![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Differentiate between family-based and population-based means to identify disease genes.
|
With family based, you use related individuals to perform linkage analysis (found markers particular to that family). Need extensive familial information.
With population-based, you use unrelated individuals and do genome-wide association analysis. This is becoming more and more in practice. |
|
|
In genetic mapping, polymorphic markers were used thus it was important/most helpful if individuals in the family were [ homozygotes / heterozygotes ].
|
Heterozygotes.
|
|
|
This type of analysis looks at polymorphisms, in most cases polymorphisms in DNA sequence consisting of differences in a single base pair, or single nucleotide polymoprhisms (SNPs), that are spaced throughout the genome to see which are found to be associated with the ocurence of the disease.
|
A. Genome-wide association.
|
|
|
The statistical analysis in which the genotypes and phenotypes of family members are studied to determine whether two or more loci (e.g. polymorphic marker and disease gene) are assorting independently or exhibiting linkage during meiosis
A. Family Based Methods B. Population Based Methods |
A. Family Based Method
|
|
|
What does it mean if loci are "syntenic"?
|
"Syntenic" just means they are located on the same chromosome. Syntenic loci may or may not be linked.
|
|
|
The further apart two syntenic loci are the [ less likely / more likely ] recombination will occur between them and the [ less likely / more likely ] the loci are linked
|
further apart = more likely recombination will occur = less likely they are linked.
|
|
|
In linkage analysis, the distance between two loci is estimated by theta which represents....
A. recombination frequency B. syntenic frequency C. LOD score value |
A. recombination frequency
( # of recombinant gametes / total # gametes) |
|
|
If things sort independently, what recombination frequency would you expect?
A. 0 B. 0.25 C. 0.5 D. 1 |
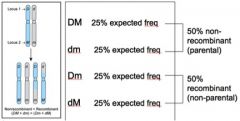
C. 0.5
|
|
|
What is the minimum and maximum value for recombination frequency, or theta, and what do they mean?
|
Minimum = 0 , no recombination occured in gametes.
Maximum = 0.50 , alleles assorted completely independently. |
|
|
Theta, besides being recombination frequency, also is a measure of the distance between two loci. [ Larger / Smaller ] values of theta mean that the two loci are close together.
|
Smaller.
|
|
|
_______ refers to the orientation of alleles on a chromosome. What does coupling and repulsion refer to?
|
Phase; coupling refers to the alleles in question being on the same chromosome whereas repulsion refers to the alleles in question being on different chromosomes.
|
|
|
What is true about a scenario where there is synteny with no recombination?
A. Theta = 0.5. B. The two loci assort independently. C. None of the above. |
C. None of the above.
Theta in a case with no recombination = 0! And if there is NO recombination this means they are linked because also remember small theta value indicates closer together on chromosome. |
|
|
A way to define linkage is that there
is less than ______ recombination between the two loci. |
50%
|
|
|
Can you have a recombination event between two loci if they are linked?
A. Yes, if they are far enough apart. B. No, linked alleles stay together nearly all the time. |
A. YES, you can if they are far apart.
|
|
|
The map unit of genetic linkage is the __________, cM where 1 cM = ___% recombination = ____ bases
|
centiMorgan; 1 cM = 1 % recomb = 10 ^6 bases!
note: 1cM = 1,000 kb = 10 ^6 bases disclaimer: A relationship between genetic distance and physical distance exists but is not absolute. |
|
|
In linkage analysis, what three things do we absolutely need:
A. correct clinical diagnosis B. Polymorphic markers C. Large informative families D. to study diseases that are very common in population E. to study complex diseases |
A, B and C only.
D & E are things that family based studies are NOT effective in identifying mutations for. |
|
|
[ Positive / Negative ] LOD scores are in support of linkage and [ positive / negative ] LOD scores are in support of no linkage
|
+ = linkage ; - = no linkage
scores of 3 are generally accepted as linkage. score of -2 is accepted as no linkage. anything in between is indeterminate |
|
|
True or False:
With genome wide association analyses, you map the gene and then clone the gene to help identify the disease-causing mutation. |
False. That is what you do with Family-based method of gene mapping. In genome-wide association analyses you are looking at complex diseases with genetic component so you identify the associated polymorphism and then identify the ones that are functionally significant.
|
|
|
True or False:
In genome-wide analyses, we try to see which polymorphisms (SNPs, or single nucleotide base pair changes) are associated with having the disease. |
True
|
|
|
Disease odds ratios are used to determine whether a given polymorphism is associated with a given disease. What is the formula/ setup to calculate this?
|
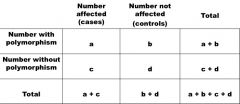
disease odds ratio = ad/bc
|
|
|
Genome-wide association analyses examine the association between polymorphisms (SNPs) located throughout the genome and the presence of disease to localize susceptibility genes. They take advantage of ______________ to find polymorphisms that contribute to disease susceptibility.
A. linkage disequilibrium B. LOD scores C. linkage |
A. linkage disequilibrium, or the tendency for alleles of loci that are situated close to each other to be passed on together. Linkage disequilibrium is a characteristic of loci IN A POPULATION, NOT OF LOCI ON A CHROMOSOME.
|
|
|
[ Linkage / Linkage disequilibrium ] refers to the relationship between two loci (a genetic marker and a disease gene which are situated close enough to each other such that crossover between them rarely occurs)
[ Linkage / Linkage disequilibrium] refers to the relationship between a segment of DNA (and all the loci contained in that segment) and the locus that carries the polymorphism that confers susceptibility for the disease |
Linkage
Linkage disequilibrium |
|
|
Regarding diagnostic approaches for the detection of a mutation, _____________ detects large deletions or insertions and can in some cases detect a point mutation at a restriction site.
A. DNA sequencing B. PCR w/out restriction enzyme digestion C. PCR w/ restriction enzyme digestion D. Southern Blotting E. ASO |
D. Southern Blotting
|
|
|
True or False:
Southern Blotting can in some cases detect a point mutation at a restriction site. |
TRUE!
More commonly though it detects large deletions or insertions (100 bp- 100Mb) |
|
|
______ can be used to detect deletions; _________ can be used to detect point mutations at a restriction site.
A. PCR w/ restriction ; PCR w/out restriction B. PCR w/out restriction; PCR w/ restriction |
B. PCR w/out restriction; PCR w/ restriction
|
|
|
What diagnostic approach is best to detect known mutations:
A. DNA sequencing B. PCR w/out restriction enzymes C. PCR w/ restriction enzymes D. Southern Blotting |
A. DNA sequencing for known mutations
|
|
|
_______ is a sequence variation which can be detected in more than 1% of the population and which does not result in a disease phenotype.
|
Polymorphism!
Ex. phenotype: blood pressure, eye color. Protein polymorph: blood groups |
|
|
_______ results from variation in DNA sequences at sites recognized by various restriction enzymes. It leads to creation of a new site or abolition of an existing cleavage site.
A. RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) B. STRP markers (short tandem repeat polymorphic markers/ repetitive DNA) |
A. RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism)
|
|
|
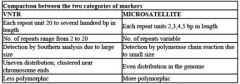
What are the two types of Short Tandem Repeat Polymorphic markers / repetitive DNA?
|
|
|
|
Label which is VNTR and which describes a microsatellite in each pair:
A. Each repeat unit is 20- several hundred bp in length VS each repeat is 2, 3, 4, 5 bp in length B. no. of repeats is 2-20 VS number of repeats is variable C. detection via PCR ; detection via Southern D. uneven distribution (near chromosome ends) ; even distribution in genome |
VNTRS: Each repeat unit is 20- several hundred bp in length , no. of repeats is 2-20, detection via Southern, uneven distribution (near chromosome ends)
|
|
|
What are the four general steps to cloning a gene based on its position?
a.k.a. Positional Cloning, Reverse Genetics, or Cloning a Disease Gene of Unkown Function |
1) Narrow the location of the disease to a specific chromosomal region using linkage analysis, with polymorphic genetic markers. This is called identifying the gene critical region. Should be able to narrow down gene location to 1-3 Mb. STEP2: Identify the several genes located in the region. STEP 3: Evaluate and prioritize the genes selected to determine the best candidate for the gene. STEP 4: Search for disease causing mutation in candidate genes.
|
|
|
How is an LOD score calculated?
|
The log (base 10) of (probability of linkage) / (probability of no linkage).
LOD scores are calculated at different thetas. |

