![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
physiological functions of lipids
|
constituents of membranes
bioregulation cofactors for enzymes structure food and digestion |
|
|
seven classes of lipids
|
fatty acids
fats (triglycerides) waxes phospholipids sphingolipids prostaglandins steroids |
|
|
functions of fatty acids
|
- storage
- precursors to metabolic intermediates - membrane anchors |
|
|
structure of fatty acids
|
long chain (n-alkyl) organic acids, which can be saturated or unsaturated
|
|
|
pharmaceutically, fatty acids are used in ____.
|
ointments
|
|
|
What is the trend in melting point of saturated fatty acids, with increasing number of carbons? Why?
|
With increasing number of carbons, the melting point increases. Larger molecules have more van der Waal's interactions, and thus they adhere more tightly in a solid structure.
|
|
|
Saturated fatty acids have [higher / lower] melting points than their unsaturated counterparts. Why?
|
higher... The kinks in unsaturated fatty acids render them less capable of packing into solid structure; thus, they have lower melting points.
|
|
|
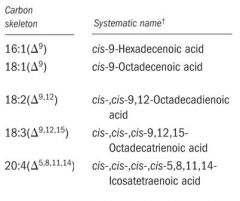
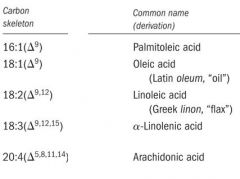
carbon skeleton of Palmitoleic acid
|
16:1(Δ9)
|
|
|
carbon skeleton of Oleic acid
|
18:1(Δ9)
|
|
|
carbon skeleton of Linoleic acid
|
18:2(Δ9,12)
|
|
|
carbon skeleton of α-Linolenic acid
|
18:3(Δ9,12,15)
|
|
|
carbon skeleton of Arachidonic acid
|
20:4(Δ5,8,11,14)
|
|
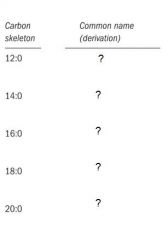
Fill in the table.
|
- Lauric acid
- Myristic acid - Palmitic acid - Stearic acid - Arachidic acid |
|
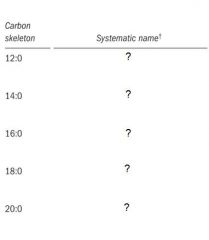
Fill in the table.
|
n-Dodecanoic acid
n-Tetradecanoic acid n-Hexadecanoic acid n-Octadecanoic acid n-Eicosanoic acid |
|

|
|
|
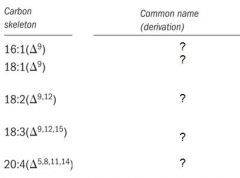
|
|
|
|
What are the carbon skeletons of the essential fatty acids?
|
18:2
18:3 20:4 |
|
|
What are the common names of the essential fatty acids?
|
Linoleic acid
α-Linolenic acid Arachidonic acid |
|
|
Fatty acids form ____ in water.
|
micelles
|
|
|
Fatty acids are ____ ("loving either") and act as ____.
|
amphiphilic; detergents
|
|
|
Detergents are used for ___ and ___.
|
cleaning
emulsifying fats |

