![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ordering of water around apolar molecules drives __________ interactions.
|
hydrophpbic
|
|
|
Kw = [H+] [OH-] = _____
|
1.0 X 10-14 M2
|
|
|
For pure water or any neutral solution, [H+] = [OH-] =
|
10-7 M
|
|
|
Given Kw = [H+] [OH-] = 1.0 X 10-14 M2, if another base is added to the solution, OH- will be [ decreased / increased ] to the extent that H+ is [ decreased / increased ].
|
OH- will be increased to the extent that H+ is lowered.
|
|
|
What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation?
|
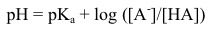
|
|
|
Smaller pKa values indicate [ stronger / weaker ] acids.
|
Smaller pKa values indicate stronger acids.
|
|
|
The pKa is the pH at which the weak acid is ....
|
half (50%) ionized
think of HendersonHasselback eq! |
|
|
pH + pOH = _____
|
14
|
|
|
True or False: Carbonic acid is a diprotic acid that dissociates twice.
|
True.
|
|
|
As a rule of thumb, when titrating, the buffering region is + or - ____ from the pKa.
|
+ or - 2 from the pKa is the buffering region
|
|
|
A _______ is a solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base that resists changes to pH when acid or base or added.
|
buffer
note: a buffer has its maximum buffering capacity at the pKa of its weak acid. |
|
|
pI , or isoelectric point is the pH at which...
|
the net charge on the amino acid or protein is zero, i.e. the numbers of positive and negative charges are exactly balance. this has implications for whether an amino acid will move in an electric field or how it will combine with others
|
|
|
The amino acids with three ionizable groups, where is the pI?
|
It depends. If it is basic ( + charged as in lys, arg, his) then it will be in between the pKr and pK2. If it is acidic ( - charged as in asp, glu ) then it will be between the pK1 and pKr! Note that pK1 is always about 2 and pK2 is always about 9.
|
|
|
A molecule is in a solution with a pH at its pI. What happens if you perform electrophoresis?
|
The molecule will not migrate since it has no net charge.
|
|
|
A molecule is in a solution with a pH at its pI. What happens if you perform ion exchange chromatography?
|
The molecule will not bind to an ion exchange column since it has no net charge.
|

