![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
lipid |
-fat, oil, wax, steroids -insoluble in polar(charged) solvents (water) and will dissolve in non-polar solvents -non- polar |
|
|
triglycerides - fats |
combined of glycerol bonded to 3 fatty acids |
|
|
nucleotides |
A compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group. Nucleotides form the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. Formed by a condensation reaction to for polynucleotides. |
|
|
Ribose |
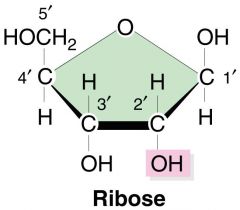
RNA |
|
|
Dioxyribose |
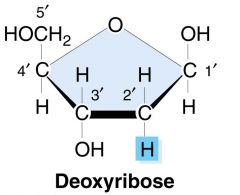
DNA |
|
|
DNA double helix formation |
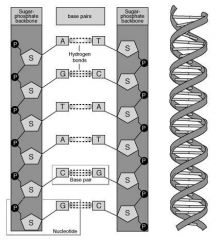
DNA is made of 2 polynucleotide strands linked by hydrogen bonds between adjacent bases |
|
|
phosphodiester bond |
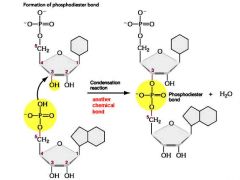
Adjacent nucleotides are held together by a phospho-di-ester bridge. |
|
|
the four DNA nucleotides |
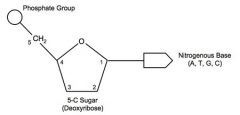
guanine cytosine adenine thymine |
|
|
RNA Nucleotides |
Single polynucleotide chain. The sugar is ribose. |
|
|
DNA Nucleotides |
Double polynucleotide chain. The sugar is deoxyribose.
|
|
|
4 RNA nucleotides |
guanine cytosine adenine uracil |
|
|
3 types of RNA |
1. mRNA (Formed in the nucleus and is involved in protein synthesis by attaching to a ribosome) 2. rRNA (Joins with proteins to form ribosomes) 3. tRNA (Formed when RNA strand folds and the complementary base pairs hold the shape. Involved in protein synthesis.) |
|
|
mRNA |
mRNA (Formed in the nucleus and is involved in protein synthesis by attaching to a ribosome) Messenger RNA |
|
|
rRNA |
rRNA (Joins with proteins to form ribosomes) Ribosomal RNA |
|
|
tRNA |
tRNA (Formed when RNA strand folds and the complementary base pairs hold the shape. Involved in protein synthesis.) Transfer RNA |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
single sugar molecule; glucose is the most common and important (c6 h12 o6) |

