![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function of cytoskeleton X 2
|
1.) Cell shape and structure
2.) Mechanochemical movement |
|
|
The three basic filaments of cytoskeleton
|
1.) Actin
2.) Microtubules 3.) Intermediate filament |
|
|
How are filament systems held together?
|
By weak non-covalent bonds
|
|
|
Describe the types of IF's involved in cell to cell adhesion.
|
1.) Desmosomes (connection between cells)
2.) Hemidesmosomes (connection between cells and matrix) 3.) Keratin (connection between cells and organelles) |
|
|
Describe the types of IF's involved in muscles.
|
DESMINS provide a scaffold cage for skeletal muscles.
|
|
|
Common IF structural similarities.
|
1.) Globular amino-terminal domain. (HEAD)
2.) Central alpha helical domain. (BODY) 3.) Globular C-terminus domain. (TAIL) |
|
|
How does IF's initially begin folding?
|
As coiled coil dimers.
|
|
|
Different types of IF coiled coil dimers.
|
1.) Homopolymeric
2.) Heteropolymeric |
|
|
Where are the modifications (dissociations) and regulations occuring on IF's?
|
On the C-terminus ends
|
|
|
Why are hair keratins so stable and insoluble?
|
Due to high cysteine residues on the end forming disulfide crosslinks.
|
|
|
IF's are composed of what subunits?
|
IF's consist of 4 PROTOFIBRILS
|
|
|
What are protofibrils composed of?
|
Protofibrils composed of 2 APOLAR PROTOFILAMENTS
|
|
|
What are the apolar protofilaments composed of?
|
Apolar Protofilaments composed of 2 polar coiled coil dimers in antiparallel tetramer form
|
|
|
Individual coiled coiled domains have what type of repeat?
|
heptad
|
|
|
Why do IF's not have the dynamic nature of actins or microtubules?
|
Due to lack of polarity.
|
|
|
What are the benefits of IF's in regards to actin or myosin?
|
Greater combo of strength, stability, and flexibility.
|
|
|
For the most part, how are IF's regulated?
|
By phosphorylation (sometimes by proteolysis)
in globular region. |
|
|
What enzyme breaksdown IF's in nucles?
|
Cyclin-dependent Kinase (CDK)
|
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for IF assembly?
|
Protein Phosphatase I (PP1)
|
|
|
Functions of IF's X 2.
|
1.) Mechanical(protection and structure)
2.) Non-mechanical (stress sensor and signaling) |
|
|
Two diseases associated with gene mutations affecting the mechanical mechanism of IF.
|
1.) EBS (Epidermolysis Bulbosis Simplex)
2.) EH (Epidermolysis Hyperkeratosis) |
|
|
Disease associated with defect in LMNA gene.
|
Hutchingson-Gilford Progeria
|
|
|
What are the globular, nucleotide-binding protein subunits in actin?
|
Actin monomers
|
|
|
What are the globular, nucleotide-binding protein subunits in microtubules?
|
Alpha and beta tubulin heterodimers.
|
|
|
Describe the ends of actin.
|
Barbed polar (+) end
Pointed polar (-) end |
|
|
Describe the ends of microtubules.
|
Just (+) and (-) ends
|
|
|
Nucleotide binding for actin?
|
ADP/ATP
|
|
|
Nucleotide binding for microtubules?
|
GDP/GTP
|
|
|
Where do you find actins X 6?
|
1.) Muscle
2.) Microvilli of intestintal brush border 3.) Movement/Growth of Cell 4.) Cleavage Furrow of cytokinesis 5.) Vesicle movement 6.) Stero cilia in ear. |
|
|
What are the two forms that actin can exist as?
|
1.) Parallel bundles
2.) 2D or 3D networks |
|
|
Two important concepts of actin.
|
1.) Dynamic polymerization/depolymerization.
2.) Association with molecular motors. |
|
|
Why is nucleation of a helical polymer difficult?
|
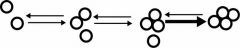
Because you need multiple and simultaneous contacts. You need at least three to spontaneously join to get the required fourth.
|
|
|
What causes the rate limiting for polymerization in actin?
|
Concentration of polymers
|
|
|
What are the principles that govern actin dynamics?
|
1.) Regulation of Bound nucleotide.
2.) Regulation of Elongation 3.) Regulation of Nucleation 4.) Regulation of Severing filaments. |
|
|
Describe Regulation of Bound Nucleotide.
|
Factors that facilitate ADP/ATP exchange on actin....
and GDP/GTP exchange on microtubules. |
|
|
Describe Elongation regulation.
|
Factors that alter rate of elongation?
|
|
|
Give an example of protein that regulates bound nucleotides?
|
PROFILIN facilitates ADP/ATP exchange in actin.
|
|
|
Give an example of Elongation regulation protein?
|
End-specific capping proteins.
|
|
|
Describe regulation of nucleation?
|
Proteins that regulate nucleation.
|
|
|
Provide example of nucleation regulation protein.
|
Arp complex
|
|
|
Describe regulation of severing filaments.
|
Proteins that sever filament in middle
|
|
|
Provide example of regulation protein that severs filaments.
|
Gelsolin
|
|
|
Give an example of non-mechanical function of IF's.
|
Wound signalling for healing
|
|
|
In regards to LMNA, what is the reason for disease phenotypes such as Progeria?
|
Accumulation of farnesylated Lamin A.
|
|
|
What is the most abundant type of protein in cell?
|
Actin
|

