![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Logic is...
|
The study of correct reasoning
The theory of inference A symbolic or mechanical system for representing and testing patterns of arguments |
|
|
Defective argument
|
The truth of the premises guarantees the truth of the conclusion
|
|
|
Inductive argument
|
Truth of the premises supports but DOES NOT GUARANTEE the truth of the conclusion
|
|
|
Valid argument
|
Valid only If the conclusion follows deductively from the premises
|
|
|
Sound argument
|
Sound if (1) it is valid (2) if the premises are true
|
|
|
Valid is a question of...
|
Form
|
|
|
True or false is a question of...
|
Content
|
|
|
Sound is a question of...
|
Form & content
|
|
|
Statements
|
Are true and false but NEVER valid, sound or unsound
|
|
|
Cogency
|
If the conclusion is well supported by the premises
If premises are well supported by the evidence If we are considering all the available relevant |
|
|
Appeal to Force
|
Arguer threatens reader/listener
|
|
|
Appeal to Pity
|
Argued elicits pity from reader/listener
|
|
|
Appeal to the people
|
Arguer incites a mod mentality or appeals to desire for security love or respect
|
|
|
Argument against the person
|
Abusive - arguer personally verbally attacks
Circumstantial- presents opponent as predisposed Tu quoque- presents opponent as a hypocrite |
|
|
Accident
|
General rule is applied to a specific case wasn't intended to cover
|
|
|
Straw Man
|
Arguer distorts an opponents argument and then attacks the distorted argument
|
|
|
Missing the point
|
Arguer draws conclusion different from the one supported by the premises
|
|
|
Red Herrig
|
Arguer leads reader/listening off track
|
|
|
Appeal to unqualified authority
|
Weak induction: arguer cities untrustworthy authority
|
|
|
Appeal to Ignorance
|
Weak induction: premises report nothing is known/proved and a conclusion is drawn
|
|
|
Hasty generalization.
|
Weak induction: a general conclusion is drawn from a typical sample
|
|
|
False Cause
|
Conclusion depends on nonexistent or minor casual connection
|
|
|
Slippery slope
|
Conclusion depends on an unlikely chain reaction of causes
|
|
|
Weak Analogy
|
Conclusion depends on a defective analogy
|
|
|
Begging the question
|
Arguer creates similarity that inadequate premises are adequate by leaving out a key premises
|
|
|
Complex question
|
Multiple questions are concealed as a single question
|
|
|
False Dictotomy
|
An either...or..."premise hides additional alternative"
|
|
|
Suppressed Evidence
|
Arguer ignores important evidence that requires a different conclusion
|
|
|
Equivocation
|
Conclusion depends on a sniff in meaning of word or phrase
|
|
|
Amphiboly
|
Conclusion depends on an incorrect interpretation of an ambiguous statement made by someone other than the arguer
|
|
|
Composition
|
An attribute is wrongly transferred from the parts to the whole
|
|
|
Division
|
An attribute is wrongly transferred from the whole to the parts
|
|
|
Basic Truth Function Table
|

|
|
|
Rule for Truth Table
|
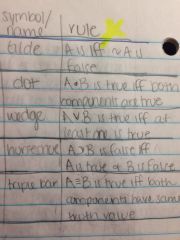
|
|
|
Tautology
|
Everything under main operator are all true
|
|
|
Self-contradictory
|
Everything under main operator is false
|
|
|
Contingent
|
Under main operator, at least one true, at least one false
|
|
|
Logically equivalent
|
Same truth value of each line
|
|
|
Sufficient condition
|
Occurrence of event A is all that's required for occurrence event B
|
|
|
Necessary condition
|
Event B cannot occur without the occurrence of Event A
|
|
|
Enthymematic
|
An argument missing a premise
|
|
|
Contradiction
|
False in every valuation
|
|
|
Translations
|

|

