Anterior sternoclavicular
2. Posterior sternoclavicular 3. Costoclavicular 4. Interclavicular 5. Articular disc |
|
|
1. Costoclavicular
2. Anterior sternoclavicular 3. Posterior sternoclavicular 4. Interclavicular 5. Articular disc |
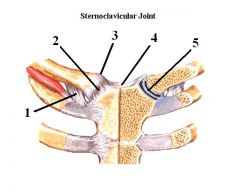
Name the ligaments
|
|
|
Capsular atresia
|
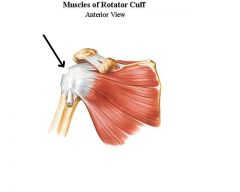
What condition is this?
|
|
|
1. Rotator cuff
2. Coracohumeral 3. Glenohumeral 4. Transverse humeral 5. Long head of biceps |
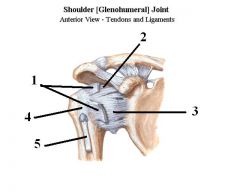
Ligaments
|
|
|
Shoulder separation is when what happens?
|
In the AC joint, there is a tear in the:
- acromioclavicular ligament - coracoclavicular ligament |
|
|
The glenoid cavity has what tendon attach to it?
|
The long head of biceps
|
|
|
Define bursa.
|
Synovial fluid filled sac
(like a cushion) |
|
|
What are the muscles of the rotator cuff?
|
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis |
|
|
What is capsular atresia?
|
Overuse of shoulder causes loss of synovial capsule, leading to abrasion and erosion of rotator cuff.
|
|
|
1. Coracoacromial
2. Acromioclavicular 3. Coracoclavicular |
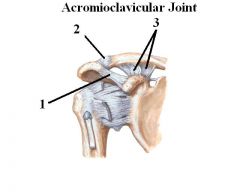
Ligaments
|
|
|
Describe a shoulder dislocation.
|
Tearing of the glenohumeral ligament in the glenohumeral joint.
|
|
|
What are the ligaments of the elbow joint?
|
Radial collateral
Ulnar collateral Anular |
|
|
A "pulled elbow" is what?
|
A subluxation of anular ligmanet.
|
|
|
1. Capsule
2. Radial Collateral ligament 3. Ulnar Collateral ligament 4. Anular 5. Radial tuberosity 6. Ulnar tuberosity |
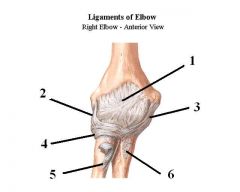
name
|
|
|
What inserts in to the radial tuberosity?
|
Biceps
|
|
|
What inserts in to the ulnar tuberosity?
|
Brachialis
|
|
|
In rotating from supine to pronation of the forearm, what is the only bone that moves?
|
Radius
|
|
|
What dense connective tissue holds the radius and ulna together?
|
interosseous membrane
|

