![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Risk factors that lead to hyperlipidemia |
Genetics (not sole reason) Diet/Lifestyle Hypothyroidism Obesity Smoking Obstructive liver disease Advanced age Diabetes (affects the metabolism of glycoproteins) |
|
|
What are 2 major conditions that can occur with a patient that has untreated hyperlipidemia? |
Liver Disease Atherosclerosis |
|
|
Untreated hyperlipidemia leads to... |
Acute pancreatitis (hyperglycerides)Atherosclerosis (hypercholestermia) |
|
|
Atherosclerosis leads to 2 types of vascular complications... |
-Macro-vascular complications (USA, MI, CAD, ischemic cerebrovascular Dx) -Microvascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy) |
|
|
Lipid protein portions are inversely related (lower the proteins, higher the lipids) |
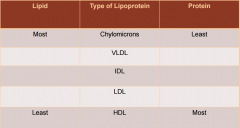
|
|
|
Lipoprotein Metabolism: Exogenous |
What you take inoccurs in the small intestine |
|
|
Lipoprotein Metabolism: Endogenous |
Hepatic cholesterol synthesis |
|
|
AHA advocates for statin use in 4 high-risk groups |
1.Clinical evidence of ASCVD 2. LDL>190 3. Age 40-70 with diabetes and LDL 70-189 4. Age 40-75 without DM, LDL 70-189 and an estimated 10 year risk of ASCVD |
|
|
Statins (What they do) |
*Best drugs to lower LDL levels -decrease LDL concentration from 20-60% -increase HDL by 10% -not sufficient enough response for treatment increased triglycerides |
|
|
Statins (types) |
Natural- Lovastatin Semi-synthetic- Simvastatin, Pravastatin Synthetic- Atorvastatin, Fluvastatin, Rosuvastatin |
|
|
How does Ezetimibe do to statins and trigylcerides? |
Enhances statins and reduces triglycerides |
|
|
Statins are structurally related to HMG-CoA. What are the two mechanisms of action |
1. Inhibit cholesterol synthesis 2. Competitively inhibit this enzyme causing increased Hepatic LDL (receptor) |
|
|
Do statins increase or decrease HDL? |
Increase HDL by 10% |
|
|
Do statins provide sufficient enough response for treatment for increased triglycerides? |
No |
|
|
Statin pharmakokinetics |
-Lovastatin and Simvastatin are prodrugs needing metabolism to become active -most all undergo metabolism by hepatic CP450 -DOA for most is about 24 hours |
|
|
What is an absolute contraindication for statins |
Pregnancy |
|
|
Statin Side Effects |
Skeletal muscle issues Liver enzyme changes (plasma aminotransferase increases) Drug interactions GI upset Fatigue Headache |
|
|
Bile Acid Resins |
powders MOA: increase hepatic bile sythesis from cholesterol stores, increasing LDL-R and the uptake of LDL from the blood Uses: Primary increased LDL with normal triglycerides Drugs: Colesevelam, cholestyramine, colesipol NO synthetic absorption (SOA in gut) side effect-constipation |
|
|
Niacin (Nicotinic Acid) MOA and Uses |
MOA: inhibits synthesis of VLDL in the liver, inhibits the release of free fatty acid from adipose, increases the activity of lipoprotein lipase Uses: Lowers LDL and Triglycerides **most effective drug at increasing HDL** |
|
|
Niacin Pharmakokinetics and side effects |
Extensive first pass hepatic metabolism Side effects: Flushing, pruritus, GI upset, hepatic dysfunction, hyperglycemia, gout, drug interactions (antiHTN cause MORE hypotension) |
|
|
Fibrates |
MOA: increased activity of lipoprotein lipase Uses: **Most effective drugs at decreasing trigylceridides (50%)**, increases HDL Drugs: Gemfibrozil, fenofibrate, bezafibrate Side effects: *statin interaction, GI upset, headache, gallstones, prolonged PTT |
|
|
Ezetimibe |
MOA: selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption leading to secondary up-regulation of LDL-R Uses: Alone it decreases LDL up to 22%, **potentiates the effects of statins by 17%** |
|
|
Omega-3 fatty acids |
Uses: decreases triglycerides does to effect is unclear and not FDA approved |
|
|
Statin metabolism |
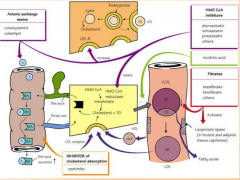
|

