![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Lipids |
Can be TRIGLYCERIDES or PHOSPHOLIPIDS Includes fats and oils Contains CARBON,HYDROGEN & OXYGEN but the proportion of oxygen is very small compared to carbohydrates |
Are not polymers |
|
|
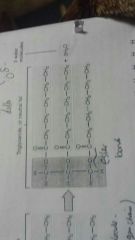
Triglyceride |
Contains one molecule of glycerol joined by covalent ester bonds formed in condensation reactions to 3 fatty acids |
There are over 70 fatty acids each with a COOL group with a hydrocarbon attached |
|
|
Triglyceride Functions |
Source of energy:Lipid have a higher proportion of Hydrogen to Oxygen atoms and when oxidised release twice the energy as the same mass of carbs & proteins Act as Insulators: fat is a slow conductor of heat and helps retain body heat also acts as an electrical insulator as the myelin sheath in nerve cells Large non-polar molecules: so insoluble in water so useful for waterproofing eg waxy cuticle in plants Protection:Fat is stored around delicate organs and act as a shock absorber
|
|
|
|
Saturated Triglycerides |
No C=C bonds,all carbon atoms are linked to the max number of hydrogen atoms |
|
|
|
Mono-unsaturated triglycerides |
Only one C=C bond |
|
|
|
Polyunsaturated triglyceride |
More than one C=C bonds |
|
|
|
Phospholipids |
Found in cell membrane Contain a glycerol molecule,two fatty acids and a PHOSPHATE GROUP The phosphate group is electrically charged which makes it attracted to water-Hydrophilic and the hydrocarbon chain is Hydrophobic |
|
|
|
Phospholipid bilayer |
In water phospholipids for a bilayer in which the hydrophobic tail points towards the center and the hydrophilic head points outwards This forms a barrier which controls the movement of molecules. The hydrophobic tail prevents water soluble molecules passing through the bilayer but lipid soluble molecules can diffuse right through |
|

