![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA is a long polymer of :
a) deoxynucleosides b) deoxynucleotides |
b) deoxynucleotides
|
|
|
RNA are polymers of
a) ribonucleosides b) ribonucleotides |
b) ribonucleotides
|
|
|
What are the components of a nucleotide?
|
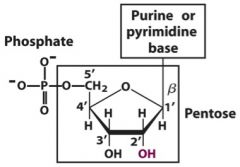
|
|
|
On the pentose of a nucleotide, which number carbon is the one connected
a) to the base? b) to the phosphate group? |
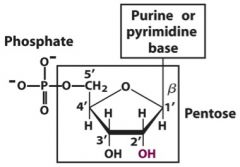
a) 1'
b) 5' (numbering is clockwise) remember: note the primes (sugar in nucleic acids are #'d this way) |
|
|
Nucleoside is a nucleotide without...
|
a phosphate group.
|
|
|
On a pentose, if hydroxy is "up" then it is [ alpha / beta ] . If hydroxy is "down then it is [ alpha / beta ].
|
up is beta ; down is alpha
|
|
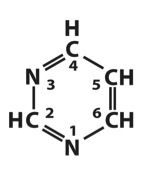
Identify whether this is a purine or pyrimidine.
|
Pyrimidine!
|
|
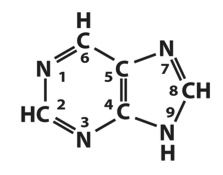
Identify whether this is a purine or pyrimidine.
|
Purine!
|
|
|
Bases are covalently joined to the C-__ of the sugar at N-___ for pyrimidines and N-___ for purines.
|
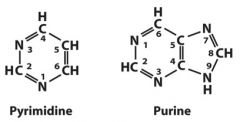
Bases are covalently joined to the C-1' of the sugar at
N-1 for pyrimidines and N-9 for purines. The bond is termed an N-β-glycosyl bond. |
|
|
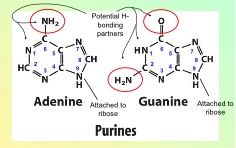
Name the purines.
|
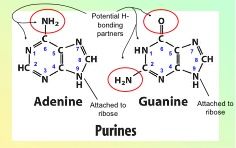
|
|
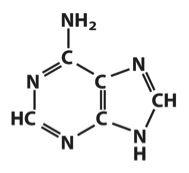
Identify this base and number it correctly.
|
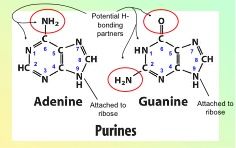
|
|
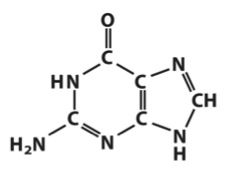
Identify this base and number it correctly.
|
|
|
|
List the pyrimidines.
|
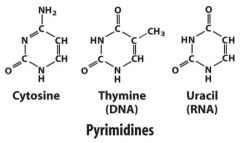
|
|
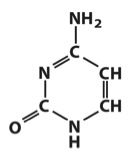
Identify and number this base.
|
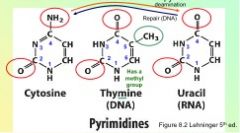
|
|
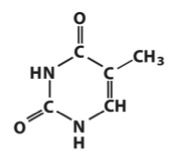
Identify the base and number it.
|
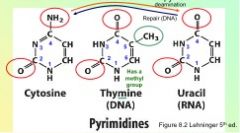
|
|
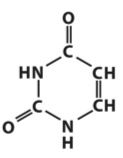
Identify the base and number it.
|
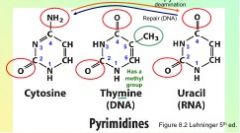
|
|
|
To build a nucleic acid, the hydroxy group in position ____ ' on the sugar will attack the ___ phosphate of a nucleotide triphosphate (like GTP, ATP) and the pyrophosphate goes
|
hydroxy group in position 3' of the sugar will attack the alpha phosphate of an nucleotide triphosphate.
|
|
|
Two other nucleotides that function as second messengers in hormonal signaling (nucleotides do not only form nucleic acids!) are...
|
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
and cyclic GMP (cGMP) |
|
|
Purine nucleosides end in " - _____" while pyrimidine nucleosides end in " - ___ ".
|
Purine nucleosides - > "sine"
pyrimidine nucleosides -> "dine" |
|
|
Purine nucleotides end in "-____" while pyrimidine nucleotides end in "-____".
|
purine nucleotides -> "ylate"
pyrimidine nucleotides -> "ylate" |
|
|
What are the five key features of a DNA double helix?
|
1. Phosphodiester bonds link nucleotides forming a hydrophyllic, covalent backbone that is the "outside" of the helix.
2. Each chain has a polarity (5' to 3' ends). And the 2 chains form an anti-parallel helix. 3. negative charges are neutralized by proteins, metal cations or polyamines. 4. bases are planar, and form H-bonded complementary base pairing. 5. "inside" of helix is hydrophobic 5. |
|
|
What kind of bonds link nucleotides, thereby forming a hydrophyllic backbone that is the outside of the helix?
|
Phosphodiester
|
|
|
Each nucleotide chain in DNA has a polarity (___' to ____' ends). And the two chains form what type of helix?
|
5' -> 3'
antiparallel |
|
|
How many H-bonds does each have?
a) G-C b) A-T |
a) 3
b) 2 G-C bonds more strongly than A-T. Thus, A-T will denature at a lower melting temperature than G-C. |
|
|
What are the three helical structures of DNA / RNA?
|
B-form: DNA/DNA is right handed
A-form: DNA/RNA hybrids and RNA/RNA is right handed Z-form: DNA/DNA is left handed because purines are in syn configuration. Z-form found in regulatory segments. |
|
|
True or False:
The DNA structure is clearly defined whereas RNA structures don't have a single simple standard structure. |
True. Can have single strands, double, bulges, internal loops, hairpins.... just remember that they do intramolecular interactions. Note though that where complementary sequences are present (common) the single stranded double helical RNA structure is a R handed double helix hairpin called an A-form.
|

