![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why should pleural fluid accumulate? |
1. Transudation (due to increased hydrostatic pressure, decreased oncotic pressure or capillary leak) 2. Increased production of pleural fluid (inflamed pleura, pleural neoplasm) 3. Decreased pleural absorption of fluid (lymphatic obstruction, systemic venous hypertension) 4. Bleeding into pleural space |
|
|
What can we find in pleural fluid? |
1.Transudate or exudate (clear) 2. Purulent (pyothorax or empyema thoracis) 3. Bloody (hemothorax) 4. Chylous (chylothorax) |
|
|
Causes of pleural effusion |
1. Increased transudaction (CHF, hypoalbuminemia, pulmonary embolism, SVC syndrome) 2. Increased production (mesothelioma, metastatic k, infections, pulmonary infarction, after heart or lung surgery) 3. Decrease absorption (lymphatic obstruction, heart failure, SVC syndrome) 4. Bleeding (rupture of aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, trauma, post-op) |
|
|
What is Transudate? |
Results from disturbance in Starling forces. It is a simple outflow of water from blood vessels to ISF. |
|
|
What is Exudate? |
Results from damage to the capillary wall. It is an outflow of high protein content fluid with also WBCs in the ISF |
|
|
How do we distinguish Transudate from Exudate if both are clear? |
Use Rivalta's test: a drop of the fluid is put in a glass with distilled water. If precipitates is exudate, otherwise is transudate |
|
|
Cough definition |
Sudden, usually involuntary, expulsion of air from the lungs with a characteristic and easily recognizable sound. Is the most common symptom of respiratory disorder and the most common reason that brings people to the GP |
|
|
Gunction of cough |
Defend the respiratory system against noxious substances and maintain airway patency |
|
|
Categories of cough |
Acute (lasting less than 3 weeks) Subacute (lasting 3 to 8 weeks) Chronic (lasting more than 8 weeks) |
|
|
Causes of WET cough |
1. Acute bronchitis 2. Bronchiectasis (destruction and widening of airways) 3. Bronchiolitis (inflammation of smallest airways of lungs) 4. Common cold 5. CF 6. Influenza 7. TB |
|
|
Causes of DRY cough |
1. Airway irritation (bronchospasm) 2. Asthma & allergies 3. COPDs 4. Congestive heart failure 5. Lung cancer 6. Pleurisy 7. Smoking |
|
|
Cough is a red flag for...? |
-Postnasal drip -GERD -Pollution/irritants -Medication-induced -Asthma -Lung k -Aspiration -Heart filure -Chronic bronchitis -Pneumonia |
|
|
Causes of prolonged cough |
Non-infectious cause (Asthma, GERD, Smoking, CF, Foreign body aspiration) Infectious cause (Chronic sinusitis, bacterial pneumonia and bronchitis, TB, Pertussis, Viral infections) |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of Sinus infections |
Dull or intense pressure-like pain Erythema Swelling of cheek and anterior axilla Pressure of fullness in vicinity of maxillary sinus Headache Malaise Fever Oral malodor Mucopurulent thinorrhea Nasal congestion Postnasal drip |
|
|
Symptoms of pneumonia |
Depend according to type. Common are fever, chest/muscle pain, cough with mucus, lack of energy |
|
|
Virus that infect the URT |
Rhinovirus, Coronavirus, Influenza virus, Parainfluenza virus, RSV, Herpesvirus, Adenovirus, Bocavirus, Coxsackievirus |
|
|
Viruses that infect the LRT |
Influenza virus, Parainfluenza virus, RSV, Adenovirus, Bocavirus, Metapneumovirus |
|
|
Common causes of Chronic cough |
Chronic bronchitis Upeer Airways Cough Syndrome GERD Asthma Nonasthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis Bronchiectasis |
|
|
What influences the rate of breathing and how? |

|
|
|
Breath sounds can be |

Vesicular (low-pitched, low-intensity heard over healthy lung tissue) Bronchovesicular (heard over major bronch and are typically moderated) Bronchial (tubular) (heard only over trachea, high pitch) |
|
|
Crackle definition |
Abnormal respiratory sound heard more often during inspiration. Are discrete discontinuous sounds, lasting just few milliseconds. May be fine, high pitched and short in duration or coarse, low pitched and long in duration. They are caused by disruptive passage of air through small airways in respiratory tree. |
|
|
How are URT crackles? |
Dry, crisp, sibilant and low pitched. Easily heard with open mouth with respect to LRT crackles |
|
|
Rhonchi definition |
Rhonchi are sonorous wheezes, deep, rumbling, more pronounced during expiration, prolonged and less discrete than crackles. Caused by passage of air through an airway obstrcted by thick secretions or by spasms. Sibliant, high pitched sounds come from small bronchi (asthma), lower pitched rhonchi arise from larger bronchi (tracheobronchitis). Rhonchi tend to disappear after coughing whereas crackles do not |
|
|
Wheezes defintion |
Sibilant, continuous, high-pitched sound, almost a whistle caused by high velocity air flow through narrowed or obtructed airway. The longer and higher pitch, the wrose the obstruction. If heard bilaterally can be bronchospasm (asthma or acute chronic bronchitis), unilateral occur usually due to a foreign body, but can also be due to a compressing tumour |
|
|
Friction rub |
Outside repiratory tree, is a dry, crackly, grating, low-pitched sound heard in both inspiration and expiration. Usually if heard on heart or lungs is due to inflamed roughened surfaces rubbing together (pericarditis or pleurisy). Stops if breath is held (not on heart of course) |
|
|
Atelectasis definition |
Incomplete expansion oflungs at birth, or lung collapse at any age |
|
|
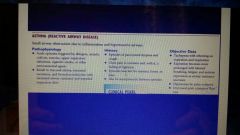
Asthma definition |
|
|
|
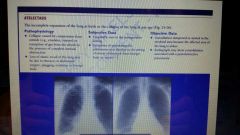
Atelectasis definition |
|
|
|
Bronchitis definition |

|
|
|
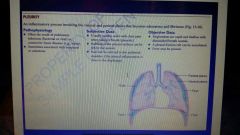
Pleurisy definition |
|
|
|
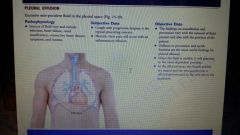
Pleural effusion |
|
|
|
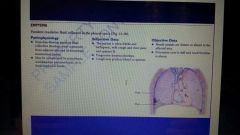
Empyema definition |
|
|
|
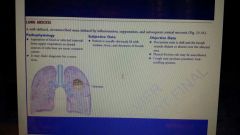
Lung abscess |
|
|
|
Pneumonia definition |
|
|
|
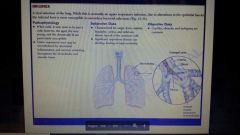
Influenza definition |
|
|
|
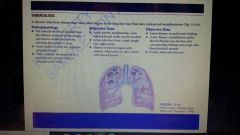
TB definition |
|
|
|
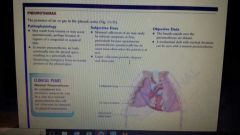
PNX definition |
|
|
|
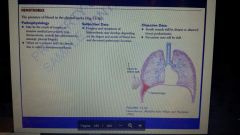
Hemothorax definition |
|
|
|
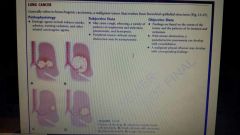
Lung k definition |
|
|
|
Cor pulmonare definition |
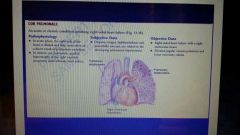
|
|
|
Pulmonary embolism definition |
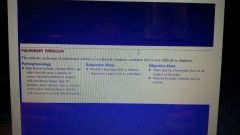
|
|
|
COPD definition |
Group of repiratory problems in which coughs, chronic and excessive sputum production, dyspnea are prominet features. Ultimately irreversible obstruction occurs. Chronic bronchitis, brochiectasis and emphysema are main conditions. Smoke and age are risk factors |
|
|
Emphysema definition |
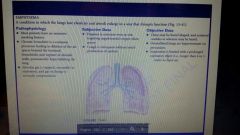
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis definition |
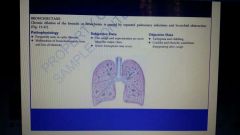
|
|
|
Chronic bronchitis definition |
|
|
|
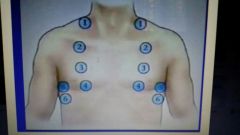
Lung auscultation points |
|

